
Dosulepin, also known as dothiepin and sold under the brand name Prothiaden among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) which is used in the treatment of depression. Dosulepin was once the most frequently prescribed antidepressant in the United Kingdom, but it is no longer widely used due to its relatively high toxicity in overdose without therapeutic advantages over other TCAs. It acts as a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) and also has other activities including antihistamine, antiadrenergic, antiserotonergic, anticholinergic, and sodium channel-blocking effects.

Dipivefrine, or dipivefrin, also known as epinephrine pivalate and sold under the brand name Propine among others, is a sympathomimetic medication which is used in the treatment of open-angle glaucoma. It is available as a 0.1% ophthalmic solution.
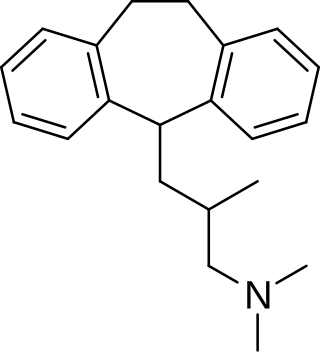
Butriptyline, sold under the brand name Evadyne among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) that has been used in the United Kingdom and several other European countries for the treatment of depression but appears to no longer be marketed. Along with trimipramine, iprindole, and amoxapine, it has been described as an "atypical" or "second-generation" TCA due to its relatively late introduction and atypical pharmacology. It was very little-used compared to other TCAs, with the number of prescriptions dispensed only in the thousands.

Methoxamine, sold under the brand names Vasoxine, Vasoxyl, and Vasylox among others, is a sympathomimetic medication used as an antihypotensive agent. It has mostly or entirely been discontinued.

Bromazine, sold under the brand names Ambodryl, Ambrodil, and Deserol among others, also known as bromodiphenhydramine, is an antihistamine and anticholinergic medication of the ethanolamine class. It is an analogue of diphenhydramine with a bromine substitution on one of the phenyl rings.

Etafedrine, sold under the brand name Nethaprin among others and also known as N-ethylephedrine, is a sympathomimetic agent used as a bronchodilator to treat asthma. It was previously commercially available as both the free base and as the hydrochloride salt from Sanofi-Aventis but is now no longer marketed.

Ditran (JB-329) is an anticholinergic drug mixture, related to the chemical warfare agent 3-Quinuclidinyl benzilate (QNB).
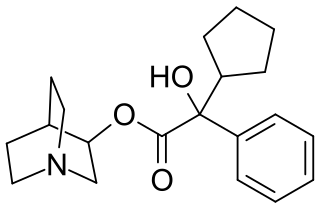
EA-3167 is a potent and long-lasting anticholinergic deliriant drug, related to the chemical warfare agent 3-quinuclidinyl benzilate (QNB) and to the bronchodilator drug tiotropium bromide. It was developed under contract to Edgewood Arsenal during the 1960s as part of the US military chemical weapons program, in an attempt to develop non-lethal incapacitating agents. EA-3167 has identical effects to QNB, but is even more potent and longer-lasting, with an effective dose when administered by injection of as little as 2.5 μg/kg, and a duration of 120–240 hours. However unlike QNB, EA-3167 was never weaponized or manufactured in bulk.

Iproheptine, sold under the brand names Metron and Susat, is a nasal decongestant which has been marketed in Japan. It is described as a vasoconstrictor and antihistamine. The drug is available over-the-counter in Japan.
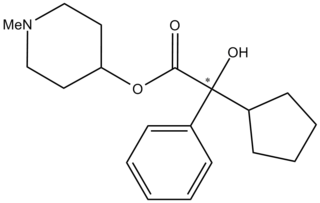
EA-3443 is a potent and long lasting anticholinergic deliriant drug, related to the chemical warfare agent 3-Quinuclidinyl benzilate (QNB). It was developed under contract to Edgewood Arsenal during the 1960s as part of the US military chemical weapons program, during research to improve upon the properties of earlier agents such as QNB.

