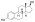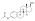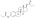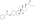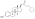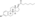17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases, also 17-ketosteroid reductases (17-KSR), are a group of alcohol oxidoreductases which catalyze the reduction of 17-ketosteroids and the dehydrogenation of 17β-hydroxysteroids in steroidogenesis and steroid metabolism. This includes interconversion of DHEA and androstenediol, androstenedione and testosterone, and estrone and estradiol.
Combined injectable contraceptives (CICs) are a form of hormonal birth control for women. They consist of monthly injections of combined formulations containing an estrogen and a progestin to prevent pregnancy.

Estradiol benzoate (EB), sold under the brand name Progynon-B among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low estrogen levels in women, in hormone therapy for transgender women, and in the treatment of gynecological disorders. It is also used in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. Estradiol benzoate is used in veterinary medicine as well. When used clinically, the medication is given by injection into muscle usually two to three times per week.

Estradiol cypionate (EC), sold under the brand name Depo-Estradiol among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low estrogen levels in women, in hormone therapy for trans women, and in hormonal birth control for women. It is given by injection into muscle once every 1 to 4 weeks.
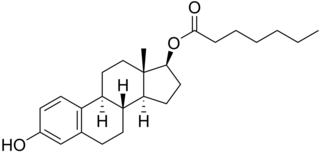
Estradiol enantate, also spelled estradiol enanthate and sold under the brand names Perlutal and Topasel among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in hormonal birth control for women. It is formulated in combination with dihydroxyprogesterone acetophenide, a progestin, and is used specifically as a combined injectable contraceptive. Estradiol enantate is not available for medical use alone. The medication, in combination with DHPA, is given by injection into muscle once a month.

Estradiol undecylate, also known as estradiol undecanoate and formerly sold under the brand names Delestrec and Progynon Depot 100 among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. It has also been used as a part of hormone therapy for transgender women. Although estradiol undecylate has been used in the past, it was discontinued and hence is no longer available. The medication has been given by injection into muscle usually once a month.
An estrogen ester is an ester of an estrogen, most typically of estradiol but also of other estrogens such as estrone, estriol, and even nonsteroidal estrogens like diethylstilbestrol. Esterification renders estradiol into a prodrug of estradiol with increased resistance to first-pass metabolism, slightly improving its oral bioavailability. In addition, estrogen esters have increased lipophilicity, which results in a longer duration when given by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection due to the formation of a long-lasting local depot in muscle and fat. Conversely, this is not the case with intravenous injection or oral administration. Estrogen esters are rapidly hydrolyzed into their parent estrogen by esterases once they have been released from the depot. Because estradiol esters are prodrugs of estradiol, they are considered to be natural and bioidentical forms of estrogen.
Estradiol palmitate, or estradiol monopalmitate, also known as estradiol 17β-hexadecanoate, is a naturally occurring steroidal estrogen and an estrogen ester – specifically, the C17β palmitate ester of estradiol. It occurs in the body as a very long-lasting metabolite and prohormone of estradiol. The compound has no affinity for the estrogen receptor, requiring transformation into estradiol for its estrogenic activity. In addition to its endogenous role, estradiol palmitate was formerly used as a fattening agent in chickens under the brand name Esmopal.
Estradiol stearate (E2-17-St), also known as estradiol octadecanoate and sold under the brand name Depofollan, is a naturally occurring estrogen and an estrogen ester – specifically, the C17β stearate ester of estradiol. It occurs in the body as a very long-lasting metabolite and prohormone of estradiol. The compound is one of the components that collectively constitute lipoidal estradiol, another of which is estradiol palmitate. It is extremely lipophilic and hydrophobic. Estradiol stearate has no affinity for the estrogen receptor, requiring transformation into estradiol via esterases for its estrogenic activity. The compound does not bind to sex hormone-binding globulin or α-fetoprotein, instead being transported by lipoproteins such as high-density lipoprotein and low-density lipoprotein.

Estradiol dienanthate (EDE), sold under the brand names Climacteron among others, is a long-acting estrogen medication which was previously used in menopausal hormone therapy for women and to suppress lactation in women. It was formulated in combination with estradiol benzoate (EB), a short-acting estrogen, and testosterone enanthate benzilic acid hydrazone (TEBH), a long-acting androgen/anabolic steroid. EDE has not been made available for medical use alone. The medication, in combination with EB and TEBH, was given by injection into muscle once or at regular intervals, for instance once every 6 weeks.

