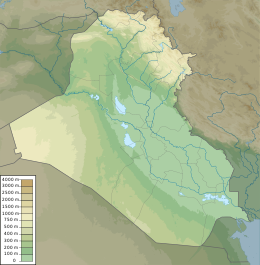
Sumer is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia, emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. Like nearby Elam, it is one of the cradles of civilization, along with Egypt, the Indus Valley, the Erligang culture of the Yellow River valley, Caral-Supe, the Cucuteni–Trypillia culture of the Carpathian Mountains, and Mesoamerica. Living along the valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, Sumerian farmers grew an abundance of grain and other crops, a surplus which enabled them to form urban settlements. The world's earliest known texts come from the Sumerian cities of Uruk and Jemdet Nasr, and date to between c. 3350 – c. 2500 BC, following a period of proto-writing c. 4000 – c. 2500 BC.

The history of Sumer spans the 5th to 3rd millennia BCE in southern Mesopotamia, and is taken to include the prehistoric Ubaid and Uruk periods. Sumer was the region's earliest known civilization and ended with the downfall of the Third Dynasty of Ur around 2004 BCE. It was followed by a transitional period of Amorite states before the rise of Babylonia in the 18th century BCE.
Uruk, known today as Warka, was an ancient city in the Near East, located east of the current bed of the Euphrates River, on an ancient, now-dried channel of the river. The site lies 93 kilometers northwest of ancient Ur, 108 kilometers southeast of ancient Nippur, and 24 kilometers southeast of ancient Larsa. It is 30 km (19 mi) east of modern Samawah, Al-Muthannā, Iraq.

The Diyala is a river and tributary of the Tigris. It is formed by the confluence of the Sirwan and Tanjaro rivers in Darbandikhan Dam in the Sulaymaniyah Governorate of Northern Iraq. It covers a total distance of 445 km (277 mi).
Shuruppak, modern Tell Fara, was an ancient Sumerian city situated about 55 kilometres (35 mi) south of Nippur and 30 kilometers north of ancient Uruk on the banks of the Euphrates in Iraq's Al-Qādisiyyah Governorate. Shuruppak was dedicated to Ninlil, also called Sud, the goddess of grain and the air.
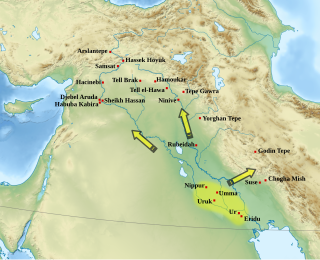
The Uruk period existed from the protohistoric Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age period in the history of Mesopotamia, after the Ubaid period and before the Jemdet Nasr period. Named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. The late Uruk period saw the gradual emergence of the cuneiform script and corresponds to the Early Bronze Age; it has also been described as the "Protoliterate period".

The Proto-Elamite period, also known as Susa III, is a chronological era in the ancient history of the area of Elam, dating from c. 3100 BC to 2700 BC. In archaeological terms this corresponds to the late Banesh period. Proto-Elamite sites are recognized as the oldest civilization in Iran. The Proto-Elamite script is an Early Bronze Age writing system briefly in use before the introduction of Elamite cuneiform.
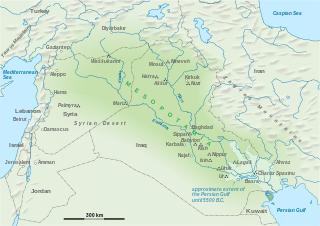
The Civilization of Mesopotamia ranges from the earliest human occupation in the Paleolithic period up to Late antiquity. This history is pieced together from evidence retrieved from archaeological excavations and, after the introduction of writing in the late 4th millennium BC, an increasing amount of historical sources. While in the Paleolithic and early Neolithic periods only parts of Upper Mesopotamia were occupied, the southern alluvium was settled during the late Neolithic period. Mesopotamia has been home to many of the oldest major civilizations, entering history from the Early Bronze Age, for which reason it is often called a cradle of civilization.
Jemdet Nasr is a tell or settlement mound in Babil Governorate (Iraq) that is best known as the eponymous type site for the Jemdet Nasr period, and was one of the oldest Sumerian cities. It is adjacent to the much larger site of Tell Barguthiat. The site was first excavated in 1926 by Stephen Langdon, who found Proto-Cuneiform clay tablets in a large mudbrick building thought to be the ancient administrative centre of the site. A second season took place in 1928, but this season was very poorly recorded. Subsequent excavations in the 1980s under British archaeologist Roger Matthews were, among other things, undertaken to relocate the building excavated by Langdon. These excavations have shown that the site was also occupied during the Ubaid, Uruk and Early Dynastic I periods. Based on texts found there mentioning an ensi of NI.RU that is thought to be its ancient name. During ancient times the city was on a canal linking it to other major Sumerian centers.