CAR-302,196 is a moderately potent and relatively short lasting anticholinergic deliriant drug, related to the chemical warfare agent 3-Quinuclidinyl benzilate (QNB). It was developed under contract to Edgewood Arsenal during the 1960s as part of the US military chemical weapons program, during research to improve upon the properties of earlier agents such as QNB.
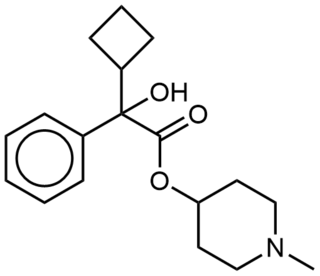
EA-3580 is a potent anticholinergic deliriant drug with a fairly long duration of action, related to the chemical warfare agent 3-Quinuclidinyl benzilate (QNB). It was developed under contract to Edgewood Arsenal during the 1960s as part of the US military chemical weapons program, during research to improve upon the properties of earlier agents such as QNB.

Azacosterol, or azacosterol hydrochloride, also known as 20,25-diazacholesterol, is a cholesterol-lowering drug (hypocholesteremic), which was marketed previously, but has since been discontinued. It is also an avian chemosterilant used to control pest pigeon populations via inducing sterility. The drug is a sterol and derivative of cholesterol in which two carbon atoms have been replaced with nitrogen atoms.

Racepinefrine, or racepinephrine, sold under the brand name Vaponefrin among others, is a sympathomimetic medication described as a vasoconstrictor, bronchodilator, cardiostimulant, mydriatic, and antiglaucoma agent. It is the racemic form of epinephrine (adrenaline) and is also known as dl-epinephrine and (±)-epinephrine. The drug is used pharmaceutically as the hydrochloride salt. It has been marketed in the United States and Canada.

Ampyzine, also known as dimethylaminopyrazine or as ampyzine sulfate in the case of the sulfate salt, is a drug described as a "central stimulant" or "CNS stimulant" and "euphoriant". It is said to be a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). Ampyzine was first described in the scientific literature by 1960.

Somantadine, or somantadine hydrochloride in the case of the hydrochloride salt, is an experimental antiviral drug of the adamantane family related to amantadine and rimantadine that was never marketed. It was first described by 1978.

Bufenadrine, also known as 2-tert-butyldiphenhydramine, is a drug described as an antiemetic, antihistamine, anticholinergic, and antiparkinsonian agent which was never marketed. It is the 2-tert-butyl analogue of diphenhydramine. The drug was found to produce stereoselective hepatotoxicity in animals and this led to the discontinuation of its development. Bufenadrine was first described in the literature by 1967. Its INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name suffix "-drine" is generally for sympathomimetics but bufenadrine itself is not actually a sympathomimetic or related agent.

Soterenol, also known as soterenol hydrochloride in the case of the hydrochloride salt, is a drug of the phenethylamine family described as an adrenergic, bronchodilator, and antiasthmatic which was never marketed. It is an analogue of salbutamol and acts as a β-adrenergic receptor agonist. The drug was first developed in 1964 and was first described in the literature by 1967.

Clorprenaline, also known as isoprophenamine and known as clorprenaline hydrochloride in the case of the hydrochloride salt, is a sympathomimetic and bronchodilator medication which is marketed in Japan. It acts as a β-adrenergic receptor agonist or as a β-sympathomimetic. Brand names of clorprenaline in Japan are numerous and include Asnormal, Bazarl, Bronchon, Clopinerin, Conselt, Cosmoline, Fusca, Kalutein, Pentadoll, Restanolon, and Troberin. The drug was first described in the literature by 1956.

Triampyzine, also known as triampyzine sulfate in the case of the sulfate salt, as (dimethylamino)trimethylpyrazine, or as 3,5,6-trimethylampyzine, is a drug described as an anticholinergic and antisecretory agent which was never marketed. It was first described in the literature by 1966. The drug is the 3,5,6-trimethylated derivative of ampyzine (W-3580B), which is also a drug and is, conversely, described as a "central stimulant".




















