
Dopaminergic means "related to dopamine", a common neurotransmitter. Dopaminergic substances or actions increase dopamine-related activity in the brain.
An autoreceptor is a type of receptor located in the membranes of nerve cells. It serves as part of a negative feedback loop in signal transduction. It is only sensitive to the neurotransmitters or hormones released by the neuron on which the autoreceptor sits. Similarly, a heteroreceptor is sensitive to neurotransmitters and hormones that are not released by the cell on which it sits. A given receptor can act as either an autoreceptor or a heteroreceptor, depending upon the type of transmitter released by the cell on which it is embedded.

Quinpirole is a psychoactive drug and research chemical which acts as a selective D2 and D3 receptor agonist. It is used in scientific research. Quinpirole has been shown to increase locomotion and sniffing behavior in mice treated with it. At least one study has found that quinpirole induces compulsive behavior symptomatic of obsessive compulsive disorder in rats. Another study in rats show that quinpirole produces significant THC-like effects when metabolic degradation of anandamide is inhibited, supporting the hypothesis that these effects of quinpirole are mediated by cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Quinpirole may also reduce relapse in adolescent rat models of cocaine addiction.

Pramipexole, sold under the brand Mirapex among others, is a medication used to treat Parkinson's disease (PD) and restless legs syndrome (RLS). In Parkinson's disease it may be used alone or together with levodopa. It is taken by mouth. Pramipexole is a dopamine agonist of the non-ergoline class.

A dopamine agonist is a compound that activates dopamine receptors. There are two families of dopamine receptors, D1-like and D2-like. They are all G protein-coupled receptors. D1- and D5-receptors belong to the D1-like family and the D2-like family includes D2, D3 and D4 receptors. Dopamine agonists are primarily used in the treatment of the motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease, and to a lesser extent, in hyperprolactinemia and restless legs syndrome. They are also used off-label in the treatment of clinical depression. Impulse control disorders are associated with the use of dopamine agonists for whatever condition.

Piribedil (trade names Pronoran, Trivastal Retard, Trastal, Trivastan, Clarium and others) is an antiparkinsonian agent and piperazine derivative which acts as a D2 and D3 receptor agonist. It also has α2-adrenergic antagonist properties.
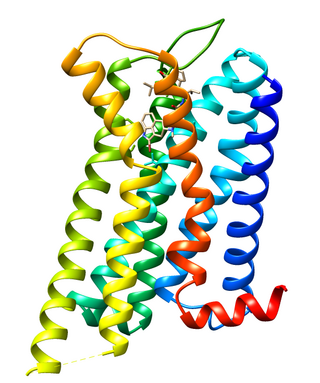
Dopamine receptor D2, also known as D2R, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the DRD2 gene. After work from Paul Greengard's lab had suggested that dopamine receptors were the site of action of antipsychotic drugs, several groups, including those of Solomon H. Snyder and Philip Seeman used a radiolabeled antipsychotic drug to identify what is now known as the dopamine D2 receptor. The dopamine D2 receptor is the main receptor for most antipsychotic drugs. The structure of DRD2 in complex with the atypical antipsychotic risperidone has been determined.

Dopamine receptor D1, also known as DRD1. It is one of the two types of D1-like receptor family — receptors D1 and D5. It is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD1 gene.

Dopamine receptor D3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD3 gene.

N-n-Propylnorapomorphine (NPA) is an aporphine derivative dopamine agonist closely related to apomorphine. In rodents it has been shown to produce hyperactivity, stereotypy, hypothermia, antinociception, and penile erection, among other effects. Notably, its effects on locomotion are biphasic, with low doses producing inhibition and catalepsy and high doses resulting in enhancement of activity. This is likely due to preferential activation of D2/D3 autoreceptors versus postsynaptic receptors, the latter of which overcomes the former to increase postsynaptic dopaminergic signaling only with high doses.

