
The Constitution of India designates the official languages of India as Hindi and English. [1] The number of bilingual speakers in India is 314.9 million, which is 26% of the population in 2011. [2]

The Constitution of India designates the official languages of India as Hindi and English. [1] The number of bilingual speakers in India is 314.9 million, which is 26% of the population in 2011. [2]
Hindi is one of the official languages of India and had 528 million native speakers as of the 2011 Census. About 139 million Indians speak Hindi as a second language and 24 million speak it as their third language.
| Language | First language speakers [5] | First language speakers as a percentage of total population | Second language speakers [6] | Third language speakers [6] | Total speakers | Total speakers as a percentage of total population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hindi | 528,347,193 | 43.63 | 139,000,000 | 24,000,000 | 692,000,000 | 57.1 |
| English | 259,678 | 0.02 | 83,000,000 | 46,000,000 | 129,000,000 | 10.6 |
| Bengali | 97,237,669 | 8.3 | 9,000,000 | 1,000,000 | 107,000,000 | 8.9 |
| Marathi | 83,026,680 | 7.09 | 13,000,000 | 3,000,000 | 99,000,000 | 8.2 |
| Telugu | 81,127,740 | 6.93 | 12,000,000 | 1,000,000 | 95,000,000 | 7.8 |
| Tamil | 69,026,881 | 5.89 | 7,000,000 | 1,000,000 | 77,000,000 | 6.3 |
| Gujarati | 55,492,554 | 4.74 | 4,000,000 | 1,000,000 | 60,000,000 | 5 |
| Urdu | 50,772,631 | 4.34 | 11,000,000 | 1,000,000 | 63,000,000 | 5.2 |
| Kannada | 43,706,512 | 3.73 | 14,000,000 | 1,000,000 | 59,000,000 | 4.94 |
| Odia | 37,521,324 | 3.2 | 5,000,000 | 390,000 | 43,000,000 | 3.56 |
| Malayalam | 34,838,819 | 2.97 | 500,000 | 210,000 | 36,000,000 | 2.9 |
| Punjabi | 33,124,726 | 2.83 | 2,230,000 | 720,000 | 36,600,000 | 3 |
| Assamese | 15,311,351 | 1.26 | 7,488,153 | 740,402 | 23,539,906 | 1.94 |
| Sanskrit | 0 [7] [8] [9] | 0 | 1,230,000 | 1,960,000 | 3,190,000 | 0.19 |
Combined percentages of first, second and third language speakers of Hindi and English in India from the 2011 Census. [10]


| State or union territory | Hindi | English |
|---|---|---|
| India | 57.11% | 10.62% |
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands | 79.87% | 21.94% |
| Andhra Pradesh (incl. Telangana) | 12.59% | 13.06% |
| Arunachal Pradesh | 62.76% | 23.08% |
| Assam | 25.24% | 8.05% |
| Bihar | 89.37% | 2.72% |
| Chandigarh | 94.05% | 41.62% |
| Chhattisgarh | 93.64% | 2.29% |
| Dadra and Nagar Haveli | 57.50% | 10.34% |
| Daman and Diu | 76.19% | 15.38% |
| Delhi | 96.75% | 31.72% |
| Goa | 53.34% | 41.80% |
| Gujarat | 43.63% | 12.44% |
| Haryana | 95.34% | 15.59% |
| Himachal Pradesh | 96.57% | 10.64% |
| Jammu and Kashmir (incl. Ladakh) | 38.00% | 15.98% |
| Jharkhand | 85.43% | 5.15% |
| Karnataka | 12.27% | 11.83% |
| Kerala | 9.12% | 20.15% |
| Lakshadweep | 17.87% | 19.30% |
| Madhya Pradesh | 95.74% | 5.44% |
| Maharashtra | 52.09% | 14.32% |
| Manipur | 18.44% | 31.62% |
| Meghalaya | 13.95% | 15.61% |
| Mizoram | 7.01% | 15.50% |
| Nagaland | 15.89% | 32.57% |
| Odisha | 18.76% | 17.23% |
| Puducherry | 3.87% | 28.10% |
| Punjab | 51.04% | 30.05% |
| Rajasthan | 95.04% | 4.55% |
| Sikkim | 47.96% | 27.69% |
| Tamil Nadu | 2.11% | 18.49% |
| Tripura | 9.95% | 7.53% |
| Uttar Pradesh | 97.40% | 6.42% |
| Uttarakhand | 97.19% | 8.36% |
| West Bengal | 13.83% | 6.70% |

Modern Standard Hindi, commonly referred to as Hindi, is the standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is the official language of India alongside English and the lingua franca of North India. Hindi is considered a Sanskritised register of Hindustani, which itself is based primarily on the Khariboli dialect of Delhi and neighbouring areas. It is an official language in nine states and three union territories and an additional official language in three other states. Hindi is also one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Republic of India.

Marathi is a classical Indo-Aryan language predominantly spoken by Marathi people in the Indian state of Maharashtra and is also spoken in other states like in Goa, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and the territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. It is the official language of Maharashtra, and an additional official language in the state of Goa, where it is used for replies, when requests are received in Marathi. It is one of the 22 scheduled languages of India, with 83 million speakers as of 2011. Marathi ranks 13th in the list of languages with most native speakers in the world. Marathi has the third largest number of native speakers in India, after Hindi and Bengali. The language has some of the oldest literature of all modern Indian languages. The major dialects of Marathi are Standard Marathi and the Varhadi Marathi. Marathi was designated as a classical language by the Government of India in October 2024.

