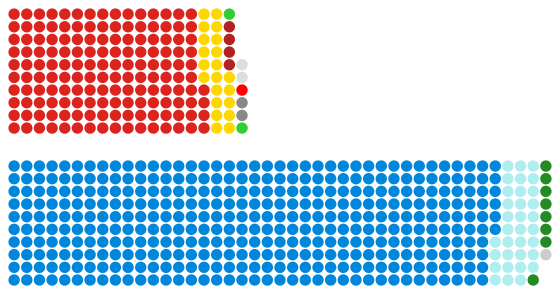
|
| Constituency | MP | Party |
|---|
| Aberavon | William Cove | Labour |
| Aberdare | George Hall | Labour |
| Aberdeen North | George Garro-Jones | Labour |
| Aberdeen South | Sir Douglas Thomson, Bt | Conservative |
| Aberdeenshire Central | Sir Robert Smith | Conservative |
| Aberdeenshire East | Robert Boothby | Conservative |
| Aberdeenshire West and Kincardine | Malcolm Barclay-Harvey | Conservative |
| Abertillery | George Daggar | Labour |
| Abingdon | Sir Ralph Glyn, Bt | Conservative |
| Accrington | Henry Procter | Conservative |
| Acton | Hubert Duggan | Conservative |
| Aldershot | Roundell Palmer | Conservative |
| Altrincham | Sir Edward Grigg | Conservative |
| Anglesey | Megan Lloyd George | Independent Liberal |
Antrim
(two members) | Hon. Sir Hugh O'Neill | Ulster Unionist |
| Sir Joseph McConnell, Bt | Ulster Unionist |
| Argyllshire | Frederick Macquisten | Conservative |
| Armagh | Sir William Allen | Ulster Unionist |
| Ashford | Patrick Spens | Conservative |
| Ashton-under-Lyne | Fred Simpson | Labour |
| Aylesbury | Michael Beaumont | Conservative |
| Ayr Burghs | Thomas Moore | Conservative |
| Ayrshire North and Bute | Sir Charles MacAndrew | Conservative |
| Ayrshire South | The Rt Hon. James Brown | Labour |
|
| Balham and Tooting | Sir Alfred Butt, Bt | Conservative |
| Banbury | Sir Albert Edmondson | Conservative |
| Banffshire | Sir John Findlay, Bt | Conservative |
| Barkston Ash | Leonard Ropner | Conservative |
| Barnard Castle | Thomas Sexton | Labour |
| Barnsley | John Potts | Labour |
| Barnstaple | Richard Acland | Liberal |
| Barrow-in-Furness | Sir Jonah Walker-Smith | Conservative |
| Basingstoke | Patrick Donner | Conservative |
| Bassetlaw | Frederick Bellenger | Labour |
| Bath | Loel Guinness | Conservative |
| Batley and Morley | Willie Brooke | Labour |
| Battersea North | William Sanders | Labour |
| Battersea South | Harry Selley | Conservative |
| Bedford | Richard Wells | Conservative |
| Bedfordshire Mid | Alan Lennox-Boyd | Conservative |
| Bedwellty | Charles Edwards | Labour |
| Belfast, East | Herbert Dixon | Ulster Unionist |
| Belfast, North | Thomas Somerset | Ulster Unionist |
| Belfast, South | William Stewart | Ulster Unionist |
| Belfast, West | Alexander Browne | Ulster Unionist |
| Belper | Herbert Wragg | Conservative |
| Bermondsey West | Alfred Salter | Labour |
| Berwick and Haddington | John McEwen | Conservative |
| Berwick-on-Tweed | Sir Hugh Seely, Bt | Liberal |
| Bethnal Green North-East | Dan Chater | Labour Co-op |
| Bethnal Green South-West | Sir Percy Harris, Bt | Liberal |
| Bewdley | The Rt Hon. Stanley Baldwin | Conservative |
| Birkenhead East | Graham White | Liberal |
| Birkenhead West | John Sandeman Allen | Conservative |
| Birmingham Aston | Hon. Arthur Hope | Conservative |
| Birmingham Deritend | Smedley Crooke | Conservative |
| Birmingham Duddeston | Oliver Simmonds | Conservative |
| Birmingham Edgbaston | Rt. Hon. Neville Chamberlain | Conservative |
| Birmingham Erdington | John Eales | Conservative |
| Birmingham Handsworth | Oliver Locker-Lampson | Conservative |
| Birmingham King's Norton | Ronald Cartland | Conservative |
| Birmingham Ladywood | Geoffrey Lloyd | Conservative |
| Birmingham Moseley | Sir Patrick Hannon | Conservative |
| Birmingham Sparkbrook | Rt. Hon. Leo Amery | Conservative |
| Birmingham West | Rt. Hon. Sir Austen Chamberlain | Conservative |
| Birmingham Yardley | Edward Salt | Conservative |
| Bishop Auckland | Hugh Dalton | Labour |
Blackburn
(two members) | W. D. Smiles | Conservative |
| George Elliston | Conservative |
| Blackpool | Roland Robinson | Conservative |
| Blaydon | William Whiteley | Labour |
| Bodmin | John Rathbone | Conservative |
Bolton
(two members) | Cyril Entwistle | Conservative |
| Sir John Haslam | Conservative |
| Bootle | Eric Errington | Conservative |
