
The geography of Antarctica is dominated by its south polar location and, thus, by ice. The Antarctic continent, located in the Earth's southern hemisphere, is centered asymmetrically around the South Pole and largely south of the Antarctic Circle. It is washed by the Southern Ocean or, depending on definition, the southern Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans. It has an area of more than 14 million km2.

Africa is a continent comprising 63 political territories, representing the largest of the great southward projections from the main mass of Earth's surface. Within its regular outline, it comprises an area of 30,368,609 km2 (11,725,385 sq mi), excluding adjacent islands. Its highest mountain is Mount Kilimanjaro, its largest lake is Lake Victoria.

The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distinguish from the Magnetic North Pole.

In geography, the antipode of any spot on Earth is the point on Earth's surface diametrically opposite to it. A pair of points antipodal to each other are situated such that a straight line connecting the two would pass through Earth's center. Antipodal points are as far away from each other as possible.

A pole of inaccessibility with respect to a geographical criterion of inaccessibility marks a location that is the most challenging to reach according to that criterion. Often it refers to the most distant point from the coastline, implying a maximum degree of continentality or oceanity. In these cases, pole of inaccessibility can be defined as the center of the largest circle that can be drawn within an area of interest without encountering a coast. Where a coast is imprecisely defined, the pole will be similarly imprecise.
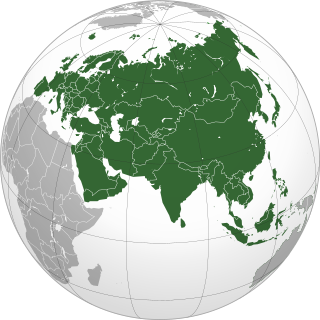
This is a list of the extreme points of Eurasia, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location on the continent. Some of these locations are open to debate, owing to the diverse definitions of Europe and Asia.

The extreme points of Norway include the coordinates that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location in Norway; and the highest and the lowest altitudes in the country. The northernmost point is Rossøya on Svalbard, the southernmost is Pysen in Mandal, the easternmost is Kræmerpynten on Svalbard, and the westernmost is Hoybergodden on Jan Mayen. The highest peak is Galdhøpiggen, standing at 2,469 m (8,100 ft) above mean sea level, while the lowest elevation is sea level at the coast.

This is a list of the extreme points of North America: the points that are highest and lowest, and farther north, south, east or west than any other location on the continent. Some of these points are debatable, given the varying definitions of North America.

Dome A or Dome Argus is the loftiest ice dome on the Antarctic Plateau, located 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) inland. It is thought to be the coldest naturally occurring place on Earth; with temperatures believed to reach −90 °C (−130 °F) to −98 °C (−144 °F). It is the highest ice feature in Antarctica, consisting of an ice dome or eminence of 4,093 metres' (13,428 ft) elevation above sea level. It is located near the center of East Antarctica, approximately midway between the enormous head of Lambert Glacier and the geographic South Pole, within the Australian claim.
This is a list of extreme points in Antarctica.
This is a list of the extreme points of The Americas, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location on the continent. The continent's southernmost point is often said to be Cape Horn, which is the southernmost point of the Chilean islands. The Americas cross 134° of longitude east to west and 124° of latitude north to south.
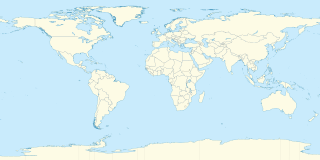
The 45×90 points are the four points on Earth which are halfway between the geographical poles, the equator, the Prime Meridian, and the 180th meridian.

Farthest South refers to the most southerly latitude reached by explorers before the conquest of the South Pole in 1911. Significant steps on the road to the pole were the discovery of lands south of Cape Horn in 1619, Captain James Cook's crossing of the Antarctic Circle in 1773, and the earliest confirmed sightings of the Antarctic mainland in 1820. From the late 19th century onward, the quest for Farthest South latitudes became in effect a race to reach the pole, which culminated in Roald Amundsen's success in December 1911.

Earth's Equator is a specific case of a planetary equator. It is about 40,075 km (24,901 mi) long, of which 78.8% lies across water and 21.3% over land.
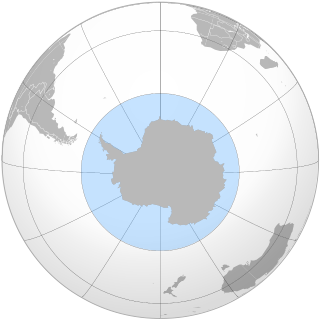
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean or the Austral Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. As such, it is regarded as the second-smallest of the five principal oceanic divisions: smaller than the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans but larger than the Arctic Ocean. Over the past 30 years, the Southern Ocean has been subject to rapid climate change, which has led to changes in the marine ecosystem.
This is a list of the extreme points of the Commonwealth of Nations — the points that are farther north, south, east or west, or higher or lower in elevation than any other location.

The borders of the oceans are the limits of Earth's oceanic waters. The definition and number of oceans can vary depending on the adopted criteria.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on January 23, 1860 during summer. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.


















