
Methcathinone is a monoamine alkaloid and psychoactive stimulant, a substituted cathinone. It is used as a recreational drug due to its potent stimulant and euphoric effects and is considered to be addictive, with both physical and psychological withdrawal occurring if its use is discontinued after prolonged or high-dosage administration. It is usually snorted, but can be smoked, injected, or taken orally.
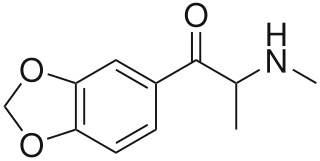
Methylone, also known as 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylcathinone (MDMC), is an empathogen and stimulant psychoactive drug. It is a member of the amphetamine, cathinone and methylenedioxyphenethylamine classes.

Pyrovalerone is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that acts as a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI). It was developed in the 1980s and had briefly been approved in Spain and France for chronic fatigue or lethargy and as an appetite suppressant, but was withdrawn from both markets around 2001 due to safety concerns including problems with abuse and dependence. It is closely related on a structural level to a number of other cathinone stimulants, such as α-PVP, MDPV and prolintane.

α-Pyrrolidinopropiophenone (α-PPP), is a stimulant drug. It is similar in structure to the appetite suppressant diethylpropion and has analogous effects in animals. Little is known about this compound, but it has been detected by laboratories in Germany as an ingredient in "ecstasy" tablets seized by law enforcement authorities. This drug has been found to produce stimulant effects in animals and produces highly stimulating effects in humans, based on the experiences of the individuals who have tried it. Most of the individuals who have tried it prefer α-PVP to it, but prefer this drug over α-PVT. It is said to lack euphoria compared to α-PVP.

2-Benzylpiperidine is a stimulant drug of the arylpiperidine family. It is similar in structure to certain other stimulants such as methylphenidate and desoxypipradrol. However, it is far less potent as a monoamine reuptake inhibitor in comparison. The drug is little used as a stimulant, with its main use being as a synthetic intermediate in the manufacture of other drugs.

A monoamine releasing agent (MRA), or simply monoamine releaser, is a drug that induces the release of one or more monoamine neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron into the synapse, leading to an increase in the extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitters and hence enhanced signaling by those neurotransmitters. The monoamine neurotransmitters include serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine; MRAs can induce the release of one or more of these neurotransmitters.

4-Methylamphetamine (4-MA), also known by the former proposed brand name Aptrol, is a stimulant and anorectic drug of the amphetamine family. It is structurally related to mephedrone (4-methylmethcathinone).

3',4'-Methylenedioxy-α-pyrrolidinobutyrophenone (MDPBP) is a stimulant of the cathinone class developed in the 1960s, which has been reported as a novel designer drug. MDPBP is sometimes sold under the name "NRG-1" as a mixture with other cathinone derivatives, including flephedrone, pentylone, MαPPP and its higher homologue MDPV. As with other cathinones, MDPBP has been shown to have reinforcing effects in rats.

α-Pyrrolidinopentiophenone (α-PVP), also known as α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone, O-2387, β-keto-prolintane, prolintanone, or desmethylpyrovalerone, is a synthetic stimulant of the cathinone class developed in the 1960s that has been sold as a designer drug and often consumed for recreational reasons. α-PVP is chemically related to pyrovalerone and is the ketone analog of prolintane.
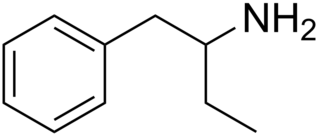
Phenylisobutylamine, also known as α-ethylphenethylamine (AEPEA) or as butanphenamine (B), is a stimulant drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine families. It is a higher homologue of amphetamine, differing from amphetamine's molecular structure only by the substitution of the methyl group at the alpha position of the side chain with an ethyl group.
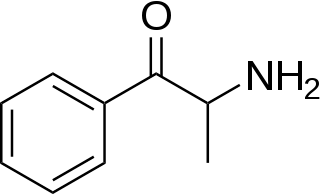
Substituted cathinones, or simply cathinones, which include some stimulants and entactogens, are derivatives of cathinone. They feature a phenethylamine core with an alkyl group attached to the alpha carbon, and a ketone group attached to the beta carbon, along with additional substitutions. Cathinone occurs naturally in the plant khat whose leaves are chewed as a recreational drug.
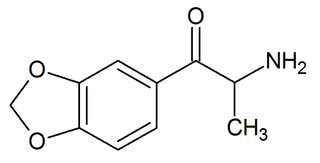
3,4-Methylenedioxycathinone is an empathogen and stimulant of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and cathinone classes and the β-keto analogue of MDA.