| Bosworth | William Edge | Liberal National |
| Bothwell | James C. Welsh | Labour |
| Bournemouth | Sir Henry Page Croft | Conservative |
| Bow and Bromley | The Rt Hon. George Lansbury | Labour |
| Bradford Central | William Leach | Labour |
| Bradford East | Joseph Hepworth | Conservative |
| Bradford North | Eugene Ramsden | Conservative |
| Bradford South | Herbert Holdsworth | Liberal |
| Brecon and Radnor | Hon. Ivor Guest | National |
| Brentford and Chiswick | Harold Mitchell | Conservative |
| Bridgwater | Reginald Croom-Johnson | Conservative |
| Brigg | David Quibell | Labour |
Brighton
(two members) | Cooper Rawson | Conservative |
| The Rt Hon. Sir George Tryon | Conservative |
| Bristol Central | Lord Apsley | Conservative |
| Bristol East | Sir Stafford Cripps | Labour |
| Bristol North | Robert Bernays | Liberal |
| Bristol South | Alexander Walkden | Labour |
| Bristol West | Cyril Thomas Culverwell | Conservative |
| Brixton | Nigel Colman | Conservative |
| Bromley | Sir Edward Campbell | Conservative |
| Broxtowe | Seymour Cocks | Labour |
| Buckingham | Sir George Bowyer, Bt | Conservative |
| Buckrose | Albert Braithwaite | Conservative |
| Burnley | Wilfrid Burke | Labour |
| Burslem | Andrew McLaren | Labour |
| Burton | The Rt Hon. John Gretton | Conservative |
| Bury | Alan Chorlton | Conservative |
| Bury St Edmunds | Frank Heilgers | Conservative |
|
| Caerphilly | Morgan Jones | Labour |
| Caithness and Sutherland | The Rt Hon. Sir Archibald Sinclair, Bt | Liberal |
| Camberwell North | Charles Ammon | Labour |
| Camberwell North West | Hon. Oscar Guest | Conservative |
| Camborne | Peter Agnew | Conservative |
| Cambridge | Richard Tufnell | Conservative |
| Cambridgeshire | Richard Briscoe | Conservative |
Cambridge University
(two members) | Sir John Withers | Conservative |
| Kenneth Pickthorn | Conservative |
| Cannock | William Adamson | Labour |
| Canterbury | Sir William Wayland | Conservative |
| Cardiff Central | Sir Ernest Bennett | National Labour |
| Cardiff East | Owen Temple-Morris | Conservative |
| Cardiff South | Arthur Evans | Conservative |
| Cardiganshire | Owen Evans | Liberal |
| Carlisle | Louis Spears | Conservative |
| Carmarthen | Daniel Hopkin | Labour |
| Carnarvon Boroughs | The Rt Hon. David Lloyd George | Independent Liberal |
| Carnarvonshire | Goronwy Owen | Independent Liberal |
| Chatham | Leonard Plugge | Conservative |
| Chelmsford | John Macnamara | Conservative |
| Chelsea | Rt. Hon. Sir Samuel Hoare, Bt | Conservative |
| Cheltenham | Sir Walter Preston | Conservative |
| Chertsey | Sir Archibald Boyd-Carpenter | Conservative |
| City of Chester | Sir Charles Cayzer, Bt | Conservative |
| Chesterfield | George Benson | Labour |
| Chester-le-Street | Jack Lawson | Labour |
| Chichester | John Courtauld | Conservative |
| Chippenham | Victor Cazalet | Conservative |
| Chislehurst | Sir Waldron Smithers | Conservative |
| Chorley | The Rt Hon. Sir Douglas Hacking | Conservative |
| Cirencester and Tewkesbury | William Morrison | Conservative |
City of London
(two members) | Sir Alan Anderson | Conservative |
| Sir Vansittart Bowater, Bt | Conservative |
| Clapham | Sir John Leigh, Bt | Conservative |
| Clay Cross | Alfred Holland | Labour |
| Cleveland | Robert Bower | Conservative |
| Clitheroe | Sir William Brass | Conservative |
| Coatbridge | James Barr | Labour |
| Colchester | Oswald Lewis | Conservative |
| Colne Valley | Ernest Marklew | Labour |
Combined English Universities
(two members) | Eleanor Rathbone | Independent |
| Sir Reginald Craddock | Conservative |
Combined Scottish Universities
(Three members) | John Graham Kerr | Conservative |
| George Morrison | Liberal National |
| Noel Skelton | Conservative |
| Cornwall North | Rt Hon. Sir Francis Dyke Acland, Bt | Liberal |
| Consett | David Adams | Labour |
| Coventry | William Strickland | Conservative |
