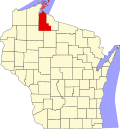
La Pointe County, Wisconsin | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Wisconsin |
La Pointe County was created on February 19, 1845, by the Territory of Wisconsin [1] [2] from the northern portion of the existing territorial St. Croix County, encompassing the remaining portions of the Northwest Territory in Wisconsin Territory north of the line drawn from the confluence of the Ripple River with the Mississippi River (today, near Aitkin, Minnesota) to the western edge of Lac Courte Oreilles, to the eastern edge of Lac Courte Oreilles, and to the western branch of the Montreal River. The county was named for the community of La Pointe, Wisconsin on Madeline Island, which was its county seat from 1858 until 1866.
When Wisconsin achieved statehood on May 29, 1848, La Pointe County was divided between the present day Minnesota and Wisconsin. That portion of the Wisconsin Territory's La Pointe County between the Mississippi and St. Croix Rivers became 'de facto Wisconsin Territory' [3] [4] [5] until it was incorporated, along with unorganized federal land north of Iowa, in the creation of the Minnesota Territory on March 3, 1849. [6] Itasca, Washington, Ramsey, and Benton Counties were created by the Minnesota Territory on October 27, 1849 [7] from the de facto Wisconsin Territory that had been separated from the Wisconsin Territory's La Pointe County.
The remainder of La Pointe County became part of Wisconsin and portions of it later became the parent county to Douglas (1854) and Ashland (1860) Counties. With La Pointe itself now in Ashland County, La Pointe County was renamed Bayfield County effective May 1, 1866, returning the county seat to Bayfield. [8]