
A cotton mill is a building that houses spinning or weaving machinery for the production of yarn or cloth from cotton, an important product during the Industrial Revolution in the development of the factory system.

Ancoats is an area of Manchester, England, next to the Northern Quarter, the northern part of Manchester city centre.

Cottonopolis was a 19th-century nickname for Manchester, as it was a metropolis and the centre of the cotton industry.
The Manchester warehouse which we lately visited, was a building fit for the Town Hall of any respectable municipality; a stately, spacious, and tasteful edifice; rich and substantial as its respectable proprietors, the well-known firm of Banneret and Co. There are nearly a hundred such buildings in Manchester; –not so large, perhaps, for this is the largest; but all in their degree worthy of Cottonopolis.

Murrays' Mills is a complex of former cotton mills on land between Jersey Street and the Rochdale Canal in the district of Ancoats, Manchester, England. The mills were built for brothers Adam and George Murray.

Houldsworth Mill, also known as Reddish Mill, is a former mill in Reddish, Stockport, Greater Manchester, England. Designed by Abraham Stott, it was constructed in 1865 for Henry Houldsworth, a prominent mill owner at the time. It is a Grade II* listed building.

Tudor Mill was cotton spinning mill in Ashton-under-Lyne, in the historic county of Lancashire, England. It was built between 1901 and 1903 for the Ashton Syndicate by Sydney Stott of Oldham. Tudor Mill was next to the Ashton Canal Warehouse at Portland Basin. It ceased spinning cotton in the 1960s and was used as a warehouse until it was destroyed by fire in 1970

Cavendish Mill is a Grade II* listed former cotton spinning mill in Ashton-under-Lyne, Greater Manchester, in the United Kingdom. It was built between 1884 and 1885 for the Cavendish Spinning Company by Potts, Pickup & Dixon of Oldham. Cavendish Mill was next to the Ashton Canal Warehouse at Portland Basin. It ceased spinning cotton in 1934 and was then used for a variety of purposes before it was converted into housing in 1994.

Brunswick Mill, Ancoats is a former cotton spinning mill on Bradford Road in Ancoats, Manchester, England. The mill was built around 1840, part of a group of mills built along the Ashton Canal, and at that time it was one of the country's largest mills. It was built round a quadrangle, a seven-storey block facing the canal. It was taken over by the Lancashire Cotton Corporation in the 1930s and passed to Courtaulds in 1964. Production finished in 1967.

New Islington is an inner city area of Manchester, in North West England. Historically in Lancashire and part of Ancoats, it has taken a separate identity to reflect its changed status as a regeneration area.
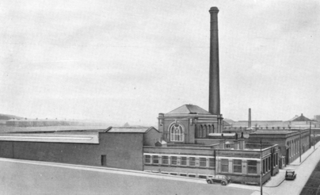
Harp Mill was a former cotton spinning mill in the Castleton, Rochdale, Greater Manchester, England. Queensway, Castleton was a hub of cotton mills including the three 't', Th'Arrow, Th'Harp, and Th'Ensor. The 1908 Castleton map includes: Marland Cotton Mill, Castleton Cotton Mill, Globe Works, Arrow Cotton Mill, Harp Cotton Mill, Globe Leather Works, Castleton Size Works and Castleton Iron Works. Th'Harp was built in 1908 for the Harp Doubling Company and was taken over by the Lancashire Cotton Corporation in 1938. The mill closed in 1958, and was sold to the hosiery manufacturer N. Corah Ltd.

Kingston Mill, Stockport is a mid nineteenth century cotton spinning mill in Edgeley, Stockport, Greater Manchester, England. It was taken over by the Lancashire Cotton Corporation in the 1930s and passed to Courtaulds in 1964. Production finished, it was made over to multiple uses.

McConnel & Kennedy Mills are a group of cotton mills on Redhill Street in Ancoats, Manchester, England. With the adjoining Murrays' Mills, they form a nationally important group.

Royal Mill, which is located on the corner of Redhill Street and Henry Street, Ancoats, in Manchester, England, is an early-20th-century cotton mill, one of the last of "an internationally important group of cotton-spinning mills" sited in East Manchester. Royal Mill was constructed in 1912 on part of the site of the earlier McConnel & Kennedy mills, established in 1798. It was originally called New Old Mill and was renamed following a royal visit by King George VI and Queen Elizabeth in 1942. A plaque commemorates the occasion. The Ancoats mills collectively comprise "the best and most-complete surviving examples of early large-scale factories concentrated in one area".

Old Mill, completed in 1798 as part of Murrays' Mills, is the oldest surviving cotton mill in Manchester, England. Sited on the Rochdale Canal in Ancoats, it was powered by a Boulton and Watt steam engine, and its narrow six-storey brick structure "came to typify the Manchester cotton mill". Old Mill was designated a Grade II* listed building on 19 June 1988.

Kearsley Mill is a 240,000 sq ft (22,000 m2), late period cotton mill located in the small village of Prestolee in Kearsley, Greater Manchester, part of the historic county of Lancashire. A near complete example of Edwardian mill architecture, the building now functions as headquarters for a number of businesses and is still used in the continued manufacturing and distribution of textiles by Richard Haworth Ltd Est (1876), part of the Ruia Group. The mill is a Grade II listed building.

Swan Lane Mills is a former cotton mill complex in Bolton, Greater Manchester, England. All three mills are Grade II* listed buildings. The mills were designed by Stott and Sons of Oldham. When completed, the double mill was the largest spinning mill in the world. It was granted Grade II* listed status on 26 April 1974. Number 3 Mill was separately listed as Grade II* on the same day.
Manchester is a city in Northwest England. The M4 postcode area is to the northeast of the city centre, and includes part of the Northern Quarter, part of New Islington, and the area of Ancoats. This postcode area contains 67 listed buildings that are recorded in the National Heritage List for England. Of these, eight are listed at Grade II*, the middle of the three grades, and the others are at Grade II, the lowest grade.























