
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Pakistan:
Contents
- General reference
- Geography of Pakistan
- Environment of Pakistan
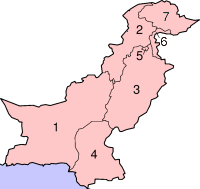
- Administrative divisions of Pakistan
- Demography of Pakistan
- Government and politics of Pakistan
- Political parties in Pakistan
- Branches of the government of Pakistan
- Foreign relations of Pakistan
- International organization membership
- Law and order in Pakistan
- Local governance in Pakistan
- Pakistan Armed Forces
- Civil Armed Forces
- History of Pakistan
- Culture of Pakistan
- Art in Pakistan
- Sports in Pakistan
- Economy and infrastructure of Pakistan
- Education in Pakistan
- See also
- References
- External links
Pakistan – sovereign country located in South Asia. [1] It has a 1,046 kilometres (650 mi) coastline along the Arabian Sea and Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan in the west, Iran in the southwest, India in the east and China in the far northeast. [2]