The Early Dynastic period is an archaeological culture in Mesopotamia that is generally dated to c. 2900 – c. 2350 BC and was preceded by the Uruk and Jemdet Nasr periods. It saw the development of writing and the formation of the first cities and states. The ED itself was characterized by the existence of multiple city-states: small states with a relatively simple structure that developed and solidified over time. This development ultimately led to the unification of much of Mesopotamia under the rule of Sargon, the first monarch of the Akkadian Empire. Despite this political fragmentation, the ED city-states shared a relatively homogeneous material culture. Sumerian cities such as Uruk, Ur, Lagash, Umma, and Nippur located in Lower Mesopotamia were very powerful and influential. To the north and west stretched states centered on cities such as Kish, Mari, Nagar, and Ebla.
Tepe Gawra is an ancient Mesopotamian settlement 15 miles NNE of Mosul in northwest Iraq that was occupied between 5000 and 1500 BC. It is roughly a mile from the site of Nineveh and 2 miles E of the site of Khorsabad. It contains remains from the Halaf period, the Ubaid period, and the Uruk period. Tepe Gawra contains material relating to the Halaf-Ubaid Transitional period c. 5,500–5,000 BC.

The Kish tablet is a limestone tablet found at the site of the ancient Sumerian city of Kish in modern Tell al-Uhaymir, Babylon Governorate, Iraq. A plaster cast of the tablet is in the collection of the Ashmolean Museum, while the original is housed at the Iraq Museum in Baghdad. It should not be confused with the Scheil dynastic tablet, which contains part of the Sumerian King List and is also sometimes called the Kish tablet.
Khafajah or Khafaje, ancient Tutub, is an archaeological site in Diyala Governorate, Iraq 7 miles (11 km) east of Baghdad. Khafajah lies on the Diyala River, a tributary of the Tigris. Occupied from the Uruk and Jemdet Nasr periods through the end of the Old Babylonian Empire, it was under the control of the Akkadian Empire and then the Third Dynasty of Ur in the 3rd millennium BC. It then became part of the empire of the city-state of Eshnunna lying 12 miles (19 km) southwest of that city, about 5 miles (8.0 km) from the ancient city of Shaduppum, and near Tell Ishchali, both which Eshnunna also controlled. It then fell to Babylonia before falling into disuse.
The archaeological site of Abu Salabikh, around 20 km (12 mi) northwest of the site of ancient Nippur and about 150 kilometers southeast of the modern city of Baghdad in Al-Qādisiyyah Governorate, Iraq marks the site of a small Sumerian city that existed from the Neolithic through the late 3rd millennium, with cultural connections to the cities of Kish, Mari and Ebla. Its ancient name is unknown though Eresh and Kesh have been suggested as well as Gišgi. Kesh was suggested by Thorkild Jacobsen before excavations began. The Euphrates was the city's highway and lifeline; when it shifted its old bed, in the late third millennium BC, the city dwindled away. Only eroded traces remain on the site's surface of habitation after the Early Dynastic Period. There is another small archaeological site named Abu-Salabikh in the Hammar Lake region of Southern Iraq, which has been suggested as the possible capital of the Sealand dynasty.
Tell Uqair is a tell or settlement mound northeast of ancient Babylon, about 25 kilometers north-northeast of the ancient city of Kish, just north of Kutha, and about 50 miles (80 km) south of Baghdad in modern Babil Governorate, Iraq. It was occupied in the Ubaid period and the Uruk period. It has been proposed as the site of the 3rd millennium BC city of Urum.
Tell Agrab is a tell or settlement mound 12.6 miles (20.3 km) southeast of Eshnunna in the Diyala region of Iraq. It is about 15 miles southeast of Tell Asmar, ancient Eshnunna. It has been suggested that the ancient name of the site was PA.GAR.

The art of Mesopotamia has survived in the record from early hunter-gatherer societies on to the Bronze Age cultures of the Sumerian, Akkadian, Babylonian and Assyrian empires. These empires were later replaced in the Iron Age by the Neo-Assyrian and Neo-Babylonian empires. Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Mesopotamia brought significant cultural developments, including the oldest examples of writing.

The art of Uruk encompasses the sculptures, seals, pottery, architecture, and other arts produced in Uruk, an ancient city in southern Mesopotamia that thrived during the Uruk period around 4200-3000 BCE. The city continued to develop into the Early Dynastic Period (Mesopotamia) around 2900-2350 BCE. Considered one of the first cities, the site of Uruk – modern-day Warka in Iraq – shows evidence of social stratification, institutionalized religion, a centralized administration, and what art historians would categorize as high art and architecture, the first in the long history of the art of Mesopotamia. Much of the art of Uruk shows a high technical skill and was often made using precious materials.

Egypt–Mesopotamia relations were the relations between the civilizations of ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, in the Middle East. They seem to have developed from the 4th millennium BCE, starting in the Uruk period for Mesopotamia and the half a millennium younger Gerzean culture of Prehistoric Egypt, and constituted a largely one way body of influences from Mesopotamia into Egypt.

The proto-cuneiform script was a system of proto-writing that emerged in Mesopotamia, eventually developing into the early cuneiform script used in the region's Early Dynastic I period. It arose from the token-based system that had already been in use across the region in preceding millennia. While it is known definitively that later cuneiform was used to write the Sumerian language, it is still uncertain what the underlying language of proto-cuneiform texts were.