
H5N1 clinical trials are clinical trials concerning H5N1 vaccines, which are intended to provide immunization to influenza A virus subtype H5N1. They are intended to discover pharmacological effects and identify any adverse reactions the vaccines may achieve in humans.

ZF2001, trade-named Zifivax or ZF-UZ-VAC-2001, is an adjuvanted protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine developed by Anhui Zhifei Longcom in collaboration with the Institute of Microbiology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The vaccine candidate is in Phase III trials with 29,000 participants in China, Ecuador, Malaysia, Pakistan, and Uzbekistan.
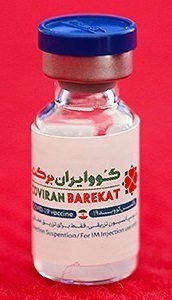
COVIran Barekat is a COVID-19 vaccine developed in Iran by Shifa Pharmed Industrial Group, a subsidiary of the Barkat Pharmaceutical Group. It is an inactivated virus-based vaccine. Iranian authorities have authorized its emergency use. This makes it the first locally developed COVID-19 vaccine to be approved for emergency use in the Middle East.

The CureVac COVID-19 vaccine was a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by CureVac N.V. and the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI). The vaccine showed inadequate results in its Phase III trials with only 47% efficacy. In October 2021 CureVac abandoned further development and production plans for CVnCoV and refocused efforts on a cooperation with GlaxoSmithKline.

ZyCoV-D is a DNA plasmid-based COVID-19 vaccine developed by Indian pharmaceutical company Cadila Healthcare, with support from the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council. It is approved for emergency use in India.

Nanocovax is a Vietnamese COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Nanogen Pharmaceutical Biotechnology JSC. It is a subunit vaccine.

iNCOVACC is an intranasal COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Bharat Biotech, American company Precision Virologics and the Washington University School of Medicine in St Louis, Missouri, United States.

The Sinopharm WIBP COVID-19 vaccine, also known as WIBP-CorV, is one of two inactivated virus COVID-19 vaccines developed by Sinopharm. Peer-reviewed results show that the vaccine is 72.8% effective against symptomatic cases and 100% against severe cases. The other inactivated virus COVID-19 vaccine developed by Sinopharm is the BIBP vaccine (BBIBP-CorV) which is comparably more successful. 1 billion doses are expected to be produced per year.

The MVC COVID-19 vaccine, designated MVC-COV1901 and also known as the Medigen COVID-19 vaccine, is a protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine developed by Medigen Vaccine Biologics Corporation in Taiwan, American company Dynavax Technologies, and the U.S. National Institutes of Health.

AWcorna, originally termed ARCoV and also known as the Walvax COVID-19 vaccine, is an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine developed by Walvax Biotechnology, Suzhou Abogen Biosciences, and the PLA Academy of Military Science. In contrast to other mRNA COVID vaccines, such as those by Pfizer-BioNtech and Moderna, this vaccine primarily targets the Sars-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain of the spike protein, rather than the entire spike protein. It is approved for Phase III trials in China, Mexico, Indonesia, and Nepal.

NDV-HXP-S is a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed under the leadership of Peter Palese, Adolfo García-Sastre, and Florian Krammer at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
EuCorVac-19 is a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by EuBiologics Co.

V-01 is a protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by a subsidiary of Livzon Pharmaceutical Group Inc.

GX-19 is a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Genexine consortium.

mRNA-1283 is a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Moderna.

FAKHRAVAC is a COVID-19 vaccine developed in Iran by the Organization of Defensive Innovation and Research, a subsidiary of Iran's Ministry of Defense. It is the third Iranian COVID-19 vaccine reaching clinical trials. It is currently in phase III. It received emergency use authorization in Iran on 9 September 2021.

COVAX-19 is a recombinant protein-based COVID-19 vaccine developed by South Australian-based biotech company Vaxine, in collaboration with CinnaGen, a private company with operations in the Middle East. It is under clinical trial in collaboration with the Iranian company CinnaGen.

COVID-19 vaccine clinical research uses clinical research to establish the characteristics of COVID-19 vaccines. These characteristics include efficacy, effectiveness, and safety. As of November 2022, 40 vaccines are authorized by at least one national regulatory authority for public use:

Noora is a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences in collaboration with Plasma Darman Sarv Sepid Co. in Iran.

S-268019-b is a protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Shionogi.




