Related Research Articles
Cartography is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.

A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes.

Anishinaabe traditional beliefs cover the traditional belief system of the Anishinaabeg peoples, consisting of the Algonquin/Nipissing, Ojibwa/Chippewa/Saulteaux/Mississaugas, Odawa, Potawatomi and Oji-Cree, located primarily in the Great Lakes region of North America.
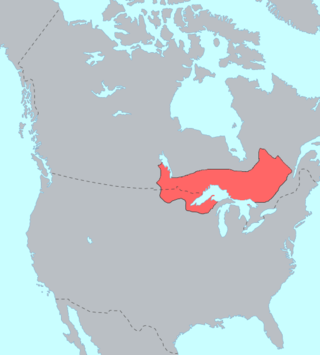
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains. They are Indigenous peoples of the Subarctic and Northeastern Woodlands.

The Red Lake Indian Reservation covers 1,260.3 sq mi in parts of nine counties in Minnesota, United States.

The Anishinaabe are a group of culturally related Indigenous peoples present in the Great Lakes region of Canada and the United States. They include the Ojibwe, Odawa, Potawatomi, Mississaugas, Nipissing and Algonquin peoples. The Anishinaabe speak Anishinaabemowin, or Anishinaabe languages that belong to the Algonquian language family.
Animated mapping is the application of animation, either a computer or video, to add a temporal component to a map displaying change in some dimension. Most commonly the change is shown over time, generally at a greatly changed scale. An example would be the animation produced after the 2004 tsunami showing how the waves spread across the Indian Ocean.
Native American studies is an interdisciplinary academic field that examines the history, culture, politics, issues, spirituality, sociology and contemporary experience of Native peoples in North America, or, taking a hemispheric approach, the Americas. Increasingly, debate has focused on the differences rather than the similarities between other Ethnic studies disciplines such as African American studies, Asian American Studies, and Latino/a Studies.

A wiigwaasabak is a birch bark scroll, on which the Ojibwa (Anishinaabe) people of North America wrote with a written language composed of complex geometrical patterns and shapes.

A thematic map is a type of map that portrays the geographic pattern of a particular subject matter (theme) in a geographic area. This usually involves the use of map symbols to visualize selected properties of geographic features that are not naturally visible, such as temperature, language, or population. In this, they contrast with general reference maps, which focus on the location of a diverse set of physical features, such as rivers, roads, and buildings. Alternative names have been suggested for this class, such as special-subject or special-purpose maps, statistical maps, or distribution maps, but these have generally fallen out of common usage. Thematic mapping is closely allied with the field of Geovisualization.

Red Cliff Band of Lake Superior Chippewa is a band of Ojibwe Native Americans. The Red Cliff Band is located on the Red Cliff Indian Reservation, on Lake Superior in Bayfield County, Wisconsin. Red Cliff, Wisconsin, is the administrative center. Red Cliff is notable for being the band closest to the spiritual center of the Ojibwe nation, Madeline Island. As of November 2010, there were 5,312 enrolled members, with about half living on the reservation and the rest living in the city of Bayfield or the Belanger Settlement.
The history of cartography refers to the development and consequences of cartography, or mapmaking technology, throughout human history. Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowing humans to explain and navigate their way through the world.
Indigenous decolonization describes ongoing theoretical and political processes whose goal is to contest and reframe narratives about indigenous community histories and the effects of colonial expansion, cultural assimilation, exploitative Western research, and often though not inherent, genocide. Indigenous people engaged in decolonization work adopt a critical stance towards western-centric research practices and discourse and seek to reposition knowledge within Indigenous cultural practices.
Traditional knowledge geographic information systems (GIS) are the data, techniques, and technologies designed to document and utilize local knowledges in communities around the world. Traditional knowledge is information that encompasses the experiences of a particular culture or society. Traditional knowledge GIS differ from ordinary cognitive maps in that they express environmental and spiritual relationships among real and conceptual entities. This toolset focuses on cultural preservation, land rights disputes, natural resource management, and economic development.
Critical cartography is a set of mapping practices and methods of analysis grounded in critical theory, specifically the thesis that maps reflect and perpetuate relations of power, typically in favor of a society's dominant group. Critical cartographers aim to reveal the “‘hidden agendas of cartography’ as tools of socio-spatial power”. While the term "critical cartography" often refers to a body of theoretical literature, critical cartographers also call for practical applications of critical cartographic theory, such as counter-mapping, participatory mapping, and neogeography.

The British Cartographic Society (BCS) is an association of individuals and organisations dedicated to exploring and developing the world of maps. It is a registered charity. Membership includes national mapping agencies, publishers, designers, academics, researchers, map curators, individual cartographers, GIS specialists and ordinary members of the public with an interest in maps.
Counter-mapping is creating maps that challenge "dominant power structures, to further seemingly progressive goals". Counter-mapping is used in multiple disciplines to reclaim colonized territory. Counter-maps are prolific in indigenous cultures, "counter-mapping may reify, reinforce, and extend settler boundaries even as it seeks to challenge dominant mapping practices; and still, counter-mapping may simultaneously create conditions of possibility for decolonial ways of representing space and place." The term came into use in the United States when Nancy Peluso used it in 1995 to describe the commissioning of maps by forest users in Kalimantan, Indonesia, to contest government maps of forest areas that undermined indigenous interests. The resultant counter-hegemonic maps strengthen forest users' resource claims. There are numerous expressions closely related to counter-mapping: ethnocartography, alternative cartography, mapping-back, counter-hegemonic mapping, deep mapping and public participatory mapping. Moreover, the terms: critical cartography, subversive cartography, bio-regional mapping, and remapping are sometimes used interchangeably with counter-mapping, but in practice encompass much more.

Web GIS, or Web Geographic Information Systems, are GIS that employ the World Wide Web to facilitate the storage, visualization, analysis, and distribution of spatial information over the Internet. The World Wide Web, or the Web, is an information system that uses the internet to host, share, and distribute documents, images, and other data. Web GIS involves using the World Wide Web to facilitate GIS tasks traditionally done on a desktop computer, as well as enabling the sharing of maps and spatial data. While Web GIS and Internet GIS are sometimes used interchangeably, they are different concepts. Web GIS is a subset of Internet GIS, which is itself a subset of distributed GIS, which itself is a subset of broader Geographic information system. The most common application of Web GIS is Web mapping, so much so that the two terms are often used interchangeably in much the same way as Digital mapping and GIS. However, Web GIS and web mapping are distinct concepts, with web mapping not necessarily requiring a Web GIS.
Indigenous resurgence is a transformative movement of resistance and decolonization. The practice of Indigenous resurgence is a form of regenerative nation-building and reconnection with all their relations. It constitutes kin-centric relationships among BIPOC peoples and with the natural world.
References
- ↑ "Decolonizing Digital: Empowering Indigeneity Through Data Sovereignty". Animikii.
- ↑ Sletto, Bjørn (1 April 2009). "Special issue: Indigenous cartographies". Cultural Geographies. 16 (2): 147–152. doi:10.1177/1474474008101514. S2CID 143473978 – via SAGE Journals.
- 1 2 "Indigenous cartographers work to decolonize mapping of traditional lands". Life at OSU. 26 October 2020. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ "Red Sky's Migration Chart: Ojibwe". The Decolonial Atlas. 18 May 2015. Retrieved 20 April 2022.