The 64 counties of the U.S. State of Colorado.
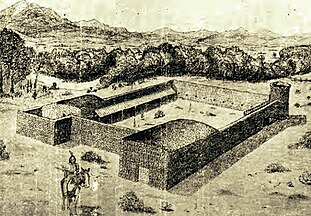
This is a partial list of trading posts established in what is now the U.S. State of Colorado from 1828 to approximately 1868. The 24 historic trading posts in Colorado traded goods produced outside the region to Native Americans for furs, food, and locally made goods. Trading posts also sold goods to travellers and settlers.