UH-232 ((+)-UH232) is a drug which acts as a subtype selective mixed agonist-antagonist for dopamine receptors, acting as a weak partial agonist at the D3 subtype, and an antagonist at D2Sh autoreceptors on dopaminergic nerve terminals. It causes dopamine release in the brain and has a stimulant effect, as well as blocking the behavioural effects of cocaine. It may also serve as a 5-HT2A receptor agonist, based on animal studies. It was investigated in clinical trials for the treatment of schizophrenia, but unexpectedly caused symptoms to become worse.

7-OH-DPAT is a synthetic compound that acts as a dopamine receptor agonist with reasonable selectivity for the D3 receptor subtype, and low affinity for serotonin receptors, unlike its structural isomer 8-OH-DPAT. 7-OH-DPAT is self-administered in several animal models, and is used to study its addiction effects to cocaine.

LY-379,268 is a drug that is used in neuroscience research, which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3).
Roxindole (EMD-49,980) is a dopaminergic and serotonergic drug which was originally developed by Merck KGaA for the treatment of schizophrenia. In clinical trials its antipsychotic efficacy was only modest but it was unexpectedly found to produce potent and rapid antidepressant and anxiolytic effects. As a result, roxindole was further researched for the treatment of depression instead. It has also been investigated as a therapy for Parkinson's disease and prolactinoma.
PNU-99,194(A) (or U-99,194(A)) is a drug which acts as a moderately selective D3 receptor antagonist with ~15-30-fold preference for D3 over the D2 subtype. Though it has substantially greater preference for D3 over D2, the latter receptor does still play some role in its effects, as evidenced by the fact that PNU-99,194 weakly stimulates both prolactin secretion and striatal dopamine synthesis, actions it does not share with the more selective (100-fold) D3 receptor antagonists S-14,297 and GR-103,691.

N-Desmethylclozapine (NDMC), or norclozapine, is a major active metabolite of the atypical antipsychotic drug clozapine. Unlike clozapine, it possesses intrinsic activity at the D2/D3 receptors, and acts as a weak partial agonist at these sites similarly to aripiprazole and bifeprunox. Notably, NDMC has also been shown to act as a potent and efficacious agonist at the M1 and δ-opioid receptors, unlike clozapine as well. It was hypothesized that on account of these unique actions, NDMC might underlie the clinical superiority of clozapine over other antipsychotics. However, clinical trials found NMDC itself ineffective in the treatment of schizophrenia. This may be because it possesses relatively low D2/D3 occupancy compared to 5-HT2 (<15% versus 64–79% at a dose of 10–60 mg/kg s.c. in animal studies). Albeit not useful in the treatment of positive symptoms on its own, it cannot be ruled out that NDMC may contribute to the efficacy of clozapine on cognitive and/or negative symptoms.

Quinelorane is a drug which acts as a dopamine agonist for the D2 and D3 receptor.

BP-897 is a drug used in scientific research which acts as a potent selective dopamine D3 receptor partial agonist with an in vitro intrinsic activity of ~0.6 and ~70x greater affinity for D3 over D2 receptors and is suspected to have partial agonist or antagonist activity in vivo. It has mainly been used in the study of treatments for cocaine addiction. A study comparing BP-897 with the potent, antagonistic, and highly D3 selective SB-277,011-A found, "SB 277011-A (1–10 mg/kg) was able to block cue-induced reinstatement of nicotine-seeking, indicating that DRD3 selective antagonism may be an effective approach to prevent relapse for nicotine. In contrast, BP 897 did not block the cue-induced reinstatement of nicotine-seeking or nicotine-taking under the FR5 schedule."

L-741,626 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the dopamine receptor D2. It has good selectivity over the related D3 and D4 subtypes and other receptors. L-741,626 is used for laboratory research into brain function and has proved particularly useful for distinguishing D2 mediated responses from those produced by the closely related D3 subtype, and for studying the roles of these subtypes in the action of cocaine and amphetamines in the brain.

Mesdopetam (INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name; developmental code names IRL-790, IPN60170) is a dopamine D2 and D3 receptor antagonist with preference for the D3 receptor which is under development for the treatment of Parkinson's disease, drug-induced dyskinesia, and psychotic disorders. It has been described by its developers as having "psychomotor stabilizing" properties.



















