
In dogs, hip dysplasia is an abnormal formation of the hip socket that, in its more severe form, can eventually cause lameness and arthritis of the joints. It is a genetic (polygenic) trait that is affected by environmental factors. It is common in many dog breeds, particularly the larger breeds, and is the most common single cause of arthritis of the hips.

Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics, is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors, and congenital disorders.
An osteotomy is a surgical operation whereby a bone is cut to shorten or lengthen it or to change its alignment. It is sometimes performed to correct a hallux valgus, or to straighten a bone that has healed crookedly following a fracture. It is also used to correct a coxa vara, genu valgum, and genu varum. The operation is done under a general anaesthetic.

Coxa vara is a deformity of the hip, whereby the angle between the head and the shaft of the femur is reduced to less than 120 degrees. This results in the leg being shortened and the development of a limp. It may be congenital and is commonly caused by injury, such as a fracture. It can also occur when the bone tissue in the neck of the femur is softer than normal, causing it to bend under the weight of the body. This may either be congenital or the result of a bone disorder. The most common cause of coxa vara is either congenital or developmental. Other common causes include metabolic bone diseases, post-Perthes deformity, osteomyelitis, and post traumatic. Shepherd's Crook deformity is a severe form of coxa vara where the proximal femur is severely deformed with a reduction in the neck shaft angle beyond 90 degrees. It is most commonly a sequela of osteogenesis imperfecta, Pagets disease, osteomyelitis, tumour and tumour-like conditions.

A bone fracture is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of a bone. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several pieces. A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, osteopenia, bone cancer, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where the fracture is then properly termed a pathologic fracture.
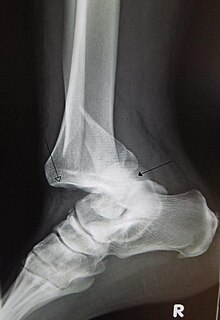
A joint dislocation, also called luxation, occurs when there is an abnormal separation in the joint, where two or more bones meet. A partial dislocation is referred to as a subluxation. Dislocations are often caused by sudden trauma on the joint like an impact or fall. A joint dislocation can cause damage to the surrounding ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves. Dislocations can occur in any major joint or minor joint. The most common joint dislocation is a shoulder dislocation.
Arthroplasty is an orthopedic surgical procedure where the articular surface of a musculoskeletal joint is replaced, remodeled, or realigned by osteotomy or some other procedure. It is an elective procedure that is done to relieve pain and restore function to the joint after damage by arthritis or some other type of trauma.

Replacement arthroplasty, or joint replacement surgery, is a procedure of orthopedic surgery in which an arthritic or dysfunctional joint surface is replaced with an orthopedic prosthesis. Joint replacement is considered as a treatment when severe joint pain or dysfunction is not alleviated by less-invasive therapies. It is a form of arthroplasty, and is often indicated from various joint diseases, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.

A hip dislocation is when the thighbone (femur) separates from the hip bone (pelvis). Specifically it is when the ball–shaped head of the femur separates from its cup–shaped socket in the hip bone, known as the acetabulum. The joint of the femur and pelvis is very stable, secured by both bony and soft-tissue constraints. With that, dislocation would require significant force which typically results from significant trauma such as from a motor vehicle collision or from a fall from elevation. Hip dislocations can also occur following a hip replacement or from a developmental abnormality known as hip dysplasia.

Madelung's deformity is usually characterized by malformed wrists and wrist bones and is often associated with Léri-Weill dyschondrosteosis. It can be bilateral or just in the one wrist. It has only been recognized within the past hundred years. Named after Otto Wilhelm Madelung (1846–1926), a German surgeon, who described it in detail, it was noted by others. Guillaume Dupuytren mentioned it in 1834, Auguste Nélaton in 1847, and Joseph-François Malgaigne in 1855.
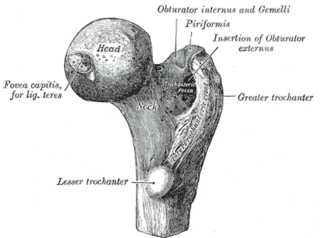
A femoral head ostectomy is a surgical operation to remove the head and neck from the femur. It is performed to alleviate pain, and is a salvage procedure, reserved for condition where pain can not be alleviated in any other way. It is common in veterinary surgery. Other names are excision arthroplasty of the femoral head and neck, Girdlestone's operation, Girdlestone procedure, and femoral head and neck ostectomy.

Ollier disease is a rare sporadic nonhereditary skeletal disorder in which typically benign cartilaginous tumors (enchondromas) develop near the growth plate cartilage. This is caused by cartilage rests that grow and reside within the metaphysis or diaphysis and eventually mineralize over time to form multiple enchondromas. Key signs of the disorder include asymmetry and shortening of the limb as well as an increased thickness of the bone margin. These symptoms are typically first visible during early childhood with the mean age of diagnosis being 13 years of age. Many patients with Ollier disease are prone to develop other malignancies including bone sarcomas that necessitate treatment and the removal of malignant bone neoplasm. Cases in patients with Ollier disease has shown a link to IDH1, IDH2, and PTH1R gene mutations. Currently, there are no forms of treatment for the underlying condition of Ollier disease but complications such as fractures, deformities, malignancies that arise from it can be treated through surgical procedures. The prevalence of this condition is estimated at around 1 in 100,000. It is unclear whether the men or women are more affected by this disorder due to conflicting case studies.
HOSMAT multispecialty Hospital Pvt. Ltd. , the Hospital for Orthopaedics, Sports Medicine, Arthritis & Trauma, is a 350-bed speciality hospital in central Bangalore, India. It also includes Hosmat Joint Replacement Center and HOSMAT Neurosciences. It is currently undergoing expansion to 500 beds, which would make it the largest speciality hospital of its kind in Asia.

A separated shoulder, also known as acromioclavicular joint injury, is a common injury to the acromioclavicular joint. The AC joint is located at the outer end of the clavicle where it attaches to the acromion of the scapula. Symptoms include non-radiating pain which may make it difficult to move the shoulder. The presence of swelling or bruising and a deformity in the shoulder is also common depending on how severe the dislocation is.
Foot and ankle surgery is a sub-specialty of orthopedics and podiatry that deals with the treatment, diagnosis and prevention of disorders of the foot and ankle. Orthopaedic surgeons are medically qualified, having been through four years of college, followed by 4 years of medical school to obtain an M.D. or D.O. followed by specialist training as a resident in orthopaedics, and only then do they sub-specialise in foot and ankle surgery. Training for a podiatric foot and ankle surgeon consists of four years of college, four years of podiatric medical school (D.P.M.), 3–4 years of a surgical residency and an optional 1 year fellowship.
Protrusio acetabuli is an uncommon defect of the acetabulum, the socket that receives the femoral head to make the hip joint. The hip bone of the pelvic bone/girdle is composed of three bones, the ilium, the ischium and the pubis. In protrusio deformity, there is medial displacement of the femoral head in that the medial aspect of the femoral cortex is medial to the ilioischial line. The socket is too deep and may protrude into the pelvis.

Hip dysplasia is an abnormality of the hip joint where the socket portion does not fully cover the ball portion, resulting in an increased risk for joint dislocation. Hip dysplasia may occur at birth or develop in early life. Regardless, it does not typically produce symptoms in babies less than a year old. Occasionally one leg may be shorter than the other. The left hip is more often affected than the right. Complications without treatment can include arthritis, limping, and low back pain.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to trauma and orthopaedics:












