Related Research Articles

Gavin Christopher Newsom is an American politician and businessman serving as the 40th governor of California since January 2019. A member of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 49th lieutenant governor of California from 2011 to 2019 and as the 42nd mayor of San Francisco from 2004 to 2011. He is a national progressive leader who was a prominent early advocate for LGBT rights, same-sex marriage, immigrant rights, affordable housing to combat the housing shortage, universal health care, environmental policies to combat climate change, gun control, and the legalization of cannabis.
The California Nurses Association/National Nurses Organizing Committee (CNA/NNOC), an affiliate of National Nurses United, is a trade union labor union and professional association of registered nurses in the United States. Since 2018, CNA/NNOC has been led by Executive Director Bonnie Castillo, RN.

The Southern Philippines Medical Center (SPMC) is a government hospital under the Department of Health of the Republic of the Philippines. It is located at the JP Laurel Ave, Bajada, Davao City. It began as the Davao Medical Center. Its name was changed on November 19, 2009 by Republic Act 9792.
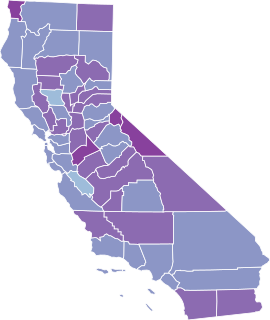
Ten of the first twenty confirmed COVID-19 cases in the United States occurred in California, the first of which was confirmed on January 26, 2020. All of the early confirmed cases were persons who had recently travelled to China, as testing was restricted to this group. On January 29, 2020, as disease containment protocols were still being developed, the U.S. Department of State evacuated 195 persons from Wuhan, China aboard a chartered flight to March Air Reserve Base in Riverside County, and in the process may have contributed to spread within the state and the US at large. On February 5, 2020, the U.S. evacuated 345 more citizens from Hubei Province to two military bases in California, Travis Air Force Base in Solano County and Marine Corps Air Station Miramar, San Diego, where they were quarantined for 14 days. A state of emergency was declared in the state on March 4, 2020 and as of February 24, 2021 remains in effect. A mandatory statewide stay-at-home order was issued on March 19, 2020 that was ended on January 25, 2021. On April 6, 2021, the state announced plans to fully reopen the economy by June 15, 2021.

Flattening the curve is a public health strategy to slow down the spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus during the COVID-19 pandemic. The curve being flattened is the epidemic curve, a visual representation of the number of infected people needing health care over time. During an epidemic, a health care system can break down when the number of people infected exceeds the capability of the health care system's ability to take care of them. Flattening the curve means slowing the spread of the epidemic so that the peak number of people requiring care at a time is reduced, and the health care system does not exceed its capacity. Flattening the curve relies on mitigation techniques such as hand washing, use of face masks and social distancing.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Texas is an ongoing viral pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a novel infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The state of Texas confirmed its first case on February 13, 2020, among U.S. nationals evacuated from China to Joint Base San Antonio–Lackland beginning in early February; however, retrospective analyses have suggested a much earlier origin than previously thought. The first documented case of COVID-19 in Texas outside of evacuees at Lackland was confirmed on March 4 in Fort Bend County, and many of the state's largest cities recorded their first cases throughout March. The state recorded its first death associated with the disease on March 17 in Matagorda County.

The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the U.S. state of Arizona in January 2020. As of June 3, 2021 Arizona public health authorities reported 322 new cases of COVID-19 and five deaths, bringing the cumulative totals since the start of the pandemic to 882,691 cases and 17,653 deaths. 12.3% of the state's population has been positively diagnosed with COVID-19 since the first case was reported on January 26, 2020.
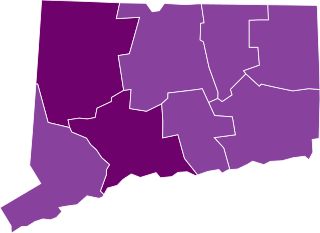
The first confirmed case of the COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S. state of Connecticut was confirmed on March 8, although there had previously been multiple people suspected of having COVID-19, all of which eventually tested negative. As of September 3, 2021, there are 341,062 confirmed cases, 34,073 suspected cases, and 8,394 COVID-associated deaths in the state.

The COVID-19 pandemic reached the U.S. state of Indiana on March 5, 2020 and was confirmed on March 6. As of July 12, 2021, the Indiana State Department of Health (ISDH) had confirmed 757,904 cases in the state and 13,496 deaths. As of July 3, 2020, all 92 counties had reported at least 10 cases with Pike County being the last to surpass this threshold.

