
The Special Region of Yogyakarta is a province-level special region of Indonesia in southern Java. It is a semi-enclave that is surrounded by on the landward side by Central Java Province to the west, north, and east, but has a long coastline on the Indian Ocean to the south.
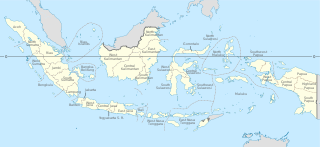
Provinces are the first-level administrative divisions of Indonesia. It is formerly called the first-level provincial region before the Reform era. Provinces have a local government, consisting of a governor and a regional legislative body. The governor and members of local representative bodies are elected by popular vote for five-year terms, but governors can only serve for two terms. Provincial governments have the authority to regulate and manage their own government affairs, subject to the limits of the central government. The average land area of all 38 provinces in Indonesia is about 50,120.23 km2 (19,351.53 sq mi), and an average population of about 7,345,233 people.

South Jakarta, abbreviated as Jaksel, is one of the five administrative cities which form the Special Capital Region of Jakarta, Indonesia. South Jakarta is not self-governed and does not have a city council, hence it is not classified as a proper municipality. It had a population of 2,062,232 at the 2010 census and 2,226,812 at the 2020 census, and 2,244,623 as at mid 2022 according to the official estimates. It is the third most populous among the five administrative cities of Jakarta, after East Jakarta and West Jakarta. The administrative centre is at Kebayoran Baru.

The Neighborhood Association was the smallest unit of the national mobilization program established by the Japanese government in World War II. It consisted of units consisting of 10-15 households organized for fire fighting, civil defense and internal security.
Indonesia is divided into provinces. Provinces are made up of regencies and cities (kota). Provinces, regencies, and cities have their own local governments and parliamentary bodies.
In Indonesia, village or subdistrict is the fourth-level subdivision and the smallest administrative division of Indonesia below a district, regency/city, and province. Similar administrative divisions outside of Indonesia include barangays in the Philippines, Muban in Thailand, civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, communes in France and Vietnam, dehestan in Iran, hromada in Ukraine, Gemeinden in Germany, comuni in Italy, or municipios in Spain. The UK equivalent are civil parishes in England and communities in Wales. There are a number of names and types for villages in Indonesia, with desa being the most frequently used for regencies, and kelurahan for cities or for those communities within regencies which have town characteristics. According to the 2019 report by the Ministry of Home Affairs, there are 8,488 urban villages and 74,953 rural villages in Indonesia. North Aceh Regency contained the highest number of rural villages (852) amongst all of the regencies of Indonesia, followed by Pidie Regency with 730 rural villages and Bireuen Regency with 609 rural villages. Prabumulih, with only 12 rural villages, contained the fewest. Counted together, the sixteen regencies of Indonesia containing the most rural villages—namely, North Aceh (852), Pidie (730), Bireuen (609), Aceh Besar (604), Tolikara (541), East Aceh (513), Yahukimo (510), Purworejo (469), Lamongan (462), South Nias (459), Kebumen (449), Garut (421), Bojonegoro (419), Bogor (416), Cirebon (412), and Pati (401)—contain one-third of all the rural villages in Indonesia. Five of these are located in Aceh, two in Highland Papua, three in Central Java, two in East Java, three in West Java, and one in North Sumatra. An average number of rural villages in the regencies and 15 cities of Indonesia is 172 villages. A village is the lowest administrative division in Indonesia, and it is the lowest of the four levels. The average land area of villages in Indonesia is about 25.41 km2 (9.81 sq mi), while its average population is about 3,723 people.

Kartasura is a district (kecamatan) in Sukoharjo Regency, Central Java, Indonesia. Kartasura is considered Surakarta's satellite city and a junction of highways to Yogyakarta and Semarang. It can be reached within minutes southward of Surakarta's Adisumarmo International Airport.

The Ministry of Home Affairs is an interior ministry of the government of Indonesia responsible for matters of the state. The ministry was formerly known as the Department of Home Affairs until 2010 when the nomenclature of the Department of Home Affairs was changed to the Ministry of Home Affairs in accordance with the Regulation of the Minister of Home Affairs Number 3 of 2010 on the Nomenclature of the Ministry of Home Affairs.
A kampong is the term for a village in Malaysia, Brunei, Indonesia, and Singapore and a "dock" in Cambodia. The term applies to traditional villages, especially of the indigenous people, and has also been used to refer to urban slum areas and enclosed developments and neighbourhoods within towns and cities in Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Cambodia, Sri Lanka and Christmas Island. The traditional kampong village designs and architecture have been targeted for reform by urbanists and modernists and have also been adapted by contemporary architects for various projects.
Pedukuhan Ngande - Ande is located in Kelurahan Purwodadi, Kecamatan Tepus, Gunungkidul, Yogyakarta Special Region, Indonesia. The name of Ngande - Ande comes from the tree, called Ande-ande Tree.

A rukun warga is an administrative division of Indonesia under the village or kelurahan. Rukun warga not including the division of administration, and the formation of local communities is through consultation in the framework of community service set by the village or villages. An RW is further divided into rukun tetangga (RT). Most information about governance and functioning of the RW and RT is in Indonesian. Some non-Indonesian anthropologists have written about the functions and issues of the RW.
In Indonesia, district is the third-level administrative subdivision, below regency or city. The local term kecamatan is used in the majority of Indonesian areas. The term distrik is used in provinces in Papua. In the Special Region of Yogyakarta, the term kapanewon is used for districts within the regencies, while the term kemantren is used for districts within Yogyakarta, the province's only city. According to Statistics Indonesia, there are a total of 7,252 districts in Indonesia as at 2019, subdivided into 83,820 administrative villages. An average number of districts in the provinces of Indonesia is 190 districts, with an average area of 262.62 km2 (101.40 sq mi), and an average population of about 38,488 people.

Central Buton Regency is a new regency of Southeast Sulawesi established by separation from Buton Regency under Act No.15 of 2014, dated 23 July 2014. It covers an area of 837.16 km2 comprising the southern parts of Muna Island and Kabaena Island, together with several small offshore islands adjacent to these two main islands, but with no territory located on Buton Island. It had a population of 86,112 at the 2010 Census and 114,773 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 121,369. The administrative centre lies at Labungkari in Lakudo District.
In Indonesian law, the term "city" is generally defined as the second-level administrative subdivision of the Republic of Indonesia, an equivalent to regency. The difference between a city and a regency is that a city has non-agricultural economic activities and a dense urban population, while a regency comprises predominantly rural areas and is larger in area than a city. However, Indonesia historically had several classifications of cities.

The Regent of Thousand Islands, officially the Administrative Regent of Thousand Islands, is the highest office in the regency of Thousand Islands. Unlike regents in other regencies in Indonesia, the regent is appointed directly by the governor. The regency has no regional parliament, thus making the regent responsible to the governor.
Muara Gembong is a district of Bekasi Regency, West Java, Indonesia.








