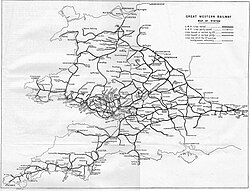
The Wessex Main Line is the railway line from Bristol Temple Meads to Southampton Central. Diverging from this route is the Heart of Wessex Line from Westbury to Weymouth. The Wessex Main Line intersects the Reading to Taunton Line at Westbury and the West of England Main Line at Salisbury.

Reading railway station is a major transport hub in Reading, Berkshire, England; it is 36 miles (58 km) west of London Paddington. It is sited on the northern edge of the town centre, near to the main retail and commercial areas and the River Thames. It is the busiest station in Berkshire, and the third busiest in South East England.

Thatcham railway station serves the market town of Thatcham in Berkshire, England. It is 49 miles 45 chains measured from the zero point at London Paddington. It is served by Great Western Railway local services between Reading and Newbury and Bedwyn.

Newbury railway station is located in the centre of the market town of Newbury, in the English county of Berkshire. The station is 53 miles 6 chains from the zero point at London Paddington. It is served by stopping services between Reading and Newbury and Bedwyn, and by faster services between London Paddington and Exeter St Davids and other parts of Devon and Cornwall. All train services at the station are operated by the Great Western Railway.

Kintbury railway station serves the village of Kintbury in Berkshire, England. It is situated on the Reading to Taunton Line, 58 miles 38 chains from London Paddington.

Hungerford railway station is a railway station that serves the historic market town of Hungerford in Berkshire, England. It is 61 miles 43 chains measured from the zero point at London Paddington.

Bedwyn railway station serves the village of Great Bedwyn in Wiltshire, England. It is 66 miles 33 chains from the zero point at London Paddington. Along with Pewsey station, it serves the market town of Marlborough which is 6 miles (10 km) away. A bus from the town connects with most trains on Mondays to Saturdays.

Taunton railway station is a junction station on the route from London to Penzance, 163 miles 12 chains (263 km) west of London Paddington station, measured via Box. It is situated in Taunton, Somerset, and is operated by Great Western Railway. The station is also served by CrossCountry trains and by the West Somerset Railway on special event days and by mainline steam excursions.

Castle Cary railway station is on the Reading to Taunton line 115.25 miles (185.48 km) south west of London Paddington and the Bristol to Weymouth line 47.75 miles (77 km) south of Bristol Temple Meads. The two routes share tracks between Westbury and Castle Cary stations and are both operated by Great Western Railway, which also manages the station. The station is 1 mile (1.6 km) north of the market town of Castle Cary and 5 miles (8 km) south of Shepton Mallet in a largely rural area of Somerset, England.

Westbury railway station serves the market town of Westbury in Wiltshire, England. The station is managed by Great Western Railway.

Bruton railway station serves a largely rural area in the county of Somerset in England. The station is situated in the market town of Bruton. The station is on the Bristol to Weymouth line some 32.75 miles (53 km) south of Bath Spa. Trains on the Reading to Taunton line pass through the station but do not normally stop. Services are operated by Great Western Railway and South Western Railway.

The Bristol and Exeter Railway (B&ER) was an English railway company formed to connect Bristol and Exeter. It was built on the broad gauge and its engineer was Isambard Kingdom Brunel. It opened in stages between 1841 and 1844. It was allied with the Great Western Railway (GWR), which built its main line between London and Bristol, and in time formed part of a through route between London and Cornwall.

Witham (Somerset) railway station was a station serving the Somerset village of Witham Friary and was located on the Frome to Yeovil section of the Wilts, Somerset and Weymouth Railway that opened in 1856.

Frome railway station serves a largely rural area of the county of Somerset in England, and is situated in the town of Frome. The station is located on a 1.5 miles (2.4 km) long branch line which loops off the main line railway, which carries services on both the Reading to Taunton line and Bristol to Weymouth route. Most of the trains which take the loop line in order to serve Frome station are on the Bristol to Weymouth route, and most trains on the Reading to Taunton line by-pass the station on the main line. The station is 22.25 miles (36 km) south of Bath Spa on the Bristol to Weymouth line, it is owned by Network Rail and is operated by Great Western Railway.
The Wilts, Somerset and Weymouth Railway (WS&WR) was an early railway company in south-western England. It obtained Parliamentary powers in 1845 to build a railway from near Chippenham in Wiltshire, southward to Salisbury and Weymouth in Dorset. It opened the first part of the network but found it impossible to raise further money and sold its line to the Great Western Railway (GWR) in 1850.

The Berks and Hants Railway comprised two railway lines built simultaneously by the Great Western Railway (GWR) south and west from Reading in an attempt to keep the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) out of the area that it considered to be its territory in England.
The Langport and Castle Cary Railway is a railway line from Castle Cary railway station to Cogload Junction near Taunton, Somerset, England, which reduced the length of the journey from London to Penzance by 20+1⁄4 miles (32.6 km).

Charlton Mackrell railway station was a minor railway station serving the village of Charlton Mackrell in Somerset, England, from 1905 until 1962.

The Bristol to Exeter line is a major branch of the Great Western Main Line in the West of England and runs from Bristol, to Exeter, from where it continues as the Exeter to Plymouth line. It was one of the principal routes of the pre-1948 Great Western Railway which were subsequently taken over by the Western Region of British Railways and are now part of the Network Rail system.
The Yeovil–Taunton line was a railway line in England, built by the Bristol and Exeter Railway (B&ER) to connect its main line with the market town of Yeovil in Somerset. It opened in 1853 using the broad gauge of 7 ft 1⁄4 in and was the first railway to serve Yeovil. It ran from a junction at Durston although in later years passenger trains on the line ran through to and from Taunton where better main and branch line connections could be made.