Punjabi, sometimes spelled Panjabi, is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Punjab region of Pakistan and India. It is one of the most widely spoken native languages in the world with approximately 150 million native speakers.

Urdu is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule language, the status and cultural heritage of which are recognised by the Constitution of India. It also has an official status in several Indian states.

Hindustani is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in North India and Pakistan, and functioning as the lingua franca of the region. It is also spoken by the Deccani people. Hindustani is a pluricentric language with two standard registers, known as Hindi and Urdu which serve as official languages of India and Pakistan, respectively. Thus, it is also called Hindi–Urdu. Colloquial registers of the language fall on a spectrum between these standards. In modern times, a third variety of Hindustani with significant English influences has also appeared, which is sometimes called Hinglish or Urdish.

Gujarati is an Indo-Aryan language native to the Indian state of Gujarat and spoken predominantly by the Gujarati people. Gujarati is descended from Old Gujarati. In India, it is one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Union. It is also the official language in the state of Gujarat, as well as an official language in the union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. As of 2011, Gujarati is the 6th most widely spoken language in India by number of native speakers, spoken by 55.5 million speakers which amounts to about 4.5% of the total Indian population. It is the 26th most widely spoken language in the world by number of native speakers as of 2007.
Indian English is a group of English dialects spoken in the Republic of India and among the Indian diaspora. English is used by the Government of India for communication, and is enshrined in the Constitution of India. English is also an official language in seven states and seven union territories of India, and the additional official language in seven other states and one union territory. Furthermore, English is the sole official language of the Judiciary of India, unless the state governor or legislature mandates the use of a regional language, or if the President of India has given approval for the use of regional languages in courts.
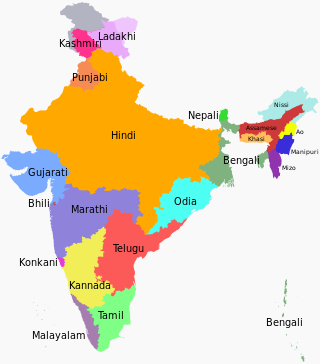
Languages of India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-Aryan languages spoken by 78.05% of Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 19.64% of Indians; both families together are sometimes known as Indic languages. Languages spoken by the remaining 2.31% of the population belong to the Austroasiatic, Sino–Tibetan, Tai–Kadai, and a few other minor language families and isolates. According to the People's Linguistic Survey of India, India has the second highest number of languages (780), after Papua New Guinea (840). Ethnologue lists a lower number of 456.

Pakistan is a multilingual country with over 70 languages spoken as first languages. The majority of Pakistan's languages belong to the Indo-Iranian group of the Indo-European language family.

Kashmiri or Koshur is a Dardic Indo-Aryan language spoken by around 7 million Kashmiris of the Kashmir region, primarily in the Kashmir Valley and Chenab Valley of the Indian-administrated union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, over half the population of that territory. Kashmiri has split ergativity and the unusual verb-second word order.

As of 2024, 22 languages have been classified as recognised languages under the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India. There is no designated national language of India.

The Hindi Belt, also known as the Hindi Heartland or the Hindi speaking states, is a linguistic region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India where various Northern, Central, Eastern and Western Indo-Aryan languages are spoken, which in a broader sense is termed as Hindi languages, with Standard Hindi serving as the lingua franca of the region.

The Hindi–Urdu controversy arose in 19th-century colonial India out of the debate over whether Modern Standard Hindi or Standard Urdu should be chosen as a national language.
Sanskrit revival is a resurgence of interest in and use of the Sanskrit language, both in India and in Western countries such as Germany, the United Kingdom, the United States, China and in many European countries.

Nagpuri is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Indian states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Odisha. It is primarily spoken in the west and central Chota Nagpur plateau region.
This is a list of States and Union Territories of India by Bengali speakers at the time of the 2011 Census.
The 2001 census of India was the 14th in a series of censuses held in India every decade since 1871.

The 2011 census of India or the 15th Indian census was conducted in two phases, house listing and population enumeration. The House listing phase began on 1 April 2010 and involved the collection of information about all buildings. Information for National Population Register (NPR) was also collected in the first phase, which will be used to issue a 12-digit unique identification number to all registered Indian residents by Unique Identification Authority of India. The second population enumeration phase was conducted between 9 and 28 February 2011. Census has been conducted in India since 1872 and 2011 marks the first time biometric information was collected. According to the provisional reports released on 31 March 2011, the Indian population increased to 1.21 billion with a decadal growth of 17.70%. Adult literacy rate increased to 74.04% with a decadal growth of 9.21%. The motto of the census was Our Census, Our Future.
Delhi's ethnic groups are diverse. The Yamuna river's flood plains provide fertile alluvial soil suitable for agriculture but are prone to recurrent floods. The Yamuna, a sacred river in Hinduism, is the only major river flowing through Delhi. The original natives of Delhi are those whose ancestors lived in the Yamuna basin, a region which spreads radially from the capital up to a distance of approximately 200 kilometres. This province was not ethnically homogeneous and large amounts of Hindi-speakers resided in the southeast, now Haryana, eastern side, now West Uttar Pradesh and in Delhi's Yamuna Basin. Today the migrant population consists largely of Punjabis, Haryanavis, Bengalis and recently, Biharis and Uttar Pradeshis etc.