Baluchistan
| Flag | Duration | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Flag of the Khanate of Kalat | ||
 | Flag of the State of Kharan | ||
 | Flag of the State of Las Bela | ||
 | Flag of the State of Makran |
This is a list of flags used by Princely states during British rule in India: [1]
| Flag | Duration | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Flag of the Khanate of Kalat | ||
 | Flag of the State of Kharan | ||
 | Flag of the State of Las Bela | ||
 | Flag of the State of Makran |
| Flag | Duration | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Flag of the Ajaigarh State | ||
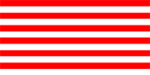 | Flag of the Alirajpur State | ||
 | Flag of Chhatarpur State | A horizontal blue-white bicolour flag. | |
 | Flag of Barwani State | ||
 | Flag of the Bhaisunda State | ||
 | Flag of the Bhopal State | A horizontal black-white-green tricolour flag. | |
 | Flag of Dewas State (Senior Branch) | A red flag featuring Hindu god Hanuman. | |
 | Flag of Dewas State (Junior Branch) | A red non-rectangular flag featuring Hindu god Hanuman. | |
 | Flag of the Dhar State | ||
 | Flag of the Gwalior State | ||
 | 1818–1950 | Flag of Indore State | |
 | 1732–1818 | Flag of Indore State | |
 | 1895–1947 | Flag of the Jaora State | |
 | c.1865–1895 | Flag of the Jaora State | |
 | Flag of Jhabua State | ||
 | Flag of Khilchipur State | ||
 | Flag of the Kurwai State | A horizontal green-black-yellow tricolour flag. | |
 | Flag of the Nagod State | ||
 | Flag of the Narsinghgarh State | ||
 | Flag of the Orchha State | ||
 | Flag of the Panna State | ||
 | Flag of the Rajgarh State | ||
 | Flag of the Ratlam State | ||
 | ?-1947 | Flag of the Rewa State | |
 | 19th century | Flag of the Rewa State | |
 | Flag of the Sitamau State | ||
 | Flag of the Sohawal State |
| Flag | Duration | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Flag of the Akkalkot State | A red field. | |
 | Flag of the Aundh State | A brownish field. | |
 | Flag of the Bhor State | ||
 | Flag of the Bhor State | ||
 | Flag of the Janjira State | ||
 | Flag of the Jath State | ||
 | Flag of the Jawhar State | ||
 | Flag of the Kapshi Jagir | ||
 | Flag of the Kolhapur State | ||
 | Flag of the Kurundvad Junior | An orange field | |
 | Flag of the Kurundvad Senior | A red field. | |
 | Flag of the Nagpur kingdom | ||
 | Flag of the Phaltan State | A horizontal orange-green bicolour. | |
 | Flag of the Sangli State | ||
 | Flag of the Surgana State | ||
 | Flag of Jamkhandi State | A brown field with the coat of arms of the Jamkhandi State in the centre. | |
 | Flag of the Mudhol State | ||
 | Flag of the Ramdurg State | ||
 | Flag of Sandur State |
| Flag | Duration | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Flag of Kharsawan State | ||
 | Flag of Saraikela State | ||
 | Flag of Bastar state | The flag of the Principality of Bastar is of two vertical parts, blue and white. On the dividing line the trident of Shiva is placed in the inverted colors. In the canton there is a crescent moon facing the fly. | |
 | Flag of Chhuikhadan State | A plain purple flag in the shape of a right-angled triangle. | |
 | Flag of Jashpur State | ||
 | Flag of Kanker State | An orange flag featuring Hindu god Hanuman as well as a crescent. | |
 | Flag of Kawardha State | ||
 | Flag of Khairagarh State | ||
 | Flag of Koriya State | ||
 | Flag of Nandgaon State | ||
 | Flag of Raigarh State | ||
 | Flag of Sarangarh State | ||
 | Flag of Surguja State | ||
 | Flag of Udaipur State | ||
 | 1891–1907 | Flag of the Kingdom of Manipur | |
 | |||
 | |||
 | Flag of the Baramba State | ||
 | Flag of the Baudh State | ||
 | Flag of Daspalla State | ||
 | Flag of the Dhenkanal State | ||
 | Flag of the Kingdom of Jeypore | ||
 | Flag of Kalahandi State | ||
 | Flag of the Keonjhar State | ||
 | Flag of the Khandpara State | ||
 | Flag of Mayurbhanj State | ||
 | Flag of the Pal Lahara State | ||
 | Flag of the Paralakhemundi Estate | ||
 | Flag of the Talcher State | ||
 | Flag of Cooch Behar State | ||
 | Flag of Twipra Kingdom | unofficial flag |
| Flag | Duration | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Flag of Ambliara State | ||
 | Flag of Balasinor State | ||
 | Flag of Bansda State | A horizontal red-yellow bicolour flag. | |
 | Flag of Bantva Manavadar | ||
 | Flag of Baria State | ||
 | ?-1874 | Flag of Baroda State | |
 | 1874–1936 | Flag of Baroda State | |
 | 1936–1949 | Flag of Baroda State | |
 | ?-1947 | Flag of Bhavnagar State | |
 | ?-1947 | Flag of Cambay State | |
 | Flag of Chhota Udaipur State | ||
 | Flag of Cutch State | ||
 | Flag of Danta State | ||
 | Flag of Dharampur State | ||
 | Flag of Dhrangadhra State | ||
 | Flag of Dhrol State | ||
 | Flag of Idar State | ||
 | Flag of Jambughoda State | ||