The first presumptive case relating to the COVID-19 pandemic in Louisiana was announced on March 9, 2020. Since the first confirmed case, the outbreak grew particularly fast relative to other states and countries. As of February 8, 2021, there have been 411,812 cumulative COVID-19 cases and 9,119 deaths. Confirmed cases have appeared in all 64 parishes, though the New Orleans metro area alone has seen the majority of positive tests and deaths. Governor John Bel Edwards closed schools statewide on March 16, 2020, restricted most businesses to takeout and delivery only, postponed presidential primaries, and placed limitations on large gatherings. On March 23, Edwards enacted a statewide stay-at-home order to encourage social distancing, and President Donald Trump issued a major disaster declaration, the fourth state to receive one.
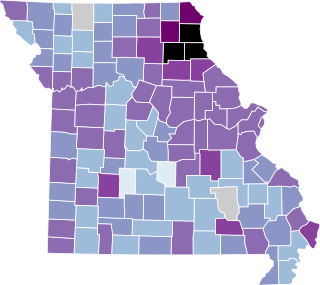
The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the U.S. state of Missouri in March 2020. A university student who had recently been to Italy, was the first index case for COVID-19 in Missouri. She was treated at Mercy Hospital St. Louis. As of February 8, 2021, the Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services has confirmed 502,432 cumulative cases and 7,562 deaths.

The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached the U.S. state of Montana on March 14, 2020. As of June 4, 2021, the Montana Department of Public Health and Human Services (MDPHHS) has reported 112,260 positive cases and 1,632 deaths in the state.
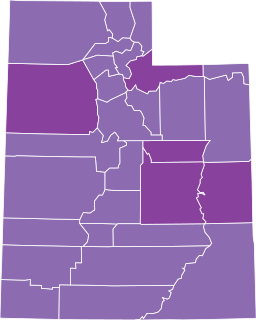
The COVID-19 pandemic began in the U.S. state of Utah in early March 2020 with travel-related cases. Residents stockpiled goods, large conferences were made remote-only, postponed, or cancelled; a state of emergency was declared, and some public universities and other colleges switched to online-only classes. After the first case of community spread was found on March 14, Utah faced a shortage of testing kits, and public schools were ordered to be closed. Community spread was confirmed in more counties, and the state issued a public health order prohibiting dine-in service in restaurants and gatherings of more than 10 people except in grocery stores. A 5.7-magnitude earthquake struck the Wasatch Front on March 18, hampering the pandemic response.

The COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S. state of Vermont is part of an ongoing worldwide viral pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019, a novel infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
The global COVID-19 pandemic struck the U.S. state of Wisconsin in early February 2020. Although Wisconsin has to date experienced 144 deaths per 100,000 residents, significantly fewer than the US national average of 196 deaths, COVID-19 was one of the three leading causes of death in Wisconsin in 2020. On August 25, 2021 Wisconsin public health authorities reported 7 day averages of 1,417 new cases and 236 probable cases per day, an increase of greater than 15 fold since late June 2021. This brings the cumulative total of COVID-19 cases in Wisconsin to 651,338. The state's death toll is 7,558, with 30 new deaths over the previous 7 days. As of August 25, 2021, 12.41% of Wisconsin's residents have been positively diagnosed with COVID-19, the 20th highest per-capita case rate among all US states. January 16's 128 COVID-19 deaths set a new single day record for Wisconsin.

The San Francisco Bay Area, which includes the major cities of San Jose, San Francisco, and Oakland, was an early center of the COVID-19 pandemic in California. The first case of COVID-19 in the area was confirmed in Santa Clara County on January 31, 2020. A Santa Clara County resident was the earliest known death caused by COVID-19 in the United States, on February 6, suggesting that community spread of COVID-19 had been occurring long before any actual documented case. This article covers the 13 members of ABAHO, which includes the nine-county Bay Area plus the counties of Monterey, San Benito, and Santa Cruz.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in Ontario:
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in California.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in Texas.

The government of California initially responded to the COVID-19 pandemic in the state with a statewide lockdown, the first of its kind during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. As the pandemic progressed in California and throughout the rest of the country, the California government, following recommendations issued by the U.S. government regarding state and local government responses, began imposing social distancing measures and workplace hazard controls.
References
- ↑ McCarthy, Niall (2020-05-22). "States Compared [Infographic]". Forbes. Retrieved 2020-12-02.
- ↑ Phelan, John (2020-11-20). "Minnesota's total ICU capacity has fallen by 229 beds – 10.6% – since early October". Center of the American Experiment. Retrieved 2020-12-02.
- ↑ "COVID-19 Data Dashboard – Patient Impact & Hospital Capacity". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. July 16, 2020.
- ↑ Soo, Kim (2020-10-20). "Utah Hospital's ICU at 104 Percent Capacity as State Sees Record COVID Hospitalizations". Newsweek.Missing or empty
|url=(help) - ↑ Simmons, Tommy (2020-12-01). "Some Treasure Valley hospitals faced decisions on ICU capacity Monday night as COVID-19 cases rise". Idaho Press.
- ↑ Moon, Sarah (2020-12-04). "Newsom issues regional stay-at-home order based on ICU capacity to battle record Covid surge in California". MSN News.