Related Research Articles

Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), also known as estrogen receptor agonists/antagonists (ERAAs), are a class of drugs that act on estrogen receptors (ERs). Compared to pure ER agonists–antagonists, SERMs are more tissue-specific, allowing them to selectively inhibit or stimulate estrogen-like action in various tissues.

Estrogen receptors (ERs) are proteins found in cells that function as receptors for the hormone estrogen (17β-estradiol). There are two main classes of ERs. The first includes the intracellular estrogen receptors, namely ERα and ERβ, which belong to the nuclear receptor family. The second class consists of membrane estrogen receptors (mERs), such as GPER (GPR30), ER-X, and Gq-mER, which are primarily G protein-coupled receptors. This article focuses on the nuclear estrogen receptors.

Raloxifene, sold under the brand name Evista among others, is a medication used to prevent and treat osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and those on glucocorticoids. For osteoporosis it is less preferred than bisphosphonates. It is also used to reduce the risk of breast cancer in those at high risk. It is taken by mouth.

Bazedoxifene, used as bazedoxifene acetate, is a medication for bone problems and possibly for cancer. It is a third-generation selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). Since late 2013 it has had U.S. FDA approval for bazedoxifene as part of the combination drug Duavee in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. It is also being studied for possible treatment of breast cancer and pancreatic cancer.

Tibolone, sold under the brand name Livial among others, is a medication which is used in menopausal hormone therapy and in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis and endometriosis. The medication is available alone and is not formulated or used in combination with other medications. It is taken by mouth.

Chlorotrianisene (CTA), also known as tri-p-anisylchloroethylene (TACE) and sold under the brand name Tace among others, is a nonsteroidal estrogen related to diethylstilbestrol (DES) which was previously used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms and estrogen deficiency in women and prostate cancer in men, among other indications, but has since been discontinued and is now no longer available. It is taken by mouth.

Arzoxifene is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the benzothiophene group which was never marketed. It is a potent estrogen antagonist in mammary and uterine tissue while acting as an estrogen agonist to maintain bone density and lower serum cholesterol. Arzoxifene is a highly effective agent for prevention of mammary cancer induced in the rat by the carcinogen nitrosomethylurea and is significantly more potent than raloxifene in this regard. Arzoxifene is devoid of the uterotrophic effects of tamoxifen, suggesting that, in contrast to tamoxifen, it is unlikely that the clinical use of arzoxifene will increase the risk of developing endometrial carcinoma.

Femarelle is a dietary supplement that is a mixture of DT56a and flaxseed powder, that may act as a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). In 2008 an application was submitted to the European Food Safety Authority to market Femarelle with a health claim, namely that it can reduce the risk for osteoporosis and other bone disorders; the EFSA found that "the food/constituent for which the claim is made, i.e. Femarelle, has not been sufficiently characterised" and that "a cause and effect relationship has not been established between the consumption of Femarelle and increased BMD, increased bone formation, or decreased risk of osteoporosis or other bone disorders in post-menopausal women."

Estetrol (E4), or oestetrol, is one of the four natural estrogenic steroid hormones found in humans, along with estrone (E1), estradiol (E2), and estriol (E3). Estetrol is a major estrogen in the body. In contrast to estrone and estradiol, estetrol is a native estrogen of fetal life. Estetrol is produced exclusively by the fetal liver and is found in detectable levels only during pregnancy, with relatively high levels in the fetus and lower levels in the maternal circulation.
Menerba, also known as Menopause Formula 101 (MF-101), is a botanical drug candidate that acts as a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) which is being studied for its potential to relieve hot flashes associated with menopause. Menerba, an estrogen receptor beta (ERβ) agonist (ERBA), is part of a new class of receptor subtype-selective estrogens, which is selective in transcriptional regulation to one of the two known estrogen receptor (ER) subtypes. Menerba consists of 22 herbs that have been used historically in traditional Chinese medicine.
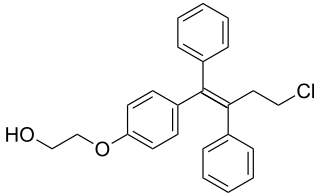
Ospemifene is an oral medication indicated for the treatment of dyspareunia – pain during sexual intercourse – encountered by some women, more often in those who are post-menopausal. Ospemifene is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) acting similarly to an estrogen on the vaginal epithelium, building vaginal wall thickness which in turn reduces the pain associated with dyspareunia. Dyspareunia is most commonly caused by "vulvar and vaginal atrophy."
Bazedoxifene/conjugated estrogens, sold under the brand name Duavee in the US and Duavive in the EU, is a fixed-dose combination medication for the treatment of menopause symptoms and postmenopausal osteoporosis. It contains the selective estrogen receptor modulator bazedoxifene and conjugated estrogens. It is taken by mouth.