| Crewe | Sir Donald Somervell | Conservative |
| Croydon North | Hon. Glyn Mason | Conservative |
| Croydon South | Herbert Williams | Conservative |
| Cumberland North | Wilfrid Roberts | Liberal |
|
| Darlington | Charles Peat | Conservative |
| Dartford | Frank Clarke | Conservative |
| Darwen | Stuart Russell | Conservative |
| Daventry | The Rt Hon. Edward FitzRoy | Speaker (Conservative) |
| Denbigh | Sir Henry Morris-Jones | Liberal National |
| Deptford | Walter Green | Labour Co-op |
Derby
(two members) | Rt. Hon. J. H. Thomas | National Labour |
| William Allan Reid | Conservative |
| Derbyshire North East | Frank Lee | Labour |
| Derbyshire South | Paul Emrys-Evans | Conservative |
| Derbyshire West | The Marquess of Hartington | Conservative |
| Devizes | Sir Percy Hurd | Conservative |
| Dewsbury | Benjamin Riley | Labour |
| Doncaster | Alfred Short | Labour |
| Don Valley | Tom Williams | Labour |
| Dorset East | Gordon Hall Caine | Conservative |
| Dorset North | Sir Cecil Hanbury | Conservative |
| Dorset, South | Viscount Cranborne | Conservative |
| Dorset West | Philip Colfox | Conservative |
| Dover | Hon. John Astor | Conservative |
Down
(two members) | Sir David Reid | Ulster Unionist |
| Viscount Castlereagh | Ulster Unionist |
| Dudley | Dudley Joel | Conservative |
| Dulwich | Bracewell Smith | Conservative |
| Dumbarton Burghs | David Kirkwood | Labour |
| Dumfriesshire | Sir Henry Fildes | Liberal National |
| Dunbartonshire | Hon. Archibald Cochrane | Conservative |
Dundee
(two members) | Dingle Foot | Liberal |
| Florence Horsbrugh | Conservative |
| Dunfermline Burghs | William McLean Watson | Labour |
| Durham | Joshua Ritson | Labour |
|
| Ealing | Sir Frank Sanderson, Bt | Conservative |
| Eastbourne | Charles Taylor | Conservative |
| East Grinstead | Sir Henry Cautley, Bt | Conservative |
| East Ham North | John Mayhew | Conservative |
| East Ham South | Alfred Barnes | Labour Co-op |
| Ebbw Vale | Aneurin Bevan | Labour |
| Eccles | Robert Cary | Conservative |
| Eddisbury | R. J. Russell | Liberal National |
| Edinburgh Central | James Guy | Conservative |
| Edinburgh East | Frederick Pethick-Lawrence | Labour |
| Edinburgh North | Alexander Erskine-Hill | Conservative |
| Edinburgh South | Sir Samuel Chapman | Conservative |
| Edinburgh West | Thomas Cooper | Conservative |
| Edmonton | Francis Broad | Labour Co-op |
| Elland | Thomas Levy | Conservative |
| Enfield | Bartle Bull | Conservative |
| Epping | The Rt Hon. Winston Churchill | Conservative |
| Epsom | Archibald Southby | Conservative |
| Essex South East | Victor Raikes | Conservative |
| Evesham | Rupert de la Bere | Conservative |
| Exeter | Arthur Reed | Conservative |
| Eye | Edgar Granville | Liberal National |
|
| Fareham | The Rt Hon. Sir Thomas Inskip | Conservative |
| Farnham | Sir Arthur Samuel, Bt | Conservative |
| Farnworth | Guy Rowson | Labour |
| Faversham | Adam Maitland | Conservative |
Fermanagh and Tyrone
(two members) | Patrick Cunningham | Irish Nationalist (Abstent.) |
| Anthony Mulvey | Irish Nationalist (Abstent.) |
| Fife East | James Henderson-Stewart | Liberal National |
| Fife West | Willie Gallacher | Communist |
| Finchley | John Crowder | Conservative |
| Finsbury | George Woods | Labour Co-op |
| Flintshire | Gwilym Rowlands | Conservative |
| Forest of Dean | M. Philips Price | Labour |
| Forfarshire | William T. Shaw | Conservative |
| Frome | Mavis Tate | Conservative |
| Fulham East | Hon. William Astor | Conservative |
| Fulham West | Sir Cyril Cobb | Conservative |
| Fylde | The Rt Hon. Edward Stanley | Conservative |
|
| Gainsborough | Harry Crookshank | Conservative |
| Galloway | John Mackie | Conservative |
| Gateshead | Thomas Magnay | Liberal National |
| Gillingham | Sir Robert Gower | Conservative |
| Glasgow Bridgeton | James Maxton | Independent Labour Party |
