
Benzylpiperazine (BZP) is a recreational drug with euphoriant and stimulant properties. The effects produced by BZP are comparable to those produced by amphetamine. Adverse effects have been reported following its use including acute psychosis, renal toxicity and seizures. Deaths from piperazine derivatives are extremely rare, but there has been at least one death apparently due to BZP alone. Its sale is banned in several countries, including Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United States, the Republic of Ireland, the United Kingdom, Bulgaria, Romania and other parts of Europe.
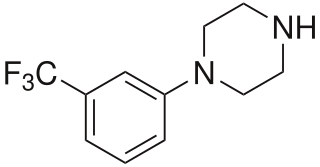
3-Trifluoromethylphenylpiperazine (TFMPP) is a recreational drug of the phenylpiperazine chemical class and is a substituted piperazine. Usually in combination with benzylpiperazine (BZP) and other analogues, it is sold as an alternative to the illicit drug MDMA ("Ecstasy").

Piperazine is an organic compound that consists of a six-membered ring containing two nitrogen atoms at opposite positions in the ring. Piperazine exists as small alkaline deliquescent crystals with a saline taste.

Oxatomide, sold under the brand name Tinset among others, is a first-generation antihistamine of the diphenylmethylpiperazine family which is marketed in Europe, Japan, and a number of other countries. It was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1975. Oxatomide lacks any anticholinergic effects. In addition to its H1 receptor antagonism, it also possesses antiserotonergic activity similarly to hydroxyzine.

meta-Chlorophenylpiperazine (mCPP) is a psychoactive drug of the phenylpiperazine class. It was initially developed in the late-1970s and used in scientific research before being sold as a designer drug in the mid-2000s. It has been detected in pills touted as legal alternatives to illicit stimulants in New Zealand and pills sold as "ecstasy" in Europe and the United States.

para-Methoxyphenylpiperazine is a piperazine derivative with stimulant effects which has been sold as an ingredient in "Party pills", initially in New Zealand and subsequently in other countries around the world.

para-Fluorophenylpiperazine is a piperazine derivative with mildly psychedelic and euphoriant effects. It has been sold as an ingredient in legal recreational drugs known as "Party pills", initially in New Zealand and subsequently in other countries around the world.
Fipexide is a psychoactive drug of the piperazine chemical class which was developed in Italy in 1983. It was used as a nootropic drug in Italy and France, mainly for the treatment of senile dementia, but is no longer in common use due to the occurrence of rare adverse drug reactions including fever and hepatitis. Fipexide is similar in action to other nootropic drugs such as piracetam and has a few similarities in chemical structure to centrophenoxine. Chemically, it is an amide union of parachlorophenoxyacetate and methylenedioxybenzylpiperazine (MDBZP), and has been shown to metabolize to the latter, which plays a significant role in its effects.

Piberaline is a psychoactive drug and member of the piperazine chemical class which was developed in the 1980s. It has stimulant and antidepressant effects which are thought to be due largely to its active metabolite benzylpiperazine. It was researched to a limited extent in Hungary and Spain, but was not widely accepted and does not seem to be in current use, although a closely related drug befuraline with similar effects has been slightly more successful.

Methylbenzylpiperazine is a stimulant drug which is a derivative of benzylpiperazine. MBZP has been sold as an ingredient in legal recreational drugs known as "party pills", initially in New Zealand and subsequently in other countries around the world.
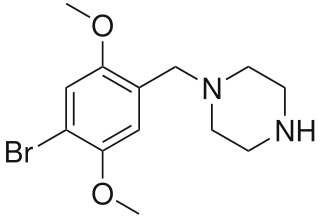
4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxy-1-benzylpiperazine (2C-B-BZP) is a psychoactive drug and research chemical of the piperazine chemical class which has been sold as a "designer drug". It produces stimulant effects similar to those of benzylpiperazine (BZP).

1-(3,4-Methylenedioxybenzyl)piperazine is a chemical compound of the piperazine chemical class related to benzylpiperazine (BZP). MDBZP has been sold as a designer drug and has even been found as an ingredient in street Ecstasy pills.

