Transport in India consists of transport by land, water and air. Road transport is the primary mode of transport for most Indian citizens, and India's road transport systems are among the most heavily used in the world.
Rail transport in India is an important mode of conveyance for people and goods in India. Indian Railways (IR) is the primary operator of rail operations throughout the country. IR is a state-owned organisation of the Ministry of Railways, which historically had its own government budget. Between 2019 and 2020, 22.15 million passengers used the Indian Railways network daily. In the same period, 3.32 million metric tons of freight was also shipped daily on the IR network.

Indian Railways (IR) is a statutory body under the ownership of the Ministry of Railways, Government of India that operates India's national railway system. It manages the fourth largest national railway system in the world by size, with a total route length of 68,043 km (42,280 mi), running track length of 102,831 km (63,896 mi) and track length of 128,305 km (79,725 mi) as of 31 March 2022. 58,812 km (36,544 mi) of all the gauge routes are electrified with 25 kV 50 Hz AC electric traction as of 1 April 2023.
The 2007 Samjhauta Express bombing was a terrorist attack that occurred around midnight on 18 February 2007 on the Samjhauta Express, a twice-weekly train service connecting Delhi, India, and Lahore, Pakistan. Bombs were set off in two carriages, both filled with passengers, just after the train passed Diwana near the Indian city of Panipat, 80 kilometres (50 mi) north of New Delhi. 70 people were killed in the ensuing fire and dozens more were injured. Of the 70 fatalities, most were Pakistani civilians. The victims also included some Indian civilians and three railway policemen.

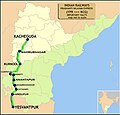
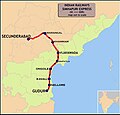
Secunderabad Junction is a major intercity junction railway station and a commuter rail hub in the Hyderabad urban area. In the city centre, the station is in the South Central Railway zone of Indian Railways. Built in 1874 by the Nizam of Hyderabad during the British era, it was the main station of Nizam's Guaranteed State Railway until the Kacheguda railway station opened in 1916. The station was taken over by Indian Railways in 1951, when NGSR was nationalized. Its main portico and concourse are influenced by Nizamesque architecture. The station, which resembles a fort, is a tourist attraction in the twin cities of Hyderabad and Secunderabad.
The Garib Rath trains are a series of no-frills trains operated by Indian Railways to provide air-conditioned train travel at a cheaper rate compared to regular trains.
The city of Nagpur is strategically located in central India. It has a vast railway network and its road network is well-maintained to avoid congestion. There are 4 modes of transportation in Nagpur. Nagpur is connected to India's four major metropolitan areas by road, rail and air. Auto rickshaws operate in most parts of the city, and are the main form of hired transport.

Expressways are the highest class of roads in India. As of July 2023, India has a total length of 5,145 km (3,197 mi) of expressways. These are controlled-access highways where entrance and exits are controlled by the use of cloverleaf or trumpet or grade separated interchanges that are incorporated into the design of the expressway and designed for maximum speed of 120 km/h, whereas National highways are flyover access or tolled, where entrance and exit is through the side of the flyover, at each intersection of highway with road, flyovers are provided to bypass the city/town/village traffic and these highways are designed for speed of 100 km/h. Some roads are not access-controlled expressways, but are still named as expressways, such as the Biju Expressway, these are actually state highways which are not declared by central government as an Expressway, hence not an Expressway or National Highway. Mumbai–Pune Expressway is the first 6-lane operational expressway in India started in 2002. Expressways follow standards set by Indian Roads Congress and Bureau of Indian Standards.

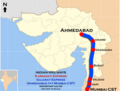
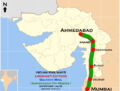
Indian Railways does not currently have any operational high-speed rail lines, though a total of eight corridors have been approved, with the corridor between Mumbai and Ahmedabad under construction. As of 2023, the fastest train services in India are the RapidX, Gatimaan Express and Rani Kamalapati (Habibganj)–Hazrat Nizamuddin Vande Bharat Express with peak operational speed of 160 km/h (99 mph) on the Tughlakabad – Agra Cantonment section of the route.

Coimbatore Junction railway station, also known as Kovai Junction railway station, is a major railway station located in the city of Coimbatore in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is one of the busiest railway stations in South India and serves as a gateway to the Nilgiri hills, a popular tourist destination. The station is operated by the Southern Railway zone of Indian Railways and has six platforms. Coimbatore is the second highest revenue generating station in the Southern Railway after Chennai Central and Egmore railway stations and is the station that generates about 45 percent of the revenue of the Salem Railway division. Coimbatore Junction is an important junction connecting major cities such as Chennai, Bangalore, Mumbai, Delhi, and Kolkata. It also serves as a gateway to several popular tourist destinations such as Ooty and Kodaikanal.

