
Khat, also known as Bushman's tea, especially in South Africa, is a flowering plant native to eastern and southeastern Africa. It has a history of cultivation originating in the Harar area and subsequently introduced at different times to countries nearby in East Africa and Southern Arabia, most notably Yemen. Cultivated by farmers, its leaves are sold on the market to be chewed as a recreational stimulant. The world's largest consumers are Eastern Africans, particularly Somalis, and nearby Yemen, with the largest producers/exporters being Ethiopia and Kenya.

Methcathinone is a monoamine alkaloid and psychoactive stimulant, a substituted cathinone. It is used as a recreational drug due to its potent stimulant and euphoric effects and is considered to be addictive, with both physical and psychological withdrawal occurring if its use is discontinued after prolonged or high-dosage administration. It is usually snorted, but can be smoked, injected, or taken orally.
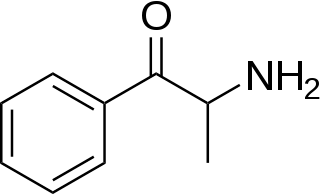
Cathinone is a monoamine alkaloid found in the shrub Catha edulis (khat) and is chemically similar to ephedrine, cathine, methcathinone and other amphetamines. It is probably the main contributor to the stimulant effect of Catha edulis, also known as khat. Cathinone differs from many other amphetamines in that it has a ketone functional group. Other phenethylamines that share this structure include the stimulants methcathinone, MDPV, mephedrone and the antidepressant bupropion.
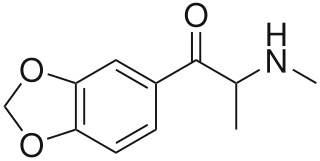
Methylone, also known as 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylcathinone (MDMC), is an empathogen and stimulant psychoactive drug. It is a member of the amphetamine, cathinone and methylenedioxyphenethylamine classes.

Ethylone, also known as 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-ethylcathinone, is a recreational designer drug classified as an entactogen, stimulant, and psychedelic of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and cathinone chemical classes. It is the β-keto analogue of MDEA ("Eve"). Ethylone has only a short history of human use and is reported to be less potent than its relative methylone. In the United States, it began to be found in cathinone products in late 2011.

Methedrone is a recreational drug of the cathinone chemical class. Chemically, methedrone is closely related to para-methoxymethamphetamine (PMMA), methylone and mephedrone. Methedrone received media attention in 2009 after the death of two young Swedish men. In both cases toxicology analysis showed methedrone was the only drug present in both men during the time of their overdose and subsequent deaths.

Phthalimidopropiophenone is a chemical intermediate used in the synthesis of cathinone. It has been found to be sold on the illicit market as a controlled substance analogue, but little is currently known about its pharmacology or toxicology.

Flephedrone, also known as 4-fluoromethcathinone (4-FMC), is a stimulant drug of the cathinone chemical class that has been sold online as a designer drug starting in 2008.

3',4'-Methylenedioxy-α-pyrrolidinobutyrophenone (MDPBP) is a stimulant of the cathinone class developed in the 1960s, which has been reported as a novel designer drug. MDPBP is sometimes sold under the name "NRG-1" as a mixture with other cathinone derivatives, including flephedrone, pentylone, MαPPP and its higher homologue MDPV. As with other cathinones, MDPBP has been shown to have reinforcing effects in rats.

α-Pyrrolidinopentiophenone (α-PVP), also known as α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone, O-2387, β-keto-prolintane, prolintanone, or desmethylpyrovalerone, is a synthetic stimulant of the cathinone class developed in the 1960s that has been sold as a designer drug and often consumed for recreational reasons. α-PVP is chemically related to pyrovalerone and is the ketone analog of prolintane.

Substituted cathinones, or simply cathinones, which include some stimulants and entactogens, are derivatives of cathinone. They feature a phenethylamine core with an alkyl group attached to the alpha carbon, and a ketone group attached to the beta carbon, along with additional substitutions. Cathinone occurs naturally in the plant khat whose leaves are chewed as a recreational drug.