| Glasgow Camlachie | Campbell Stephen | Independent Labour Party |
| Glasgow Cathcart | John Train | Conservative |
| Glasgow Central | Sir William Alexander | Conservative |
| Glasgow Gorbals | George Buchanan | Independent Labour Party |
| Glasgow Govan | Neil Maclean | Labour |
| Glasgow Hillhead | The Rt Hon. Sir Robert Horne | Conservative |
| Glasgow Kelvingrove | The Rt Hon. Walter Elliot | Conservative |
| Glasgow Maryhill | John James Davidson | Labour |
| Glasgow Partick | Arthur Young | Conservative |
| Glasgow Pollok | Rt. Hon. Sir John Gilmour, Bt | Conservative |
| Glasgow St. Rollox | William Leonard | Labour Co-op |
| Glasgow Shettleston | John McGovern | Independent Labour Party |
| Glasgow Springburn | George Hardie | Labour |
| Glasgow Tradeston | Tom Henderson | Labour Co-op |
| Gloucester | Leslie Boyce | Conservative |
| Gower | David Grenfell | Labour |
| Grantham | Sir Victor Warrender, Bt | Conservative |
| Gravesend | Sir Irving Albery | Conservative |
| Great Yarmouth | Arthur Harbord | Liberal National |
| Greenock | The Rt Hon. Sir Godfrey Collins | Liberal National |
| Greenwich | Sir George Hume | Conservative |
| Grimsby | Walter Womersley | Conservative |
| Guildford | Sir John Jarvis, Bt | Conservative |
|
| Hackney Central | Fred Watkins | Labour |
| Hackney North | Austin Hudson | Conservative |
| Hackney South | The Rt Hon. Herbert Morrison | Labour |
| Halifax | Gilbert Gledhill | Conservative |
| Hamilton | Duncan Graham | Labour |
| Hammersmith North | D. N. Pritt | Labour |
| Hammersmith South | Douglas Cooke | Conservative |
| Hampstead | George Balfour | Conservative |
| Hanley | Arthur Hollins | Labour |
| Harborough | Ronald Tree | Conservative |
| Harrow | Sir Isidore Salmon | Conservative |
| The Hartlepools | W. G. Howard Gritten | Conservative |
| Harwich | Stanley Holmes | Liberal National |
| Hastings | The Rt Hon. Eustace Percy | Conservative |
| Hemel Hempstead | Rt Hon. J. C. C. Davidson | Conservative |
| Hemsworth | George Griffiths | Labour |
| Hendon | Sir Reginald Blair | Conservative |
| Henley | Sir Gifford Fox, Bt | Conservative |
| Hereford | James Thomas | Conservative |
| Hertford | Sir Murray Sueter | Conservative |
| Hexham | Douglas Clifton Brown | Conservative |
| Heywood and Radcliffe | Richard Porritt | Conservative |
| High Peak | Sir Alfred Law | Conservative |
| Hitchin | Sir Arnold Wilson | Conservative |
| Holborn | Sir Robert Tasker | Conservative |
| Holderness | Sir Samuel Savery | Conservative |
| Holland-with-Boston | Sir James Blindell | Liberal National |
| Honiton | Cedric Drewe | Conservative |
| Horncastle | Henry Haslam | Conservative |
| Hornsey | Euan Wallace | Conservative |
| Horsham and Worthing | The Earl Winterton PC | Conservative |
| Houghton-le-Spring | William Stewart | Labour |
| Howdenshire | William Carver | Conservative |
| Huddersfield | William Mabane | Liberal National |
| Huntingdonshire | Sidney Peters | Liberal National |
| Hythe | The Rt Hon. Sir Philip Sassoon, Bt | Conservative |
|
| Ilford | Sir George Hamilton | Conservative |
| Ilkeston | George Oliver | Labour |
| Ince | Gordon Macdonald | Labour |
| Inverness | Sir Murdoch Macdonald | Liberal National |
| Ipswich | Sir John Ganzoni, Bt | Conservative |
| Isle of Ely | James de Rothschild | Liberal |
| Isle of Thanet | Harold Balfour | Conservative |
| Isle of Wight | Peter Macdonald | Conservative |
| Islington East | Thelma Cazalet-Keir | Conservative |
| Islington North | Albert Goodman | Conservative |
| Islington South | William Cluse | Labour |
| Islington West | Frederick Montague | Labour |
|
| Jarrow | Ellen Wilkinson | Labour |
|
| Keighley | The Rt Hon. Hastings Lees-Smith | Labour |
| Kennington | Sir George Harvey | Conservative |
| Kensington North | James Duncan | Conservative |
| Kensington South | Sir William Davison | Conservative |
