
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These may occur a few times a day or a few times per week. Depending on the person, asthma symptoms may become worse at night or with exercise.
A bronchodilator or broncholytic is a substance that dilates the bronchi and bronchioles, decreasing resistance in the respiratory airway and increasing airflow to the lungs. Bronchodilators may be originating naturally within the body, or they may be medications administered for the treatment of breathing difficulties, usually in the form of inhalers. They are most useful in obstructive lung diseases, of which asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are the most common conditions. Although this remains somewhat controversial, they might be useful in bronchiolitis and bronchiectasis. They are often prescribed but of unproven significance in restrictive lung diseases.
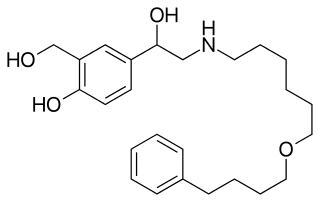
Salmeterol is a long-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist (LABA) used in the maintenance and prevention of asthma symptoms and maintenance of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) symptoms. Symptoms of bronchospasm include shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing and chest tightness. It is also used to prevent breathing difficulties during exercise.

Budesonide/formoterol, sold under the brand name Symbicort among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication used in the management of asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It contains budesonide, a steroid; and formoterol, a long-acting β2-agonist (LABA). The product monograph does not support its use for sudden worsening or treatment of active bronchospasm. However, a 2020 review of the literature does support such use. It is used by breathing in the medication.
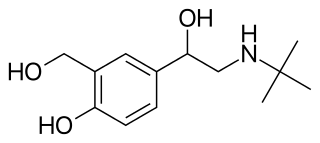
Beta2-adrenergic agonists, also known as adrenergic β2 receptor agonists, are a class of drugs that act on the β2 adrenergic receptor. Like other β adrenergic agonists, they cause smooth muscle relaxation. β2 adrenergic agonists' effects on smooth muscle cause dilation of bronchial passages, vasodilation in muscle and liver, relaxation of uterine muscle, and release of insulin. They are primarily used to treat asthma and other pulmonary disorders. Bronchodilators are considered an important treatment regime for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and are usually used in combination with short acting medications and long acting medications in a combined inhaler.
Ipratropium bromide/salbutamol, sold under the brand name Combivent among others, is a combination medication used to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It contains ipratropium and salbutamol.

Bronchoconstriction is the constriction of the airways in the lungs due to the tightening of surrounding smooth muscle, with consequent coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.

Long-acting β adrenoceptor agonists (LABAs) are beta-adrenergic agonists usually prescribed for moderate-to-severe persistent asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).

Levosalbutamol, also known as levalbuterol, is a short-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist used in the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Evidence is inconclusive regarding the efficacy of levosalbutamol versus salbutamol or salbutamol-levosalbutamol combinations, though levosalbutamol is believed to have a better safety profile due to its more selective binding to β2 receptors versus β1.

Obstructive lung disease is a category of respiratory disease characterized by airway obstruction. Many obstructive diseases of the lung result from narrowing (obstruction) of the smaller bronchi and larger bronchioles, often because of excessive contraction of the smooth muscle itself. It is generally characterized by inflamed and easily collapsible airways, obstruction to airflow, problems exhaling, and frequent medical clinic visits and hospitalizations. Types of obstructive lung disease include asthma, bronchiectasis, bronchitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Although COPD shares similar characteristics with all other obstructive lung diseases, such as the signs of coughing and wheezing, they are distinct conditions in terms of disease onset, frequency of symptoms, and reversibility of airway obstruction. Cystic fibrosis is also sometimes included in obstructive pulmonary disease.
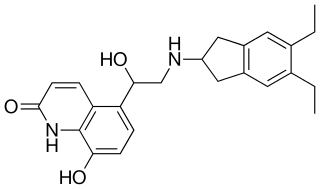
Indacaterol is an ultra-long-acting beta-adrenoceptor agonist developed by Novartis. It needs to be taken only once a day, unlike the related drugs formoterol and salmeterol. It is licensed only for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is delivered as an aerosol formulation through a dry powder inhaler.

Roflumilast, sold under the brand name Daxas among others, is a medication used for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, plaque psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, and atopic dermatitis. It acts as a selective, long-acting inhibitor of the enzyme phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE-4). It has anti-inflammatory effects.
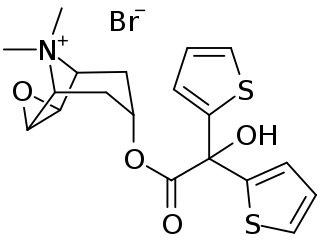
Tiotropium bromide, sold under the brand name Spiriva among others, is a long-acting bronchodilator used in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma. Specifically it is used during periods of breathing difficulty to prevent them from getting worse, rather than to prevent them from happening. It is used by inhalation through the mouth. Onset typically begins within half an hour and lasts for 24 hours.

Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. GOLD 2024 defined COPD as a heterogeneous lung condition characterized by chronic respiratory symptoms due to abnormalities of the airways and/or alveoli (emphysema) that cause persistent, often progressive, airflow obstruction.

UK-432,097 is a drug developed by Pfizer for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, which acts as a potent and selective agonist of the adenosine A2A receptor. It was discontinued from clinical trials following poor efficacy results, but its high selectivity has made it useful for detailed mapping of the internal structure of the A2A receptor.

Olodaterol is an ultra-long-acting β adrenoreceptor agonist (ultra-LABA) used as an inhalation for treating people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is manufactured by Boehringer Ingelheim.

Abediterol is a once-daily experimental drug candidate for the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), but it has never been marketed.

Vilanterol is an ultra-long-acting β2 adrenoreceptor agonist (ultra-LABA), which was approved in May 2013 in combination with fluticasone furoate for sale as Breo Ellipta by GlaxoSmithKline for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).. The combination is also approved for the treatment of asthma in Canada, Europe, Japan and New Zealand.

Indacaterol/glycopyrronium bromide, sold under the brand name Ultibro Breezhaler among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication for inhalation consisting of the following two active ingredients:
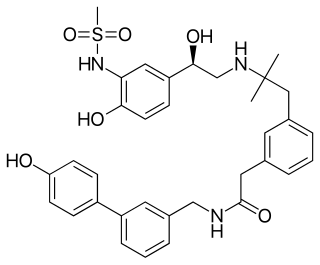
PF-610355 is an inhalable ultra-long-acting β2 adrenoreceptor agonist (ultra-LABA) that was investigated as a treatment of asthma and COPD by Pfizer. It utilizes a sulfonamide agonist headgroup, that confers high levels of intrinsic crystallinity that could relate to the acidic sulfonamide motif supporting a zwitterionic form in the solid state. Optimization of pharmacokinetic properties minimized systemic exposure following inhalation and reduced systemically mediated adverse events. Its in vivo duration on action confirmed its potential for once-daily use in humans.
















