| calcidiol 1-monooxygenase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 1.14.15.18 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9081-36-1 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
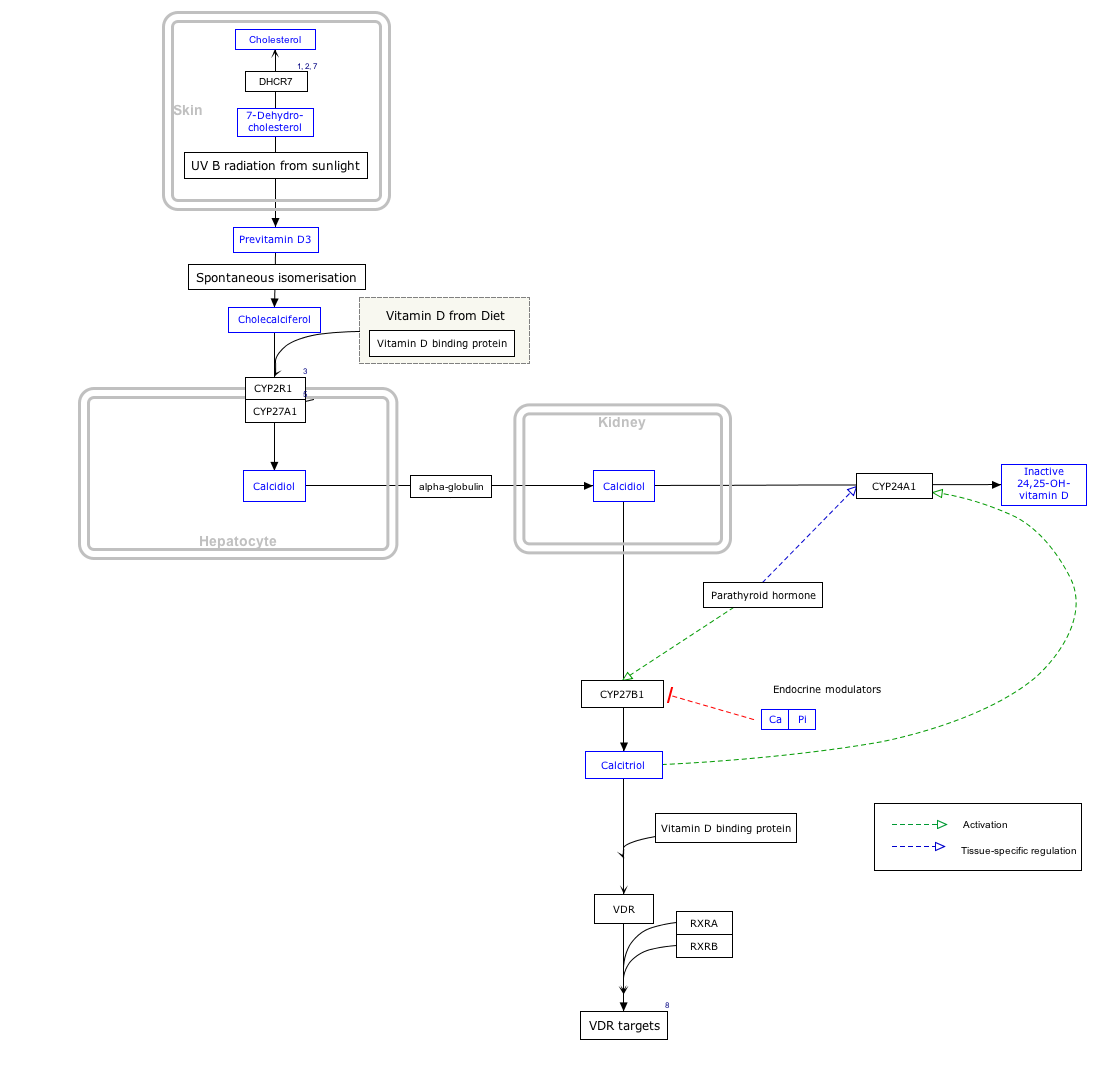
25-Hydroxyvitamin D 1-alpha-hydroxylase (VD 1A hydroxylase) also known as calcidiol 1-monooxygenase[ citation needed ] or cytochrome p450 27B1 (CYP27B1) or simply 1-alpha-hydroxylase is a cytochrome P450 enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP27B1 gene. [5] [6] [7]
Contents
VD 1A hydroxylase is located in the proximal tubule of the kidney and a variety of other tissues, including skin (keratinocytes), immune cells, [8] and bone (osteoblasts). [9]