Brilanestrant (INN) is a nonsteroidal combined selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) and selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD) that was discovered by Aragon Pharmaceuticals and was under development by Genentech for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer.
Estrogen deprivation therapy, also known as endocrine therapy, is a form of hormone therapy that is used in the treatment of breast cancer. Modalities include antiestrogens or estrogen blockers such as selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) like tamoxifen, selective estrogen receptor degraders like fulvestrant, and aromatase inhibitors like anastrozole and ovariectomy.

Etacstil is an orally active, nonsteroidal, combined selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) and selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD) that was developed for the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. It was shown to overcome antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer by altering the shape of the estrogen receptor, thus exhibiting SERD properties. Etacstil is a tamoxifen derivative and one of the first drugs to overcome tamoxifen-resistance. It is the predecessor of GW-7604, of which etacstil is a prodrug. This is analogous to the case of tamoxifen being a prodrug of afimoxifene (4-hydroxytamoxifen).
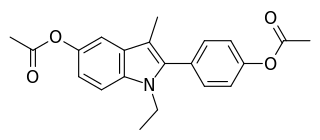
Zindoxifene is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) that was under development in the 1980s and early 1990s for the treatment of breast cancer but was not marketed. It showed estrogenic-like activity in preclinical studies and failed to demonstrate effectiveness as a treatment for breast cancer in clinical trials. Zindoxifene was the lead compound of the distinct 2-phenylindole class of SERMs, and the marketed SERM bazedoxifene was derived from the major active metabolite of zindoxifene, D-15414. Zindoxifene was first described in 1984.

An estrogen (E) is a type of medication which is used most commonly in hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy, and as part of feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women. They can also be used in the treatment of hormone-sensitive cancers like breast cancer and prostate cancer and for various other indications. Estrogens are used alone or in combination with progestogens. They are available in a wide variety of formulations and for use by many different routes of administration. Examples of estrogens include bioidentical estradiol, natural conjugated estrogens, synthetic steroidal estrogens like ethinylestradiol, and synthetic nonsteroidal estrogens like diethylstilbestrol. Estrogens are one of three types of sex hormone agonists, the others being androgens/anabolic steroids like testosterone and progestogens like progesterone.

Estetrol (E4) is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone which is used in combination with a progestin in combined birth control pills and is under development for various other indications. These investigational uses include menopausal hormone therapy to treat symptoms such as vaginal atrophy, hot flashes, and bone loss and the treatment of breast cancer and prostate cancer. It is taken by mouth.
Estradiol/raloxifene (E2/RLX) is a tissue-selective estrogen complex (TSEC) which was studied for potential use in menopausal hormone therapy but was never marketed. Today, E2/RLX is not generally used due to concerns of endometrial hyperplasia.
References
- 1 2 Pickar JH, Boucher M, Morgenstern D (September 2018). "Tissue selective estrogen complex (TSEC): a review". Menopause. 25 (9): 1033–1045. doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000001095. PMC 6110370 . PMID 29533367.
- ↑ Lello S, Capozzi A, Scambia G (2017). "The Tissue-Selective Estrogen Complex (Bazedoxifene/Conjugated Estrogens) for the Treatment of Menopause". Int J Endocrinol. 2017: 5064725. doi: 10.1155/2017/5064725 . PMC 5735652 . PMID 29358948.