| Kettering | John Eastwood | Conservative |
| Kidderminster | Sir John Wardlaw-Milne | Conservative |
| Kilmarnock | Kenneth Lindsay | National Labour |
| King's Lynn | Hon. Somerset Maxwell | Conservative |
| Kingston upon Hull Central | Walter Windsor | Labour |
| Kingston upon Hull East | George Muff | Labour |
| Kingston upon Hull North West | Sir Lambert Ward, Bt | Conservative |
| Kingston upon Hull South West | Richard Law | Conservative |
| Kingston-upon-Thames | Sir Frederick Penny, Bt | Conservative |
| Kingswinford | Arthur Henderson | Labour |
| Kinross & West Perthshire | The Duchess of Atholl | Conservative |
| Kirkcaldy District of Burghs | The Rt Hon. Tom Kennedy | Labour |
| Knutsford | Sir Ernest Makins | Conservative |
|
| Lambeth North | George Strauss | Labour |
| Lanark | Alec Douglas-Home | Conservative |
| Lanarkshire North | William Anstruther-Gray | Conservative |
| Lancaster | Herwald Ramsbotham | Conservative |
| Leeds Central | Richard Denman | National Labour |
| Leeds North | Osbert Peake | Conservative |
| Leeds North East | Sir John Birchall | Conservative |
| Leeds South | Henry Charleton | Labour |
| Leeds South East | James Milner | Labour |
| Leeds West | Vyvyan Adams | Conservative |
| Leek | William Bromfield | Labour |
| Leicester East | Abraham Lyons | Conservative |
| Leicester South | Charles Waterhouse | Conservative |
| Leicester West | Hon. Harold Nicolson | National Labour |
| Leigh | Joe Tinker | Labour |
| Leith | Rt Hon. Ernest Brown | Liberal National |
| Leominster | Ernest Shepperson | Conservative |
| Lewes | Hon. John Loder | Conservative |
| Lewisham East | Sir Assheton Pownall | Conservative |
| Lewisham West | Sir Philip Dawson | Conservative |
| Leyton East | Sir Frederick Mills, Bt | Conservative |
| Leyton West | Reginald Sorensen | Labour |
| Lichfield | James Lovat-Fraser | National Labour |
| Lincoln | Walter Liddall | Conservative |
| Linlithgowshire | George Mathers | Labour |
| Liverpool East Toxteth | Patrick Buchan-Hepburn | Conservative |
| Liverpool Edge Hill | Alexander Critchley | Conservative |
| Liverpool Everton | Bertie Kirby | Labour |
| Liverpool Exchange | Sir John Shute | Conservative |
| Liverpool Fairfield | Sir Edmund Brocklebank | Conservative |
| Liverpool Kirkdale | Robert Rankin | Conservative |
| Liverpool Scotland | David Logan | Labour |
| Liverpool Walton | Reginald Purbrick | Conservative |
| Liverpool Wavertree | Peter Stapleton Shaw | Conservative |
| Liverpool West Derby | David Maxwell Fyfe | Conservative |
| Liverpool West Toxteth | Joseph Gibbins | Labour |
| Llandaff and Barry | Patrick Munro | Conservative |
| Llanelli | John Henry Williams | Labour |
| London University | Sir Ernest Graham-Little | National |
| Londonderry | Sir Ronald Ross | Ulster Unionist |
| Lonsdale | David Lindsay | Conservative |
| Loughborough | Lawrence Kimball | Conservative |
| Louth | Arthur Heneage | Conservative |
| Lowestoft | Pierse Loftus | Conservative |
| Ludlow | George Windsor-Clive | Conservative |
| Luton | Leslie Burgin | Liberal National |
|
| Macclesfield | John Remer | Conservative |
| Maidstone | Alfred Bossom | Conservative |
| Maldon | Sir Edward Ruggles-Brise, Bt | Conservative |
| Manchester Ardwick | Joseph Henderson | Labour |
| Manchester Blackley | John Lees-Jones | Conservative |
| Manchester Clayton | John Jagger | Labour |
| Manchester Exchange | Peter Eckersley | Conservative |
| Manchester Gorton | Joseph Compton | Labour |
| Manchester Hulme | Joseph Nall | Conservative |
| Manchester Moss Side | William Duckworth | Conservative |
| Manchester Platting | Rt Hon. J. R. Clynes | Labour |
| Manchester Rusholme | Edmund Radford | Conservative |
| Manchester Withington | Edward Fleming | Conservative |
| Mansfield | Charles Brown | Labour |
| Melton | Lindsay Everard | Conservative |
| Merioneth | Sir Henry Haydn Jones | Liberal |
| Merthyr | S. O. Davies | Labour |
