
The Ministry of Strategic Affairs and Public Diplomacy is an Israeli government ministry responsible for leading the campaign of expanding the Abraham Accords and the handling of ties on White House matters.

BiondVax Pharmaceuticals Ltd. is an Israeli biopharmaceutical company focused on developing, and manufacturing immunotherapeutic products primarily for the treatment of infectious diseases and autoimmune diseases.

Michal Linial is a Professor of Biochemistry and Bioinformatics at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HUJI). Linial is the Director of The Sudarsky Center for Computational Biology at HUJI. Since 2015, she is head of the ELIXIR-Israel node.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Israel is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The first case in Israel was confirmed on 21 February 2020, when a female citizen tested positive for COVID-19 at the Sheba Medical Center after return from quarantine on the Diamond Princess ship in Japan. As a result, a 14-day home isolation rule was instituted for anyone who had visited South Korea or Japan, and a ban was placed on non-residents and non-citizens who were in South Korea for 14 days before their arrival.
A COVID‑19 vaccine is a vaccine intended to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19).
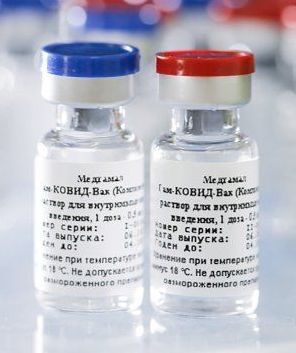
Sputnik V or Gam-COVID-Vac is an adenovirus viral vector vaccine for COVID-19 developed by the Gamaleya Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology in Russia. It is the world's first registered combination vector vaccine for the prevention of COVID-19, having been registered on 11 August 2020 by the Russian Ministry of Health.
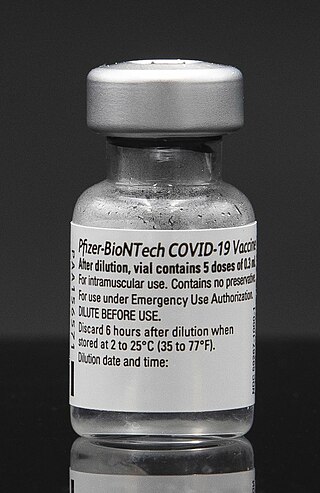
The Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, sold under the brand name Comirnaty, is an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine developed by the German biotechnology company BioNTech. For its development, BioNTech collaborated with American company Pfizer to carry out clinical trials, logistics, and manufacturing. It is authorized for use in people to provide protection against COVID-19, caused by infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The vaccine is given by intramuscular injection. It is composed of nucleoside-modified mRNA (modRNA) encoding a mutated form of the full-length spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, which is encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles. Initial advice indicated that vaccination required two doses given 21 days apart, but the interval was later extended to up to 42 days in the US, and up to four months in Canada.
The COVID-19 vaccination program in the Philippines is an ongoing mass immunization campaign against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), in response to the ongoing pandemic in the country. The vaccination program was initiated by the Duterte administration on March 1, 2021, a day after the arrival of the country's first vaccine doses which were donated by the Chinese government.

Israel's COVID-19 vaccination programme, officially named "Give a Shoulder", began on 19 December 2020, and has been praised for its speed, having given twenty percent of the Israeli population the first dose of the vaccines' two dose regimen in the span of three weeks.

SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, was isolated in late 2019. Its genetic sequence was published on 11 January 2020, triggering the urgent international response to prepare for an outbreak and hasten development of a preventive COVID-19 vaccine. Since 2020, vaccine development has been expedited via unprecedented collaboration in the multinational pharmaceutical industry and between governments. By June 2020, tens of billions of dollars were invested by corporations, governments, international health organizations, and university research groups to develop dozens of vaccine candidates and prepare for global vaccination programs to immunize against COVID‑19 infection. According to the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI), the geographic distribution of COVID‑19 vaccine development shows North American entities to have about 40% of the activity, compared to 30% in Asia and Australia, 26% in Europe, and a few projects in South America and Africa.

ARCT-021, also known as LUNAR-COV19, is a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Arcturus Therapeutics.

BriLife, also known as IIBR-100, is a replication-competent recombinant VSV viral vectored COVID-19 vaccine candidate. It was developed by the Israel Institute for Biological Research (IIBR). The IIBR partnered with the US-based NRx Pharmaceuticals to complete clinical trials and commercialize the vaccine. A study conducted in hamsters suggested that one dose of the vaccine was safe and effective at protecting against COVID-19.

COVID-19 vaccination in South Korea is an ongoing immunization campaign against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), in response to the ongoing pandemic in the country.

The COVID-19 vaccination campaign in Germany began on 26 December 2020.

Nachman Ash is an Israeli physician who is currently the director-general of the Ministry of Health.
Peter Andrew McCullough is an American cardiologist. He was vice chief of internal medicine at Baylor University Medical Center and a professor at Texas A&M University. During the COVID-19 pandemic, McCullough has promoted misinformation about COVID-19, its treatments, and mRNA vaccines.

COVID-19 vaccine clinical research uses clinical research to establish the characteristics of COVID-19 vaccines. These characteristics include efficacy, effectiveness and safety. As of November 2022, 40 vaccines are authorized by at least one national regulatory authority for public use:
Media coverage of the COVID-19 pandemic includes reporting on the deaths of anti-vaccine advocates from COVID-19 as a phenomenon occurring during the COVID-19 pandemic. The media also reported on various websites documenting such deaths, with some outlets questioning whether this practice was overly unsympathetic. Reports noted phenomena including "deathbed conversions", in which vaccine opponents reportedly changed their minds and began encouraging vaccination before dying, with these claims meeting continued skepticism by vaccination opponents; and on groups of deaths within specific demographics, such as anti-vaccine radio hosts.

A universal coronavirus vaccine, also known as a pan-coronavirus vaccine, is a theoretical coronavirus vaccine that would be effective against all coronavirus strains. A universal vaccine would provide protection against coronavirus strains that have caused disease in humans, such as SARS-CoV-2, while also providing protection against future coronavirus strains. Such a vaccine has been proposed to prevent or mitigate future coronavirus epidemics and pandemics.















