
East Nusa Tenggara is the southernmost province of Indonesia. It compires the eastern portion of the Lesser Sunda Islands, facing the Indian Ocean in the south and the Flores Sea in the north. It consists of more than 500 islands, with the largest ones being Sumba, Flores, and the western part of Timor; the latter shares a land border with the separate nation of East Timor. The province was sub-divided into 21 regencies and the regency-level city of Kupang, which is the capital and largest city.
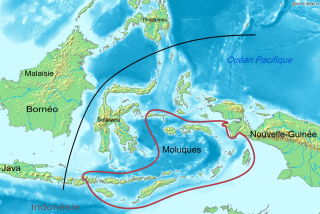
The Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian (CEMP) languages form a proposed branch of the Malayo-Polynesian languages consisting of over 700 languages.
The Sika or Sikanese language is a member of the Central Malayo-Polynesian branch of the Austronesian language family, and is spoken by around 180,000 people of the Sika ethnic group on Flores island in East Nusa Tenggara province, Indonesia. It is notable for being one of the few languages which contain a non-allophonic labiodental flap. It shows evidence of having a Papuan (non-Austronesian) substratum.
Ngadha is an Austronesian language, one of six languages spoken in the central stretch of the Indonesian island of Flores. From west to east these languages are: Ngadha, Nage, Keo, Ende, Lio, and Palu'e. These languages form the proposed Central Flores group of the Sumba–Flores languages, according to Blust (2009).
Austral is an endangered Polynesian language that is spoken by approximately 8,000 people (1987). It is spoken only on the Austral Islands and the Society Islands of French Polynesia. The language is also referred to as Tubuai-Rurutu, Tubuai, Rurutu-Tupuai, or Tupuai. In structure, it is similarly compared to Tahitian.
The Sumba–Flores languages, which correspond to the traditional Bima–Sumba subgroup minus Bima, are a proposed group of Austronesian languages spoken on and around the islands of Sumba and western–central Flores in the Lesser Sundas. The main languages are Manggarai, which has half a million speakers on the western third of Flores, and Kambera, with a quarter million speakers on the eastern half of Sumba Island.
Alorese is an Austronesian language spoken on Alor and the neighboring islands of the Alor archipelago in eastern Indonesia. It is not to be confused with non-Austronesian (Papuan) languages of the Alor–Pantar family which are also spoken in this region. It is also distinct from Alor Malay, a Malay variety which is currently supplanting Alorese as the language of wider communication in the region. Alorese is the native language of several immigrant communities located along the coast of the Alor archipelago, especially at Alor Kecil on Alor and at Baranusa and Marica on Pantar. It has also been used extensively as a trade language in the region.

East Lombok Regency is a regency of the Indonesian Province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is located on the island of Lombok and the capital is Selong.
Polapare River is a river of Sumba Barat Daya Regency in the island of Sumba, East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. The length of the river is 18 km. Offshore of the river mouth are the islands of Baholokmonegoro and Barenggemonokodi; Malondobara Island is 1¼ km to the west.

The Manggarai language is the language of the Manggarai people from the western parts of the island of Flores, in East Nusa Tenggara Province, Indonesia. There are also some pockets of Manggarai speakers in the village of Manggarai in Jakarta, the capital city of Indonesia. It is the native language of more than 730,000 people, based on statistical data reported by Central Agency on Statistics (BPS) in 2009 for the province of East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. The data include statistics for the population of the Regency of “Greater Manggarai” on Flores island, which consists of three districts: Manggarai district, West Manggarai district, and East Manggarai district.
The Hawu also known as Havu language, historically Sawu and known to outsiders as Savu or Sabu, is the language of Savu Island in Indonesia and of Raijua Island off the western tip of Savu. Traditionally classified as a Sumba language in the Austronesian family, it may be a non-Austronesian (Papuan) language. Dhao, once considered a dialect, is not mutually intelligible with Hawu.

The Savu languages, Hawu and Dhao, are spoken on Savu and Ndao Islands in East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia.
The Bima language, or Bimanese is an Austronesian language spoken on the eastern half of Sumbawa Island, Indonesia, which it shares with speakers of the Sumbawa language. Bima territory includes the Sanggar Peninsula, where the extinct Papuan language Tambora was once spoken. "Bima" is an exonym; the autochthonous name for the territory is "Mbojo" and the language is referred to as "Nggahi Mbojo." There are over half a million Bima speakers. Neither the Bima nor the Sumbawa people have alphabets of their own for they use the alphabets of the Bugis and the Malay language indifferently.
Bajaw is the language of the Bajaw 'Sea Gypsies' of Maritime Southeast Asia. Differences exist between the language's varieties in western Sabah, Cagayan in the southern Philippines, eastern Sabah, and Sulawesi/Maluku, but it is not clear how many languages these would be based on mutual intelligibility.

Komering is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken in Indonesia, in the southern part of Sumatra.
Basap is an Austronesian language spoken in Borneo, Indonesia.