| Middlesbrough East | Alfred Edwards | Labour |
| Middlesbrough West | Frank Kingsley Griffith | Liberal |
| Middleton and Prestwich | Sir Nairne Stewart Sandeman, Bt | Conservative |
| Midlothian North | John Colville | Conservative |
| Midlothian South and Peebles | Archibald Maule Ramsay | Conservative |
| Mitcham | Sir Richard Meller | Conservative |
| Monmouth | John Herbert | Conservative |
| Montgomeryshire | Clement Davies | Liberal National |
| Montrose | Charles Kerr | Liberal National |
| Moray & Nairn | Hon. James Stuart | Conservative |
| Morpeth | Robert Taylor | Labour |
| Mossley | Austin Hopkinson | National |
| Motherwell | James Walker | Labour |
|
| Neath | Sir William Jenkins | Labour |
| Nelson and Colne | Sydney Silverman | Labour |
| Newark | The Marquess of Titchfield | Conservative |
| Newbury | Howard Clifton Brown | Conservative |
| Newcastle-under-Lyme | Rt Hon. Josiah Wedgwood | Labour |
| Newcastle-upon-Tyne Central | Alfred Denville | Conservative |
| Newcastle-upon-Tyne East | Sir Robert Aske, Bt | Liberal National |
| Newcastle-upon-Tyne North | Sir Nicholas Grattan-Doyle | Conservative |
| Newcastle-upon-Tyne West | Sir Joseph Leech | Conservative |
| New Forest and Christchurch | John Mills | Conservative |
| Newport | Sir Reginald Clarry | Conservative |
| Newton | Sir Robert Young | Labour |
| Norfolk East | Viscount Elmley | Liberal National |
| Norfolk North | Sir Thomas Cook | Conservative |
| Norfolk South | James Christie | Conservative |
| Norfolk South West | Somerset de Chair | Conservative |
| Normanton | Tom Smith | Labour |
| Northampton | Sir Mervyn Manningham-Buller, Bt | Conservative |
| Northwich | Lord Colum Crichton-Stuart | Conservative |
Norwich
(two members) | Geoffrey Shakespeare | Liberal National |
| Henry Strauss | Conservative |
| Norwood | Duncan Sandys | Conservative |
| Nottingham Central | Sir Terence O'Connor | Conservative |
| Nottingham East | Louis Gluckstein | Conservative |
| Nottingham South | Frank Markham | National Labour |
| Nottingham West | Arthur Hayday | Labour |
| Nuneaton | Reginald Fletcher | Labour |
|
| Ogmore | Edward Williams | Labour |
Oldham
(two members) | John Dodd | Liberal National |
| Hamilton Kerr | Conservative |
| Orkney and Shetland | Basil Neven-Spence | Conservative |
| Ormskirk | Samuel Rosbotham | National Labour |
| Oswestry | Bertie Leighton | Conservative |
| Oxford | Rt Hon. Robert Bourne | Conservative |
Oxford University
(two members) | A. P. Herbert | Independent |
| Rt Hon. Lord Hugh Cecil | Conservative |
|
| Paddington North | Brendan Bracken | Conservative |
| Paddington South | Ernest Taylor | Conservative |
| Paisley | Hon. Joseph Maclay | Liberal |
| Peckham | Viscount Borodale | Conservative |
| Pembrokeshire | Gwilym Lloyd George | Independent Liberal |
| Penistone | Henry McGhee | Labour |
| Penrith and Cockermouth | Alan Gandar-Dower | Conservative |
| Penryn and Falmouth | Maurice Petherick | Conservative |
| Perth | Thomas Hunter | Conservative |
| Peterborough | Lord Burghley | Conservative |
| Petersfield | Sir Reginald Dorman-Smith | Conservative |
| Plymouth Devonport | Rt Hon. Leslie Hore-Belisha | Liberal National |
| Plymouth Drake | Rt Hon. Frederick Guest | Conservative |
| Plymouth Sutton | Nancy Astor | Conservative |
| Pontefract | Adam Hills | Labour |
| Pontypool | Arthur Jenkins | Labour |
| Pontypridd | David Lewis Davies | Labour |
| Poplar South | David Morgan Adams | Labour |
| Portsmouth Central | Hon. Ralph Beaumont | Conservative |
| Portsmouth North | Sir Roger Keyes, Bt | Conservative |
| Portsmouth South | Sir Herbert Cayzer, Bt | Conservative |
Preston
(two members) | William Kirkpatrick | Conservative |
| Adrian Moreing | Conservative |
| Pudsey and Otley | Sir Granville Gibson | Conservative |
| Putney | Marcus Samuel | Conservative |
|
