
WIN 35,428 is a stimulant drug used in scientific research. CFT is a phenyltropane based dopamine reuptake inhibitor and is structurally derived from cocaine. It is around 3-10x more potent than cocaine and lasts around 7 times longer based on animal studies. While the naphthalenedisulfonate salt is the most commonly used form in scientific research due to its high solubility in water, the free base and hydrochloride salts are known compounds and can also be produced. The tartrate is another salt form that is reported.
Phenyltropanes (PTs) were originally developed to reduce cocaine addiction and dependency. In general these compounds act as inhibitors of the plasmalemmal monoamine reuptake transporters. This research has spanned beyond the last couple decades, and has picked up its pace in recent times, creating numerous phenyltropanes as research into cocaine analogues garners interest to treat addiction.
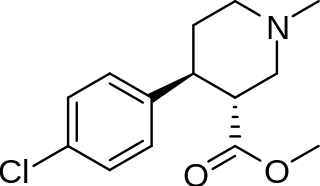
(+)-CPCA is a stimulant drug similar in structure to pethidine and to RTI-31, but nocaine lacks the two-carbon bridge of RTI-31's tropane skeleton. This compound was first developed as a substitute agent for cocaine.

Troparil is a stimulant drug used in scientific research. Troparil is a phenyltropane-based dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI) that is derived from methylecgonidine. Troparil is a few times more potent than cocaine as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor, but is less potent as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor, and has a duration spanning a few times longer, since the phenyl ring is directly connected to the tropane ring through a non-hydrolyzable carbon-carbon bond. The lack of an ester linkage removes the local anesthetic action from the drug, so troparil is a pure stimulant. This change in activity also makes troparil slightly less cardiotoxic than cocaine. The most commonly used form of troparil is the tartrate salt, but the hydrochloride and naphthalenedisulfonate salts are also available, as well as the free base.

RTI(-4229)-55, also called RTI-55 or iometopane, is a phenyltropane-based psychostimulant used in scientific research and in some medical applications. This drug was first cited in 1991. RTI-55 is a non-selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor derived from methylecgonidine. However, more selective analogs are derived by conversion to "pyrrolidinoamido" RTI-229, for instance. Due to the large bulbous nature of the weakly electron withdrawing iodo halogen atom, RTI-55 is the most strongly serotonergic of the simple para-substituted troparil based analogs. In rodents RTI-55 actually caused death at a dosage of 100 mg/kg, whereas RTI-51 and RTI-31 did not. Another notable observation is the strong propensity of RTI-55 to cause locomotor activity enhancements, although in an earlier study, RTI-51 was actually even stronger than RTI-55 in shifting baseline LMA. This observation serves to highlight the disparities that can arise between studies.

(–)-2β-Carboisopropoxy-3β-(4-iodophenyl)tropane is a stimulant drug used in scientific research, which was developed in the early 1990s. RTI-121 is a phenyltropane based, highly selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor and is derived from methylecgonidine. RTI-121 is a potent and long-lasting stimulant, producing stimulant effects for more than 10 hours after a single dose in mice which would limit its potential uses in humans, as it might have significant abuse potential if used outside a medical setting. However RTI-121 occupies the dopamine transporter more slowly than cocaine, and so might have lower abuse potential than cocaine itself.

Dichloropane ((−)-2β-Carbomethoxy-3β-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)tropane, RTI-111, O-401) is a stimulant of the phenyltropane class that acts as a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI) with IC50 values of 3.13, 18, and 0.79 nM, respectively. In animal studies, dichloropane had a slower onset and longer duration of action compared to cocaine.

RTI-126 is a phenyltropane derivative which acts as a potent monoamine reuptake inhibitor and stimulant drug, and has been sold as a designer drug. It is around 5 times more potent than cocaine at inhibiting monoamine reuptake in vitro, but is relatively unselective. It binds to all three monoamine transporters, although still with some selectivity for the dopamine transporter. RTI-126 has a fast onset of effects and short duration of action, and its pharmacological profile in animals is among the closest to cocaine itself out of all the drugs in the RTI series. Its main application in scientific research has been in studies investigating the influence of pharmacokinetics on the abuse potential of stimulant drugs, with its rapid entry into the brain thought to be a key factor in producing its high propensity for development of dependence in animals.
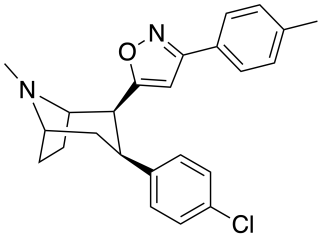
RTI(-4229)-336, is a phenyltropane derivative which acts as a potent and selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor and stimulant drug. It binds to the dopamine transporter with around 20x the affinity of cocaine, however it produces relatively mild stimulant effects, with a slow onset and long duration of action. These characteristics make it a potential candidate for treatment of cocaine addiction, as a possible substitute drug analogous to how methadone is used for treating heroin abuse. RTI-336 fully substitutes for cocaine in addicted monkeys and supports self-administration, and significantly reduces rates of cocaine use, especially when combined with SSRIs, and research is ongoing to determine whether it could be a viable substitute drug in human cocaine addicts.
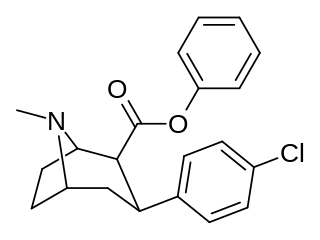
RTI(-4229)-113 is a stimulant drug which acts as a potent and fully selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI). It has been suggested as a possible substitute drug for the treatment of cocaine addiction. "RTI-113 has properties that make it an ideal medication for cocaine abusers, such as an equivalent efficacy, a higher potency, and a longer duration of action as compared to cocaine." Replacing the methyl ester in RTI-31 with a phenyl ester makes the resultant RTI-113 fully DAT specific. RTI-113 is a particularly relevant phenyltropane cocaine analog that has been tested on squirrel monkeys. RTI-113 has also been tested against cocaine in self-administration studies for DAT occupancy by PET on awake rhesus monkeys. The efficacy of cocaine analogs to elicit self-administration is closely related to the rate at which they are administered. Slower onset of action analogs are less likely to function as positive reinforcers than analogues that have a faster rate of onset.