A steroid ester is an ester of a steroid. They include androgen esters, estrogen esters, progestogen esters, and corticosteroid esters. Steroid esters may be naturally occurring/endogenous like DHEA sulfate or synthetic like estradiol valerate. Esterification is useful because it is often able to render the parent steroid into a prodrug of itself with altered chemical properties such as improved metabolic stability, water solubility, and/or lipophilicity. This, in turn, can enhance pharmacokinetics, for instance by improving the steroid's bioavailability and/or conferring depot activity and hence an extended duration with intramuscular or subcutaneous injection.
Lipoidal estradiol (LE2) is the variety of endogenous C17β long-chain fatty acid esters of estradiol which are formed as metabolites of estradiol. Important examples of these esters include estradiol arachidonate, estradiol lineolate, estradiol oleate, estradiol palmitate, and estradiol stearate. LE2 are estrogens but do not bind to the estrogen receptor, instead acting as prohormones of estradiol. Relative to estradiol, they have far longer-lasting durations of effect due to their much slower rates of metabolism and clearance. It has been hypothesized that LE2 may serve as a store of estrogen for when estradiol levels become low. LE2 are highly lipophilic and hydrophobic and are found in highest concentrations in adipose tissue and other estrogen-sensitive tissues and in low but detectable concentrations in circulation, with none excreted in urine. They have been referred to as the "endogenous counterparts of the synthetic esters of estrogens" like estradiol valerate and estradiol cypionate.

Estradiol glucuronide, or estradiol 17β-D-glucuronide, is a conjugated metabolite of estradiol. It is formed from estradiol in the liver by UDP-glucuronyltransferase via attachment of glucuronic acid and is eventually excreted in the urine by the kidneys. It has much higher water solubility than does estradiol. Glucuronides are the most abundant estrogen conjugates.
Estradiol decanoate (E2D), or estradiol decylate, also known as estradiol 17β-decanoate, is a synthetic steroidal estrogen and an estrogen ester – specifically, the 17β-decanoate (decylate) ester of estradiol – which was studied for use in hormone replacement therapy for ovariectomized women in the late 1970s but was never marketed.

Testosterone enantate benzilic acid hydrazone (TEBH), or testosterone 17β-enantate 3-benzilic acid hydrazone, is a synthetic, injected androgen/anabolic steroid and an androgen ester – specifically, the C17β enantate (heptanoate) ester and C3 benzilic acid hydrazone of testosterone. It was previously marketed in combination with estradiol benzoate and estradiol dienantate under the brand names Climacteron, Lactimex, and Lactostat. Clinical studies have assessed this formulation. TEBH was first described in the scientific literature in 1959. It is a very long-lasting prodrug of testosterone when administered in oil via intramuscular injection.

Estriol (E3), sold under the brand name Ovestin among others, is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone which is used in menopausal hormone therapy. It is also used in veterinary medicine as Incurin to treat urinary incontinence due to estrogen deficiency in dogs. The medication is taken by mouth in the form of tablets, as a cream that is applied to the skin, as a cream or pessary that is applied in the vagina, and by injection into muscle.

Estradiol benzoate cyclooctenyl ether (EBCO), or estradiol 3-benzoate 17β-cyclooctenyl ether, is a synthetic estrogen as well as estrogen ester and ether – specifically, the C3 benzoate ester and C17β cyclooctenyl ether of estradiol – which was described in the early 1970s and was never marketed. It has been found to have a dramatically prolonged duration of action with oral administration in animals, similarly to the related compound quinestrol. A single oral dose of EBCO sustained high uterus weights for 3 weeks in rats. This long-lasting activity may be due to storage of EBCO in fat. It appears that EBCO is absorbed satisfactorily from the gastrointestinal tract, at least partially survives first-pass metabolism in the liver and intestines, and is then sequestered into fat, from which it is slowly released and activated into estradiol. In contrast to quinestrol, the oral activity of EBCO is greatly improved when it is delivered in an oil solution as opposed to an aqueous vehicle.

Ethinylestradiol sulfate, also known as 17α-ethynylestradiol 3-sulfate, is an estrogen ester – specifically, the C3 sulfuric acid (sulfate) ester of the synthetic estrogen ethinylestradiol (EE) – and is the major metabolite of EE. Circulating levels of EE sulfate range from 6 to 22 times those of EE when EE is taken orally. EE sulfate can be transformed back into EE (14–21%) via steroid sulfatase, and it has been suggested that EE sulfate may serve as a circulating reservoir for EE, similarly to the case of estrone sulfate with estradiol. However, the EE sulfate pool with EE is far smaller than the pool of estrone sulfate that occurs with estradiol. In addition, in contrast to the case of estrone sulfate and estrone, the conversion rate of EE sulfate back into EE is relatively low, and has been said probably isn't of clinical significance. However, other studies have suggested that EE sulfate may nonetheless contribute up to 20% of total EE levels.

Estradiol 17β-benzoate (E2-17B) is an estrogen and an estrogen ester—specifically, the C17β benzoate ester of estradiol—which was never marketed. It is the C17β positional isomer of the better-known and clinically used estradiol ester estradiol benzoate. Estradiol 17β-benzoate was first described in the 1930s.