| Queen's University of Belfast | Thomas Sinclair | Ulster Unionist |
|
| Reading | Alfred Howitt | Conservative |
| Reigate | Gordon Touche | Conservative |
| Renfrewshire, East | Douglas Douglas-Hamilton | Conservative |
| Renfrewshire, West | Henry Scrymgeour-Wedderburn | Conservative |
| Rhondda East | William Mainwaring | Labour |
| Rhondda West | William John | Labour |
| Richmond (Yorks) | Thomas Dugdale | Conservative |
| Richmond upon Thames | William Ray | Conservative |
| Ripon | John Hills | Conservative |
| Rochdale | William Kelly | Labour |
| Romford | John Parker | Labour |
| Ross and Cromarty | The Rt Hon. Sir Ian Macpherson, Bt | Liberal National |
| Rossendale | Ronald Cross | Conservative |
| Rotherham | William Dobbie | Labour |
| Rotherhithe | Ben Smith | Labour |
| Rother Valley | Edward Dunn | Labour |
| Rothwell | William Lunn | Labour |
| Roxburgh and Selkirk | Lord William Montagu-Douglas-Scott | Conservative |
| Royton | Harold Sutcliffe | Conservative |
| Rugby | Rt Hon. David Margesson | Conservative |
| Rushcliffe | Ralph Assheton | Conservative |
| Rutherglen | Allan Chapman | Conservative |
| Rutland and Stamford | Lord Willoughby de Eresby | Conservative |
| Rye | Sir George Courthope, Bt | Conservative |
|
| Saffron Walden | Rab Butler | Conservative |
| St Albans | Sir Francis Fremantle | Conservative |
| St Helens | William Albert Robinson | Labour |
| St Ives | Rt Hon. Walter Runciman | Liberal National |
| St Marylebone | Alec Cunningham-Reid | Conservative |
| St Pancras North | Ian Fraser | Conservative |
| St Pancras South East | Sir Alfred Beit, Bt | Conservative |
| St Pancras South West | Sir George Mitcheson | Conservative |
| Salford North | John Patrick Morris | Conservative |
| Salford South | Hon. John Stourton | Conservative |
| Salford West | James Frederick Emery | Conservative |
| Salisbury | James Despencer-Robertson | Conservative |
| Scarborough and Whitby | Sir Paul Latham, Bt | Conservative |
| Seaham | Manny Shinwell | Labour |
| Sedgefield | John Leslie | Labour |
| Sevenoaks | Charles Ponsonby | Conservative |
| Sheffield, Attercliffe | Cecil Wilson | Labour |
| Sheffield, Brightside | Fred Marshall | Labour |
| Sheffield, Central | William Boulton | Conservative |
| Sheffield, Ecclesall | Sir Robert Ellis, Bt | Conservative |
| Sheffield, Hallam | Sir Louis Smith | Conservative |
| Sheffield, Hillsborough | Rt Hon. A. V. Alexander | Labour Co-op |
| Sheffield, Park | George Lathan | Labour |
| Shipley | Arthur Creech Jones | Labour |
| Shoreditch | Ernest Thurtle | Labour |
| Shrewsbury | Arthur Duckworth | Conservative |
| Skipton | George Rickards | Conservative |
| Smethwick | Roy Wise | Conservative |
Southampton
(two members) | William Craven-Ellis | Conservative |
| Sir Charles Barrie | Liberal National |
| Southend-on-Sea | Henry Channon | Conservative |
| South Molton | Rt Hon. George Lambert | Liberal National |
| Southport | Robert Hudson | Conservative |
| South Shields | James Chuter Ede | Labour |
| Southwark Central | Harry Day | Labour |
| Southwark North | Edward Strauss | Liberal National |
| Southwark South East | Thomas Naylor | Labour |
| Sowerby | Malcolm McCorquodale | Conservative |
| Spelthorne | Sir Reginald Blaker, Bt | Conservative |
| Spennymoor | Joseph Batey | Labour |
| Spen Valley | Rt. Hon. Sir John Simon | Liberal National |
| Stafford | Rt Hon. William Ormsby-Gore | Conservative |
| Stalybridge and Hyde | Philip Dunne | Conservative |
| Stepney Limehouse | Rt. Hon. Clement Attlee | Labour |
| Stepney Mile End | Daniel Frankel | Labour |
| Stirling and Falkirk | Joseph Westwood | Labour |
| Stirlingshire East and Clackmannan | MacNeill Weir | Labour |
| Stirlingshire West | Rt Hon. Tom Johnston | Labour |
Stockport
(two members) | Sir Arnold Gridley | Conservative |
| Norman Hulbert | Conservative |
| Stockton on Tees | Harold Macmillan | Conservative |