RTI-31 is a synthetic analog of cocaine that acts as a stimulant. Semi-synthesis of this compound is dependent upon the availability of cocaine starting material. According to the article, RTI-31 is 64 times the strength of cocaine in terms of its potency to elicit self-administration in monkeys. WIN 35428 was 6 times weaker than RTI-31, whereas RTI-51 was 2.6 times weaker than RTI-31.

(–)-2β-Carbomethoxy-3β-(4-bromophenyl)tropane is a semi-synthetic alkaloid in the phenyltropane group of psychostimulant compounds. First publicized in the 1990s, it has not been used enough to have gained a fully established profile. RTI-51 can be expected to have properties lying somewhere in between RTI-31 and RTI-55. It has a ratio of monoamine reuptake inhibition of dopamine > serotonin > norepinephrine which is an unusual balance of effects not produced by other commonly used compounds. It has been used in its 76Br radiolabelled form to map the distribution of dopamine transporters in the brain.

(–)-2β-Carbomethoxy-3β-(4-tolyl)tropane is a phenyltropane-based cocaine analogue that has similar properties in vitro to related drugs such as RTI-31.

RTI(-4229)-274, or 2β-( methyl)-3α-(4-fluorophenyl)nortropane is a phenyltropane homologue of paroxetine developed by the group led by F Ivy Carroll in the 1990s.

Salicylmethylecgonine, (2′-Hydroxycocaine) is a tropane derivative drug which is both a synthetic analogue and a possible active metabolite of cocaine. Its potency in vitro is around 10x that of cocaine, although it is only around three times more potent than cocaine when administered to mice Note however that the compound 2′-Acetoxycocaine would act as a prodrug to Salicylmethylecgonine in humans, and has a more efficient partition coefficient which would act as a delivery system and would circumvent this reason for a drop in potency. Salicylmethylecgonine also shows increased behavioral stimulation compared to cocaine similar to the phenyltropanes. The hydroxy branch renders the molecule a QSAR of a 10-fold increase over cocaine in its binding potency for the dopamine transporter & a 52-fold enhanced affinity for the norepinephrine transporter. It also has a reduced selectivity for the serotonin transporter though only due to its greater increase at NET binding; its SERT affinity being 4-fold increased compared to cocaine. However, in overall binding affinity it displaces ligands better across the board than cocaine in all monoamine categories.

RTI-229, also known as (–)-3β-(4-iodophenyl)tropane-2β-pyrrolidine carboxamide and RTI-4229-229, is a potent and long-lasting stimulant drug which was developed in the 1990s as part of a large group of related analogues from the phenyltropane family. With the combination of two potent dopamine transporter (DAT) binding motifs attached to the tropane ring, the p-iodophenyl group at the 3β-position and a pyrrolidine carboxamide at 2β, RTI-229 has extremely high selectivity for the dopamine transporter and is one of the most DAT-selective compounds in the RTI series.
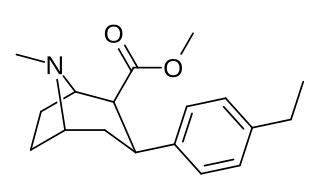
RTI-83 is a phenyltropane derivative which represents a rare example of an SDRI or serotonin-dopamine reuptake inhibitor, a drug which inhibits the reuptake of the neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine, while having little or no effect on the reuptake of the related neurotransmitter noradrenaline. With a binding affinity (Ki) of 55 nM at DAT and 28.4 nM at SERT but only 4030 nM at NET, RTI-83 has reasonable selectivity for DAT/SERT over NET

Cocaine reverse ester, (also known as Reverse ester cocaine or REC) is a tropane derivative drug which is a reverse ester of cocaine, with the 2-COOCH3 methoxycarbonyl group swapped to an isomeric OCOCH3 acetoxy group. It was synthesised because of the observation that the reverse ester pairs of several structurally related substances show similar activity to each other (see e.g. methylphenidate vs phacetoperane, pethidine vs desmethylprodine). Cocaine reverse ester however did not produce cocaine-like stimulant effects in animal studies, and is also illegal in many jurisdictions as a structural isomer of cocaine; nevertheless it has attracted attention from vendors of quasi-legal designer drugs as a potential alternative to cocaine.


















