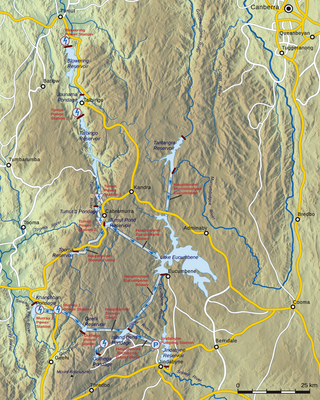
The Snowy Mountains Scheme, also known as the Snowy Hydro or the Snowy scheme, is a hydroelectricity and irrigation complex in south-east Australia. Near the border of New South Wales and Victoria, the scheme consists of sixteen major dams; nine power stations; two pumping stations; and 225 kilometres (140 mi) of tunnels, pipelines and aqueducts that were constructed between 1949 and 1974. The Scheme was completed under the supervision of Chief Engineer, Sir William Hudson. It is the largest engineering project undertaken in Australia.

The Crotty Dam, also known during construction as the King Dam, or the King River Dam on initial approval, is a rockfill embankment dam with a controlled and uncontrolled spillway across the King River, between Mount Jukes and Mount Huxley, located in Western Tasmania, Australia.

The Blowering Dam is a major ungated rock fill with clay core embankment dam with concrete chute spillway impounding a reservoir under the same name. It is located on the Tumut River upstream of Tumut in the Snowy Mountains region of New South Wales, Australia. Purposes for the dam include flood mitigation, hydro-power, irrigation, water supply and conservation. The dam is part of the Snowy Mountains Scheme, a vast hydroelectricity and irrigation complex constructed in south-east Australia between 1949 and 1974 and now run by Snowy Hydro.

Jindabyne Dam is a major ungated rockfill embankment dam across the Snowy River in the Snowy Mountains of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's main purpose is to redirect water from the Snowy River to the Murray, for the generation of hydro-power and irrigation. It is one of the sixteen major dams that comprise the Snowy Mountains Scheme, a vast hydroelectricity and irrigation complex constructed in south-east Australia between 1949 and 1974 and now run by Snowy Hydro.

Eucumbene Dam is a major gated earthfill embankment dam with an overflow ski-jump and bucket spillway with two vertical lift gates across the Eucumbene River in the Snowy Mountains of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's main purpose is for the generation of hydro-power and is one of the sixteen major dams that comprise the Snowy Mountains Scheme, a vast hydroelectricity and irrigation complex constructed in south-east Australia between 1949 and 1974 and now run by Snowy Hydro.

The Murray Region Hydroelectric Power Stations refers to two of the original seven hydroelectric power stations, both located near the town of Khancoban in the Snowy Mountains region of New South Wales, Australia. The two power stations are part of the Snowy Mountains Scheme, a vast hydroelectricity and irrigation complex constructed in south-east Australia between 1949 and 1974 and now run by Snowy Hydro. Although both power stations are physically located in New South Wales, since 1 July 2008 all power generated has been allocated to the Victorian region of the National Electricity Market. The stations are not located on the Murray River.

The Tumut Hydroelectric Power Stations is a series of three hydroelectric power stations on the Tumut River in New South Wales, Australia, that are part of the Snowy Mountains Scheme.

Tooma Dam is a major ungated earthen embankment dam across the Tooma River in the Snowy Mountains of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's main purpose is for the generation of hydro-power and is one of the sixteen major dams that comprise the Snowy Mountains Scheme, a vast hydroelectricity and irrigation complex constructed in south-east Australia between 1949 and 1974 and now run by Snowy Hydro.

Tantangara Dam is a major ungated concrete gravity dam with concrete chute spillway across the Murrumbidgee River in Tantangara, upstream of Adaminaby in the Snowy Mountains region of New South Wales, Australia. The dam is part of the Snowy Mountains Scheme, a vast hydroelectricity and irrigation complex constructed in south-east Australia between 1949 and 1974 and now run by Snowy Hydro. The purpose of the dam includes water management and conservation, with much of the impounded headwaters diverted to Lake Eucumbene. The impounded reservoir is called Tantangara Reservoir.

Talbingo Dam is a major ungated rock fill with clay core embankment dam with concrete chute spillway across the Tumut River upstream of Talbingo in the Snowy Mountains region of New South Wales, Australia. The impounded reservoir is called Talbingo Reservoir.

Tumut Pond Dam is a major gated concrete arch dam across the upper reaches of the Tumut River in the Snowy Mountains of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's main purpose is for the generation of hydro-power and is one of the sixteen major dams that comprise the Snowy Mountains Scheme, a vast hydroelectricity and irrigation complex constructed in south-east Australia between 1949 and 1974 and now run by Snowy Hydro.
Swampy Plain River, a perennial stream that is part of the Murray catchment within the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the Snowy Mountains bioregion of New South Wales, Australia.

Jounama Dam is a major ungated rockfill embankment dam across the Tumut River in the Snowy Mountains of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's main purpose is for the generation of hydro-power and is one of the sixteen major dams that comprise the Snowy Mountains Scheme, a vast hydroelectricity and irrigation complex constructed in south-east Australia between 1949 and 1974 and now run by Snowy Hydro.
Tumut Two Dam or Tumut Two is a major ungated concrete gravity dam across the upper reaches of the Tumut River in the Snowy Mountains of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's main purpose is for the generation of hydro-power and is one of the sixteen major dams that comprise the Snowy Mountains Scheme, a vast hydroelectricity and irrigation complex constructed in south-east Australia between 1949 and 1974 and now run by Snowy Hydro.
Deep Creek Dam is a major ungated concrete gravity dam across the Deep Creek in the Snowy Mountains of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's main purpose is for the diversion of water for generation of hydro-power and is the smallest of the sixteen major dams that comprise the Snowy Mountains Scheme, a vast hydroelectricity and irrigation complex constructed in south-east Australia between 1949 and 1974 and now run by Snowy Hydro.

Geehi Dam is a major ungated rockfill embankment dam across the Geehi River in the Snowy Mountains of New South Wales, Australia. The reservoir impounded by the dam is known as Geehi Reservoir.

Guthega Dam is concrete gravity dam with an uncontrolled spillway across the Snowy River in the Snowy Mountains of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's main purpose is for the storage of water used in the generation of hydro-power. It is the first to be completed of the sixteen major dams of the Snowy Mountains Scheme, a vast hydroelectricity and irrigation complex constructed in south-east Australia between 1949 and 1974 and now run by Snowy Hydro.
Happy Jacks Dam is a major ungated concrete gravity dam across the Tumut River in the Snowy Mountains region of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's main purpose is for the generation of hydro-power and is one of the sixteen major dams that comprise the Snowy Mountains Scheme, a vast hydroelectricity and irrigation complex constructed in south-east Australia between 1949 and 1974 and now run by Snowy Hydro.
Khancoban Dam is a major ungated earthfill embankment dam with a controlled spillway across the Swampy Plain River in the Snowy Mountains region of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's main purpose is for the generation of hydro-power and is one of the sixteen major dams that comprise the Snowy Mountains Scheme, a vast hydroelectricity and irrigation complex constructed in south-east Australia between 1949 and 1974 and now run by Snowy Hydro.
Murray Two Dam or Murray 2 Dam is a major ungated concrete arch dam with a controlled spillway across Khancoban Bank, a diverted flow of the Snowy and Geehi rivers in the Snowy Mountains region of New South Wales, Australia. The impounded reservoir is called the Murray Two Pondage or Murray 2 Pondage.