| Stoke Newington | Sir George Jones | Conservative |
| Stoke-on-Trent | Ellis Smith | Labour |
| Stone | Joseph Lamb | Conservative |
| Stourbridge | Robert Morgan | Conservative |
| Streatham | Sir William Lane-Mitchell | Conservative |
| Stretford | Anthony Crossley | Conservative |
| Stroud | Walter Perkins | Conservative |
| Sudbury | The Rt Hon. Henry Burton | Conservative |
Sunderland
(two members) | Stephen Furness | Liberal National |
| Samuel Storey | Conservative |
| Surrey East | Charles Emmott | Conservative |
| Swansea East | David Williams | Labour |
| Swansea West | Lewis Jones | Liberal National |
| Swindon | Wavell Wakefield | Conservative |
|
| Tamworth | Sir John Mellor, Bt | Conservative |
| Taunton | Edward Wickham | Conservative |
| Tavistock | Colin Patrick | Conservative |
| Thirsk and Malton | Robin Turton | Conservative |
| Thornbury | Derrick Gunston | Conservative |
| Tiverton | Gilbert Acland-Troyte | Conservative |
| Tonbridge | Rt Hon. Herbert Spender-Clay | Conservative |
| Torquay | Charles Williams | Conservative |
| Totnes | Ralph Rayner | Conservative |
| Tottenham North | Robert Morrison | Labour Co-op |
| Tottenham South | Fred Messer | Labour |
| Twickenham | Edward Keeling | Conservative |
| Tynemouth | Sir Alexander Russell | Conservative |
|
| University of Wales | Ernest Evans | Liberal |
| Uxbridge | John Llewellin | Conservative |
|
| Wakefield | Rt. Hon. Arthur Greenwood | Labour |
| Wallasey | John Moore-Brabazon | Conservative |
| Wallsend | Irene Ward | Conservative |
| Walsall | Joseph Leckie | Liberal National |
| Walthamstow East | Sir Brograve Beauchamp, Bt | Conservative |
| Walthamstow West | Valentine McEntee | Labour |
| Wandsworth Central | Sir Henry Jackson, Bt | Conservative |
| Wansbeck | Bernard Cruddas | Conservative |
| Warrington | Noel Goldie | Conservative |
| Warwick and Leamington | Rt Hon. Anthony Eden | Conservative |
| Waterloo | Malcolm Bullock | Conservative |
| Watford | Rt Hon. Sir Dennis Herbert | Conservative |
| Wednesbury | John Banfield | Labour |
| Wellingborough | Archibald James | Conservative |
| Wells | Anthony Muirhead | Conservative |
| Wentworth | Wilfred Paling | Labour |
| West Bromwich | Rt Hon. Frederick Roberts | Labour |
| Westbury | Robert Grimston | Conservative |
| Western Isles | Malcolm Macmillan | Labour |
| West Ham Plaistow | Will Thorne | Labour |
| West Ham Silvertown | Jack Jones | Labour |
| West Ham Stratford | Thomas Groves | Labour |
| West Ham Upton | Benjamin Gardner | Labour |
| Westhoughton | Rhys Davies | Labour |
| Westminster Abbey | Sidney Herbert | Conservative |
| Westminster St George's | Duff Cooper | Conservative |
| Westmorland | Rt Hon. Oliver Stanley | Conservative |
| Weston-super-Mare | Ian Orr-Ewing | Conservative |
| Whitechapel & St Georges | J. H. Hall | Labour |
| Whitehaven | Frank Anderson | Labour |
| Widnes | Richard Pilkington | Conservative |
| Wigan | John Parkinson | Labour |
| Willesden East | Daniel Somerville | Conservative |
| Willesden West | Samuel Viant | Labour |
| Wimbledon | Sir John Power, Bt | Conservative |
| Winchester | Gerald Palmer | Conservative |
| Windsor | Annesley Somerville | Conservative |
| Wirral | Alan Graham | Conservative |
| Wolverhampton Bilston | Ian Hannah | Conservative |
| Wolverhampton East | Geoffrey Mander | Liberal |
| Wolverhampton West | Sir Robert Bird, Bt | Conservative |
| Woodbridge | Walter Ross-Taylor | Conservative |
| Wood Green | Beverley Baxter | Conservative |
| Woolwich East | George Hicks | Labour |
| Woolwich West | Rt Hon. Sir Kingsley Wood | Conservative |
| Worcester | Crawford Greene | Conservative |
| Workington | Tom Cape | Labour |
| The Wrekin | James Baldwin-Webb | Conservative |
| Wrexham | Robert Richards | Labour |
| Wycombe | Sir Alfred Knox | Conservative |
|
| Yeovil | George Davies | Conservative |
| York | Roger Lumley | Conservative |