 | Flag of Jasdan State | ||
 | 1948 | Flag of Junagadh State | |
 | Flag of Lunavada State | ||
 | Flag of Malpur State | ||
 | Flag of Makaji Meghpar | ||
 | Flag of Makaji Meghpar | ||
 | Flag of Mansa State | ||
 | Flag of Mohanpur State | ||
 | Flag of Morvi State | ||
 | Flag of Nawanagar State | ||
 | Flag of Palanpur State | A horizontal green-yellow-red tricolour flag. | |
 | ?–1948 | Flag of the Kingdom of Porbandar | A yellow-orange flag with a purple border with the draw of a red swallowtailed flag inside. |
 | Flag of Rajkot State | ||
 | Flag of Rajpipla State | ||
 | Flag of Rajpara State | ||
 | Flag of Ranasan State | ||
 | Flag of Sachin State | ||
 | Flag of Sant State | ||
 | Flag of Surat State | ||
 | Flag of Vala State | ||
 | Flag of Vav State | ||
 | Flag of Vijaynagar State | ||
 | Flag of Wadagam State | ||
 | Flag of Wadhwan State | ||
 | Flag of Wankaner State |
| Flag | Duration | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1803–1947 | Flag of Loharu State | Green-yellow bicolour. |
 | 1804–1948 | Flag of Pataudi State | |
 | Flag of Chamba State | ||
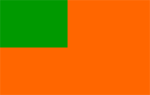 | Flag of Dhami State | An orange field with a green canton. | |
 | Flag of Bilaspur State | ||
 | Flag of Kangra State | ||
 | Flag of Kumarsain State | ||
 | Flag of Kutlehar State | ||
 | Flag of Mandi State | ||
 | Flag of Suket State | ||
 | 1799–1849 | Flag of the Sikh Empire ( Nishan Sahib ) [2] | |
 | 1799–1849 | Flag of the Sikh Empire (variant) | |
 | 1716–1799 | Flag of The Sikh Confederacy | |
 | Flag of the Faridkot State | ||
 | Flag of the Kapurthala State | ||
 | Flag of Nabha State | ||
 | Flag of the Patiala State |
| Flag | Duration | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1846–1936 | Flag of Jammu and Kashmir | |
 | 1936–1953 |
| Flag | Duration | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1700–1819 | Flag of the Arakkal Kingdom | A white banner with a border of 22 red triangles. |
 | 1545–1700 | Flag of the Arakkal Kingdom | A red banner with a crescent and star. |
 | 1799–1949 | Flag of Kingdom of Cochin | |
 | 1103–1750 | Flag of Kingdom of Thekkumkur | |
 | 1729–1949 | Flag of the Kingdom of Travancore | Red flag with a dextrally-coiled silver conch shell (Turbinella pyrum) at its centre. |
 | Flag of Banganapalle State | ||
 | Flag of the Pudukkottai state |
| Flag | Duration | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1799–1950 | Flag of the Kingdom of Mysore | Red and Brown coloured flag of the Kingdom of Mysore which ruled over most of Karnataka and at its zenith most of South India. |
| Flag | Duration | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1775–1931 | Flag of the Alwar State [3] | |
 | 1931–1948 | ||
 | 1880–1943 | Flag of Bharatpur State | |
 | 1943–1947 | ||
 | Flag of the Bikaner State | A horizontal red-orange bicolour flag. | |
 | Flag of the Banswara State | ||
 | Flag of Bundi State | A yellow field. | |
 | Flag of the Dholpur State | A horizontal blue-yellow bicolour flag. | |
 | Flag of the Jodhpur State | ||
 | Flag of the Gaurati State | ||
 | Flag of the Mewar State | ||
 | Flag of the Dungarpur State | ||
 | 1877–1922 | Flag of Jaipur State | |
 | 1922–1946 | ||
 | 1699–1818 | ||
 | Flag of the Jaisalmer State | ||
 | Flag of the Jhalawar State | ||
 | Flag of Jiliya Kingdom | ||
 | Flag of the Karauli State | ||
 | Flag of the Kishangarh State | A horizontal black-white-red tricolour flag. Not be confused with the flag of the German Empire. | |
 | Flag of the Kota State | ||
 | Flag of the Pratapgarh State | ||
 | Flag of the Shahpura State | ||
 | Flag of the Tonk State | ||
 | Flag of the Sirohi State | ||
 | Unofficial flag of the Rajputana Agency |
| Flag | Duration | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 1947–1948 | Flag of The Hyderabad State | An orange flag with 6 black stripes and 4 white stripes. The script along the top reads Al Azmatulillah meaning "All greatness is for God". The bottom script reads Ya Uthman which translates to "Oh Osman". The writing in the middle reads "Nizam-ul-Mulk Asif Jah". |
 | 1900–1947 | 2 striped green and red flag with a white crescent and star | |
 | 1700–1900 | An orange triangular flag with a green crescent. |
| Flag | Duration | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Flag of Garhwal Kingdom | A horizontal white-green bicolour flag. | |
 | Flag of Kumaon Kingdom | ||
 | Flag of Baoni State | A horizontal green-yellow-green tricolour flag. | |
 | Flag of Benares State | ||
 | Flag of Beri State | A horizontal red-yellow bicolour flag. | |
 | Flag of Charkhari State | ||
 | Flag of Dhurwai State | ||
 | Flag of Rampur State | ||
 | Flag of Sailana State | A plain red flag in the shape of a right-angled triangle. | |
 | Flag of Tori Fatehpur |