Dyskinesia refers to a category of movement disorders that are characterized by involuntary muscle movements, including movements similar to tics or chorea and diminished voluntary movements. Dyskinesia can be anything from a slight tremor of the hands to an uncontrollable movement of the upper body or lower extremities. Discoordination can also occur internally especially with the respiratory muscles and it often goes unrecognized. Dyskinesia is a symptom of several medical disorders that are distinguished by their underlying cause.

Dopaminergic means "related to dopamine", a common neurotransmitter. Dopaminergic substances or actions increase dopamine-related activity in the brain.
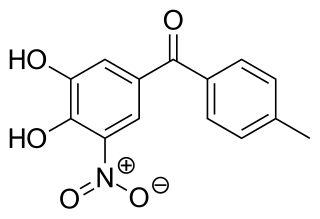
Tolcapone, sold under the brand name Tasmar, is a medication used to treat Parkinson's disease (PD). It is a selective, potent and reversible nitrocatechol-type inhibitor of the enzyme catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT). It has demonstrated significant liver toxicity, which has led to suspension of marketing authorisations in a number of countries.

A dopamine agonist is a compound that activates dopamine receptors. There are two families of dopamine receptors, D1-like and D2-like. They are all G protein-coupled receptors. D1- and D5-receptors belong to the D1-like family and the D2-like family includes D2, D3 and D4 receptors. Dopamine agonists are primarily used in the treatment of the motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease, and to a lesser extent, in hyperprolactinemia and restless legs syndrome. They are also used off-label in the treatment of clinical depression. Impulse control disorders are associated with the use of dopamine agonists for whatever condition.
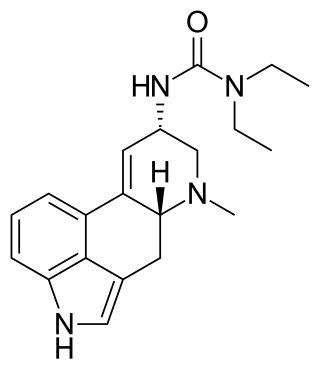
Lisuride, sold under the brand name Dopergin among others, is a monoaminergic medication of the ergoline class which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, migraine, and high prolactin levels. It is taken by mouth.
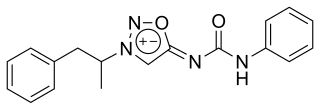
Mesocarb, sold under the brand name Sidnocarb or Sydnocarb and known by the developmental code name MLR-1017, is a psychostimulant medication which has been used in the treatment of psychiatric disorders and for a number of other indications in the Soviet Union and Russia. It is currently under development for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and sleep disorders. It is taken by mouth.

A catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitor is a drug that inhibits the enzyme catechol-O-methyltransferase. This enzyme methylates catecholamines such as dopamine, norepinephrine and epinephrine. It also methylates levodopa. COMT inhibitors are indicated for the treatment of Parkinson's disease in combination with levodopa and an aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase inhibitor. The therapeutic benefit of using a COMT inhibitor is based on its ability to prevent the methylation of levodopa to 3-O-methyldopa, thus increasing the bioavailability of levodopa. COMT inhibitors significantly decrease off time in people with Parkinson's disease also taking carbidopa/levodopa.
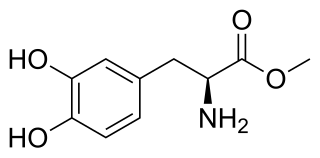
Melevodopa, also known as levodopa methyl ester (LDME) and sold under the brand name Levomet, is a dopaminergic agent. It is the methyl ester of levodopa. It is used in oral tablet form as an effervescent prodrug with 250 times the water solubility of tablet levodopa. In combination with carbidopa, as melevodopa/carbidopa, it is approved for use in the treatment of Parkinson's disease.

