Kinesin-like protein KIF3A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF3A gene. [5] [6]
Kinesin-like protein KIF3A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF3A gene. [5] [6]
KIF3A is one subunit of the heterotrimeric motor protein, kinesin-2, that was initially isolated from sea urchin egg/embryo cytosol using microtubule affinity purification. [7] This motor consists of two kinesin-related subunits (called KIF3A and KIF3B or 3C in vertebrates) and an associated protein (KAP3), and it transports protein complexes, nucleic acids and organelles towards the "plus" ends of microtubule tracks within cells. Work done in a broad range of eukaryotic cells has revealed that heterotrimeric kinesin-2 is the primary motor protein driving the intraflagellar transport of tubulins and other axonemal building blocks from the base of the ciliary/flagellar axoneme to their site of assembly at the distal tips. [8] This process is required for cilium assembly/maintenance and cilium-based signalling which play key roles in various cell and developmental processes. For example, in vertebrate embryos, kinesin-2 function is required for cilia-dependent nodal flow and the development of left-right asymmetry. [9]
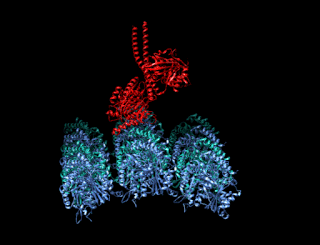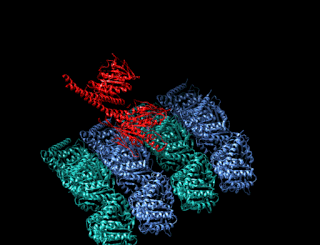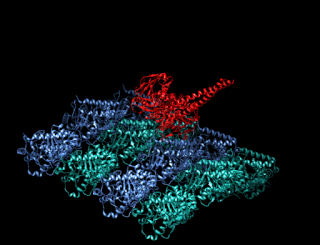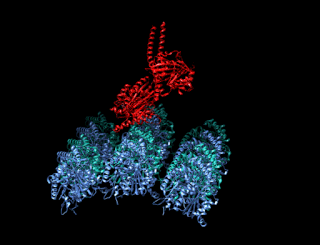
A kinesin is a protein belonging to a class of motor proteins found in eukaryotic cells.

Kinesin-like protein KIF23 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF23 gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF1B gene.

Kinesin family member 5B (KIF5B) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF5B gene.

Kinesin family member 4A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF4A gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF22 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF22 gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF2C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF2C gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF21A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF21A gene.

Kinesin-associated protein 3 (KAP3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIFAP3 gene. It is a non-motor, accessory subunit which co-oligomerizes with the motor subunits KIF3A and KIF3B or KIF3C, to form heterotrimeric kinesin-2 motor proteins. Kinesin-2 KAP subunits were initially characterized in echinoderms and mice.

Kinesin-like protein KIF3B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF3B gene. KIF3B is an N-type protein that complexes with two other kinesin proteins to form two-headed anterograde motors. First, KIF3B forms a heterodimer with KIF3A ; (KIF3A/3B), that is membrane-bound and has ATPase activity. Then KIFAP3 binds to the tail domain to form a heterotrimeric motor. This motor has a plus end-directed microtubule sliding activity that exhibits a velocity of ∼0.3 μm/s a. There are 14 kinesin protein families in the kinesin superfamily and KIF3B is part of the Kinesin-2 family, of kinesins that can all form heterotrimeric complexes. Expression of the three motor subunits is ubiquitous. The KIG3A/3B/KAP3 motors can transport 90 to 160 nm in diameter organelles.

Kinesin family member 5A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF5A gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF14 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF14 gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIFC1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIFC1 gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF1C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF1C gene. Kif1C is a fast, plus-end directed microtubule motor. Kif1C transports α5β1-integrins in human cells. Kif1C has been shown to be non-essential in mouse with other proteins able to perform the same function. However, mutations in KIF1C lead to spastic paraplegia and cerebellar dysfunction in humans.

Kinesin-like protein KIF17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF17 gene. KIF17 and its close relative, C. elegans OSM-3, are members of the kinesin-2 family of plus-end directed microtubule-based motor proteins. In contrast to heterotrimeric kinesin-2 motors, however, KIF17 and OSM-3 form distinct homodimeric complexes. Homodimeric kinesin-2 has been implicated in the transport of NMDA receptors along dendrites for delivery to the dendritic membrane, whereas both heterotrimeric and homodimeric kinesin-2 motors function cooperatively in anterograde intraflagellar transport (IFT) and cilium biogenesis.

Kinesin-like protein KIF2A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF2A gene.

Kinesin family member 16B, also known as KIF16B, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the KIF16B gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF1A, also known as axonal transporter of synaptic vesicles or microtubule-based motor KIF1A, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF1A gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF11 is a molecular motor protein that is essential in mitosis. In humans it is coded for by the gene KIF11. Kinesin-like protein KIF11 is a member of the kinesin superfamily, which are nanomotors that move along microtubule tracks in the cell. Named from studies in the early days of discovery, it is also known as Kinesin-5, or as BimC, Eg5 or N-2, based on the founding members of this kinesin family.

Kinesin family member 15 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF15 gene.