3-Fluoromethcathinone is a chemical compound of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and cathinone classes that has been sold online as a designer drug. It is a structural isomer of flephedrone (4-fluoromethcathinone).

Pentylone is a stimulant developed in the 1960s. It is a substituted cathinone that has been identified in some samples of powders sold as "NRG-1", along with varying blends of other cathinone derivatives including flephedrone, MDPBP, MDPV, and 4-MePPP. It was also found in combination with 4-MePPP being sold as "NRG-3". Reports indicate side effects include paranoia, agitation, and insomnia, with effects lasting for several days at high doses.
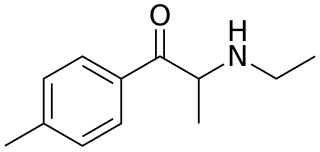
4-Methylethcathinone or 4-MEC is a chemical that bears a chemical resemblance to mephedrone. Due to its similarity to mephedrone, it is thought to be a stimulant and entactogen drug of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and cathinone chemical classes. It has been marketed alone or in mixtures with other substituted cathinones under the name "NRG-2", although other blends such as "NRG-1" may have been more ambiguous with their ingredients.

Pentedrone is a stimulant of the cathinone class that has been sold as a designer drug and has been found since 2010 as an ingredient in a number of "bath salt" mixes sold as legal highs.

Bath salts are a group of recreational designer drugs. The name derives from instances in which the drugs were disguised as bath salts. The white powder, granules, or crystals often resemble Epsom salts, but differ chemically. The drugs' packaging often states "not for human consumption" in an attempt to circumvent drug prohibition laws. Additionally, they may be described as "plant food", "powdered cleaner", or other products.
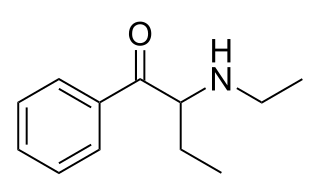
N-Ethylbuphedrone is a stimulant of the cathinone class that has been sold as a designer drug. It is the β-ketone analogue of N,alpha-diethylphenylethylamine.

3-Methylmethcathinone (3-MMC), also known as metaphedrone, is a designer drug from the substituted cathinone family. 3-MMC is a monoamine transporter substrate that potently releases and inhibits the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine, as well as displaying moderate serotonin releasing activity.
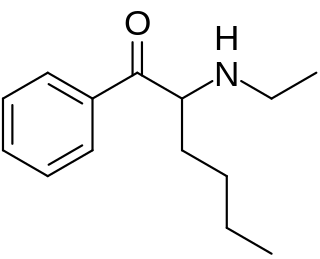
N-Ethylhexedrone (also known as α-ethylaminocaprophenone, N-ethylnorhexedrone, hexen, and NEH) is a stimulant of the cathinone class that acts as a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) with IC50 values of 0.0978 and 0.0467 μM, respectively. N-Ethylhexedrone was first mentioned in a series of patents by Boehringer Ingelheim in the 1960s which led to the development of the better-known drug methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV). Since the mid-2010s, N-ethylhexedrone has been sold online as a designer drug. In 2018, N-ethylhexedrone was the second most common drug of the cathinone class to be identified in Drug Enforcement Administration seizures.
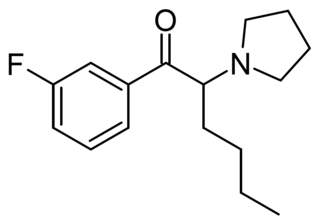
3-Fluoro-alpha-PHP (3F-PHP) is a substituted cathinone derivative with stimulant effects which has been sold as a designer drug. It was first identified in Sweden in 2020 and continues to be detected in seized drug samples, though it appears to have been less widely used than related compounds such as 3F-PVP and 3F-PiHP.



