Vijayawada Junction Railway Station is an Indian Railways station in Vijayawada of Andhra Pradesh, categorized as a Non-Suburban Grade-2 (NSG-2) station in Vijayawada railway division. Situated at the junction of Howrah–Chennai and New Delhi–Chennai main lines, it is the fourth busiest railway station in the country after Howrah Junction, Kanpur Central and New Delhi. The station serves about 1.40 lakh passengers, over 190 express and 170 freight trains every day. It is one of the major railway junctions of the Indian Railways and is a nationally important halt.

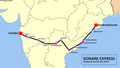
Duronto Express is a category of long-distance fast trains run by the Indian Railways. Initially these trains did not have any passenger stops between the origin and the destination, but since January 2016 it is possible to book tickets from those technical stops. These trains were introduced in 2009 and were named 'Duronto', meaning 'speedster' in Bengali, as it was the fastest train of that time. Duronto Express services connect the several metros and major state capitals of India.
The Intercity Express is an express-train service in India which connects major railway junctions and state capitals. These act as long-distance reserved and unreserved suburban trains with sitting accommodation. These are quite fast and maintain a high average speed for short distances along with priority over other trains.

Urban rail transit in India plays an important role in intracity transportation in the major cities which are highly populated. It consists of rapid transit, suburban rail, monorail and tram systems. According to a report published in 2021, a total of 2.63 billion people travelled annually in metro systems across India's fifteen major cities, placing the country as one of the busiest urban rapid transit hubs in the world in terms of ridership. The combined length of 895 kilometres of metro systems in India makes it the third longest in operation in the world.

Gaya Junction railway station is a junction station serving the city of Gaya, the headquarters of Gaya district and Magadh Division in the Indian state of Bihar. Gaya is in the Pandit Deen Dayal Upadhyaya railway division of the East Central Railway zone. Grand Chord rail-line that connects Howrah and New Delhi passes through Gaya. It lies between Pandit Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Junction on the Delhi side and Dhanbad Junction on the Howrah side. It is located at 24°48′13″N84°59′57″E. It has an elevation of 117 metres (384 ft). Gaya is connected with most of the states through rail network. Very few trains do-not stop here- sealdah duranto, bhubaneswar duranto, jharkhand sampark kranti and Odisha sampark kranti. There are also two other broad-gauge train lines from Gaya, one to Patna and the other to Kiul Junction. The city has two major railway stations: Gaya Junction & Manpur Junction. Gaya is well connected with Patna, Jehanabad, Biharsharif, Rajgir, Islampur, Nawada through daily passenger and express train services.

Mathura Junction railway station is an important station on Agra–Delhi chord of Delhi–Mumbai and Delhi–Chennai lines. It is located in Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is one of the important North-Central Railway stations. It serves Mathura and Vrindavan.

Katni Junction is a major rail junction in Katni, India. Rail links from the junction travel in five directions — Bina, Jabalpur, Satna, Bilaspur, Singrauli. Rail links from the junction travel to New Delhi, Mumbai, Vadodara, Howrah, Chennai, Bangalore, Dhanbad, Prayagraj, Kanpur, Lucknow, Bhopal, Indore, Gwalior, Agra, Gorakhpur, Muzaffarpur, Patna, Chandigarh, Ludhiana, Ambala, Bathinda, Jaipur, Jodhpur, Ajmer, Nagpur, Pune, Jammu, Raipur, Bhubaneswar, Visakhapatnam, Hyderabad, Hubli, Madurai, Vasco, Rameshvaram, Kanyakumari, Ernakulam and other Indian cities. To reduce the junction's load the new Katni Murwara & Katni South has been opened to carry trains from Bina and Jabalpur respectively.

The 12615 / 12616 Grand Trunk Express is a daily Superfast Express train on Indian Railways, running between New Delhi and Chennai Central. It is a historic train and is one of the oldest trains starting services in 1929. It originally ran between Peshawar in the North West Frontier Province and Mangalore Central in the Madras Presidency. From September 2021, it runs with modern new LHB coach with revised coach position.
The 20973/20974 Firozpur – Rameswaram Humsafar Express is an express train of the Indian Railways connecting Firozpur Cantonment with Rameswaram. It is currently being operated with 20973/20974 train numbers on a weekly basis. After its extension from Ajmer to Firozpur, It became as the Longest Running Humsafar category train by just surpassing SMVT Bangalore Agartala Humsafar express. And also became as 5th longest train service by Indian Railways.