The global COVID-19 pandemic arrived in Europe with its first confirmed case in Bordeaux, France, on 24 January 2020, and subsequently spread widely across the continent. By 17 March 2020, every country in Europe had confirmed a case, and all have reported at least one death, with the exception of Vatican City.

The first cases of the COVID-19 pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 in North America were reported in the United States on 23 January 2020. Cases were reported in all North American countries after Saint Kitts and Nevis confirmed a case on 25 March, and in all North American territories after Bonaire confirmed a case on 16 April.
The COVID-19 pandemic in New Zealand was part of the pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The first case of the disease in New Zealand was reported on 28 February 2020. The country recorded over 2,274,370 cases. Over 3,000 people died as a result of the pandemic, with cases recorded in all twenty district health board (DHB) areas. The pandemic first peaked in early April 2020, with 89 new cases recorded per day and 929 active cases. Cases peaked again in October 2021 with 134 new cases reported on 22 October.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Latvia was a part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached Latvia on 2 March 2020, having been brought along with people returning from abroad.

The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached Oceania on 25 January 2020 with the first confirmed case reported in Melbourne, Australia. The virus has spread to all sovereign states and territories in the region. Australia and New Zealand were praised for their handling of the pandemic in comparison to other Western nations, with New Zealand and each state in Australia wiping out all community transmission of the virus several times even after re-introduction in the community.
The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached Cyprus on 9 March 2020. Data released by the Cypriot government includes cases in the British Overseas Territory of Akrotiri and Dhekelia, but does not include cases in Northern Cyprus due to the long-running Cyprus dispute.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Samoa is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached Samoa on 18 November 2020. The country reported its second case on 27 November.

The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the French overseas collectivity of French Polynesia in March 2020. As of 24 August 2021, French Polynesia has been the worst affected country in Oceania both in terms of proportion relative to population of total confirmed cases and total deaths. French Polynesia has experienced two significant outbreak waves, the first between September 2020 - January 2021, and the ongoing second wave which began in July 2021.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Tuvalu is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached Tuvalu on 20 May 2022. As of 31 August 2022, a total of 25,591 vaccine doses have been administered.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Fiji is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The first case of the disease in Fiji was reported on 19 March 2020 in Lautoka. as of 3 January 2022, the country has had a total of 55,009 cases as of which 2,417 are currently active and 702 deaths, with cases reported on all divisions of the country. Apart from the COVID-19 deaths, 621 COVID-19 positive patients have died from pre-existing non-COVID-19 related illnesses. In March 2021, Fiji became the first Pacific island country to receive COVID-19 vaccines through the COVAX initiative with frontline workers and first responders the first to be vaccinated. As of 2 January 2022, more than 600,000 (98%) Fijians have received their first jab of the vaccine and almost 560,000 (92%) Fijians have received their second jab and are fully vaccinated. To date, only the AstraZeneca vaccine, Moderna vaccine and the Pfizer BioNTech vaccine have been deployed in the country. The country have also administered booster shots. Vaccination is mandated, however only to the adult population.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Vanuatu is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached Vanuatu on 11 November 2020.
The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached Tonga on 29 October 2021 with a traveller who tested positive in quarantine. Several more cases were found in January and February 2022 in a minor outbreak during the aftermath of the 2022 Hunga Tonga–Hunga Ha'apai eruption and tsunami as other countries delivered aid. Tonga had followed a "Covid-free" policy.
The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the French overseas collectivity of New Caledonia on 18 March 2020. All cases are on the main island of Grand Terre and are related to travel abroad. On 7 May, all cases had recovered.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Anguilla is part of the ongoing global viral pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which was confirmed to have reached the British Overseas Territory of Anguilla on 26 March 2020. On 26 April 2020, all patients had recovered and on 22 November a new imported case was announced.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Niue is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Niue reported its first confirmed case on 9 March 2022.
The COVID-19 pandemic in American Samoa is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the unincorporated United States territory of American Samoa on November 9, 2020.
A four-tier alert level restrictions system was in place in during the COVID-19 pandemic in New Zealand between March 2020 and December 2021, with levels 3 and 4 being forms of lockdown. In level 1 there were no restrictions; in level 2 there were limits on gatherings; in level 3 only purposeful travel was allowed and there were strict limits on gatherings; and in level 4 only essential travel was allowed and gatherings were banned.
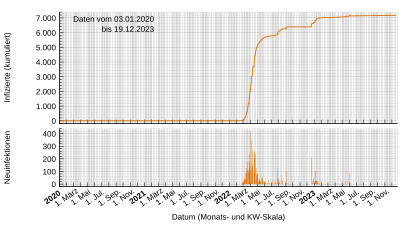
The COVID-19 pandemic in Tokelau is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Tokelau reported its first confirmed case on 21 December 2022. COVID-19 reached all three of Tokelau's main atolls in July 2023, when the government confirmed the community spread of the virus on Fakaofo, the last atoll without infections.

The New Zealand Government responded to the COVID-19 pandemic in New Zealand in various ways. In early February 2020, the Government imposed travel restrictions on China in response to the global COVID-19 pandemic originating in Wuhan and also repatriated citizens and residents from Wuhan. Following the country's first case which originated in Iran, the Government imposed travel restrictions on Iran.

The COVID-19 pandemic in New Zealand has had far-reaching consequences on the country that went beyond the spread of the disease itself and efforts to eliminate it, including education, faith communities, Māori, mass gatherings, sports, recreation, and travel. In addition, there were several recorded cases of lockdown violations, leaks, and misinformation about the COVID-19 virus and vaccines.