4-Methylcathinone (4-MC), also known as normephedrone is a stimulant drug of the cathinone group. It is an active metabolite of the better known drug mephedrone.

3',4'-Dimethoxy-α-pyrrolidinopentiophenone is a synthetic stimulant drug of the cathinone class that has been sold online as a designer drug. It is a relatively weak inhibitor of serotonin reuptake and has little affinity in vitro for dopamine or noradrenaline transporters.
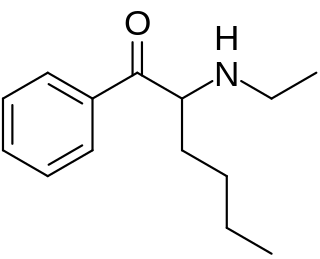
N-Ethylhexedrone (also known as α-ethylaminocaprophenone, N-ethylnorhexedrone, hexen, and NEH) is a stimulant of the cathinone class that acts as a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) with IC50 values of 0.0978 and 0.0467 μM, respectively. N-Ethylhexedrone was first mentioned in a series of patents by Boehringer Ingelheim in the 1960s which led to the development of the better-known drug methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV). Since the mid-2010s, N-ethylhexedrone has been sold online as a designer drug. In 2018, N-ethylhexedrone was the second most common drug of the cathinone class to be identified in Drug Enforcement Administration seizures.

3-Chloromethcathinone (3-CMC), also known as clophedrone, is a synthetic substance belonging to the cathinone class of psychoactive compounds. It is very similar in structure to other methcathinone derivatives such as 3-MMC and 4-CMC. Unlike cathinone, which occurs naturally in the khat plant Catha edulis, 3-CMC is not found in nature and is solely produced through chemical synthesis.

α-PCyP (α-PyrrolidinoCyclohexanoPhenone) is a stimulant drug of the cathinone class that has been sold online as a designer drug. In a series of alpha-substituted pyrrolidinyl cathinone derivatives developed in 2015, the alpha-cyclopentyl derivative was found to have around the same potency in vitro as an inhibitor of the dopamine transporter as the alpha-propyl derivative α-PVP, while the alpha-cyclohexyl derivative α-PCyP was around twice as strong.
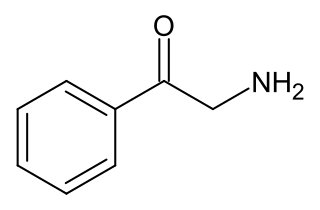
2-Aminoacetophenone, also known as β-ketophenethylamine, α-desmethylcathinone, or phenacylamine, is a substituted phenethylamine derivative. It is the phenethylamine homologue of cathinone (β-ketoamphetamine) and hence is a parent compound of a large number of stimulant and entactogen drugs.

3-Chlorocathinone (3-CC) is a psychostimulant drug of the cathinone family. It is the analogue of the antidepressant and norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) bupropion in which the N-tert-butyl group has been removed. The drug is also the analogue of the stimulant 3-chloromethcathinone in which the N-methyl group has been removed.

α-Propylphenethylamine, also known as 1-phenyl-2-aminopentane, is a stimulant drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine families. It is the analogue of the β-phenethylamine (PEA) derivatives amphetamine and phenylisobutylamine in which the α-alkyl chain has been further lengthened to be a propyl group.




