Droxidopa, also known as L-threo-dihydroxyphenylserine (L-DOPS) and sold under the brand names Northera and Dops among others, is sympathomimetic medication which is used in the treatment of hypotension and for other indications. It is taken by mouth.
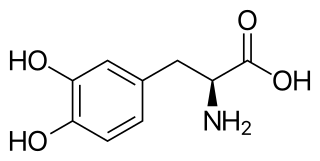
Levodopa, also known as L-DOPA and sold under many brand names, is a dopaminergic medication which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and certain other conditions like dopamine-responsive dystonia and restless legs syndrome. The drug is usually used and formulated in combination with a peripherally selective aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AAAD) inhibitor like carbidopa or benserazide. Levodopa is taken by mouth, by inhalation, through an intestinal tube, or by administration into fat.

Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease of mainly the central nervous system that affects both the motor and non-motor systems of the body. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and, as the disease progresses, non-motor symptoms become more common. Usual symptoms include tremors, slowness of movement, rigidity, and difficulty with balance, collectively known as parkinsonism. Parkinson's disease dementia, falls and neuropsychiatric problems such as sleep abnormalities, psychosis, mood swings, or behavioral changes may also arise in advanced stages.

A-86929 is a synthetic compound that acts as a selective dopamine receptor D1 agonist. It was developed as a possible treatment for Parkinson's disease, as well as for other applications such as treatment of cocaine addiction, but while it had reasonable efficacy in humans it also caused dyskinesias and has not been continued. It has mainly been used as its diacetate ester prodrug adrogolide (ABT-431), which has better bioavailability.
Levodopa-induced dyskinesia (LID) is a form of dyskinesia associated with levodopa (l-DOPA), used to treat Parkinson's disease. It often involves hyperkinetic movements, including chorea, dystonia, and athetosis.

UWA-101 is a phenethylamine derivative researched as a potential treatment for Parkinson's disease. Its chemical structure is very similar to that of the illegal drug MDMA, the only difference being the replacement of the α-methyl group with an α-cyclopropyl group. MDMA has been found in animal studies and reported in unauthorised human self-experiments to be effective in the short-term relief of side-effects of Parkinson's disease therapy, most notably levodopa-induced dyskinesia. However the illegal status of MDMA and concerns about its potential for recreational use, neurotoxicity and potentially dangerous side effects mean that it is unlikely to be investigated for medical use in this application, and so alternative analogues were investigated.

Foslevodopa is a drug which acts as a prodrug for levodopa, originally invented in the 1980s but not developed for medical use at that time. It has more recently attracted renewed interest due to its improved pharmacokinetics compared to levodopa itself, and is now approved for use in a subcutaneous infusion as a fixed-dose combination with foscarbidopa for the treatment of Parkinson's disease, under the trade name Vyalev.

Glovadalen (developmental code name UCB-0022) is a dopamine D1 receptor positive allosteric modulator which is under development for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. It has been found to potentiate the capacity of dopamine to activate the D1 receptor by 10-fold in vitro with no actions on other dopamine receptors. As of May 2024, glovadalen is in phase 2 clinical trials for this indication. The drug is under development by UCB Biopharma. It is described as an orally active, centrally penetrant small molecule.

A neurotransmitter prodrug, or neurotransmitter precursor, is a drug that acts as a prodrug of a neurotransmitter. A variety of neurotransmitter prodrugs have been developed and used in medicine. They can be useful when the neurotransmitter itself is not suitable for use as a pharmaceutical drug owing to unfavorable pharmacokinetic or physicochemical properties, for instance susceptibility to metabolism or lack of blood–brain barrier permeability. Besides their use in medicine, neurotransmitter prodrugs have also been used as recreational drugs in some cases.

Mesdopetam (INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name; developmental code names IRL-790, IPN60170) is a dopamine D2 and D3 receptor antagonist with preference for the D3 receptor which is under development for the treatment of Parkinson's disease, drug-induced dyskinesia, and psychotic disorders. It has been described by its developers as having "psychomotor stabilizing" properties.
Pirepemat is a drug which is under development for the prevention of falls in people with Parkinson's disease and Parkinson's disease dementia. It has been referred to as a "nootrope".

Melevodopa/carbidopa, sold under the brand name Sirio, is a combination of melevodopa, a prodrug of the dopamine precursor and hence non-selective dopamine receptor agonist levodopa (L-DOPA), and carbidopa, a peripherally selective aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AAAD) inhibitor, which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease in Italy. It is taken orally in the form of tablets.