Clocinizine is a first-generation antihistamine of the diphenylmethylpiperazine class. It is marketed in Spain in combination with phenylpropanolamine under the brand name Senioral.

para-Chlorophenylpiperazine (pCPP) is a psychoactive drug of the phenylpiperazine class. It is relatively obscure, with limited human use, and produces slightly psychedelic effects. It has been encountered in illicit capsules as a recreational drug similarly to other piperazines like mCPP. Scientific research has demonstrated pCPP to have serotonergic effects, likely acting as a non-selective serotonin receptor agonist and/or releasing agent.
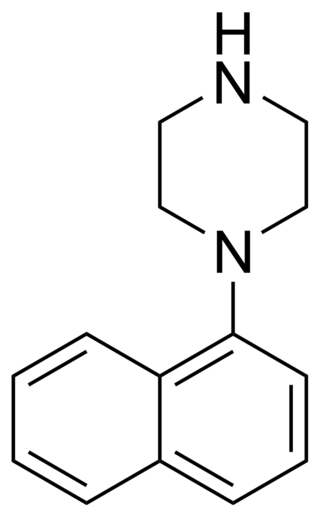
1-(1-Naphthyl)piperazine (1-NP) is a drug which is a phenylpiperazine derivative. It acts as a non-selective, mixed serotonergic agent, exerting partial agonism at the 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, 5-HT1E, and 5-HT1F receptors, while antagonizing the 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptors. It has also been shown to possess high affinity for the 5-HT3, 5-HT5A, 5-HT6, and 5-HT7 receptors, and may bind to 5-HT4 and the SERT as well. In animals it produces effects including hyperphagia, hyperactivity, and anxiolysis, of which are all likely mediated predominantly or fully by blockade of the 5-HT2C receptor.

MT-45 (IC-6) is an opioid analgesic drug invented in the 1970s by Dainippon Pharmaceutical Co. It is chemically a 1-substituted-4-(1,2-diphenylethyl)piperazine derivative, which is structurally unrelated to most other opioid drugs. Racemic MT-45 has around 80% the potency of morphine, with almost all opioid activity residing in the (S) enantiomer. It has been used as a lead compound from which a large family of potent opioid drugs have been developed, including full agonists, partial agonists, and antagonists at the three main opioid receptor subtypes. Fluorinated derivatives of MT-45 such as 2F-MT-45 are significantly more potent as μ-opioid receptor agonists, and one of its main metabolites 1,2-diphenylethylpiperazine also blocks NMDA receptors.

1-(3-Chlorophenyl)-4-(2-phenylethyl)piperazine (3C-PEP) is a designer drug of the piperazine class of chemical substances. 3C-PEP is related to meta-cholorophenylpiperazine (mCPP) and phenethylamine that can be thought of as mCPP having a phenylethyl group attached to the nitrogen atom at its 4-position. It was first described in 1994 in a patent disclosing a series of piperazine compounds as sigma receptor ligands. Later, it was discovered to be a highly potent dopamine reuptake inhibitor.
Substituted piperazines are a class of chemical compounds based on a piperazine core. Some are used as recreational drugs and some are used in scientific research.

Diphenpipenol is an opioid analgesic drug invented in the 1970s by Dainippon Pharmaceutical Co. It is chemically a 1-substituted-4-(1,2-diphenylethyl)piperazine derivative related to compounds such as MT-45 and AD-1211, but diphenpipenol is the most potent compound in the series, with the more active (S) enantiomer being around 105 times the potency of morphine in animal studies. This makes it a similar strength to fentanyl and its analogues, and consequently diphenpipenol can be expected to pose a significant risk of producing life-threatening respiratory depression, as well as other typical opioid side effects such as sedation, itching, nausea and vomiting.

CPD-1 (LS-193743) is a drug with a benzofuranyl piperazine structure, which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the 5-HT2 receptor family, with highest affinity and full agonist efficacy at the 5-HT2C subtype, and lower affinity and partial agonist action at the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B subtypes.


















