
The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin.

The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus.

The upper limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the shoulder, elbow, wrist and knuckle joints. In humans, each upper limb is divided into the arm, forearm and hand, and is primarily used for climbing, lifting and manipulating objects.

In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm.

The popliteal artery is a deeply placed continuation of the femoral artery opening in the distal portion of the adductor magnus muscle. It courses through the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it branches into the anterior and posterior tibial arteries.

The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial artery. It is palpable on the anterior and medial aspect of the wrist.

The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.

The posterior interosseous artery is an artery of the forearm. It is a branch of the common interosseous artery, which is a branch of the ulnar artery.

The lateral circumflex femoral artery is an artery in the upper thigh. It is usually a branch of the profunda femoris artery, and produces three branches. It is mostly distributed to the muscles of the lateral thigh, supplying arterial blood to muscles of the knee extensor group.

The deep artery of arm is a large artery of the arm which arises from the brachial artery. It descends in the arm before ending by anastomosing with the radial recurrent artery.
The cruciate anastomosis is a circulatory anastomosis in the upper thigh formed by the inferior gluteal artery, the lateral and medial circumflex femoral arteries, the first perforating artery of the deep femoral artery, and the anastomotic branch of the posterior branch of the obturator artery.
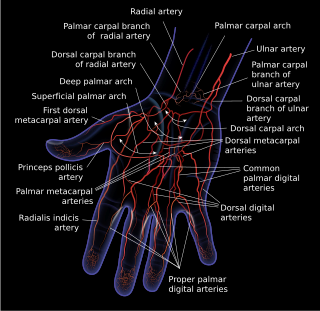
The dorsal carpal arch is an anatomical term for the combination (anastomosis) of dorsal carpal branch of the radial artery and the dorsal carpal branch of the ulnar artery near the back of the wrist.

The anterior interosseous nerve is a branch of the median nerve that supplies the deep muscles on the anterior of the forearm, except the ulnar (medial) half of the flexor digitorum profundus. Its nerve roots come from C8 and T1.

The patellar network is an intricate network of blood vessels around and above the patella, and on the contiguous ends of the femur and tibia, forming a superficial and a deep plexus.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The genicular arteries are six arteries in the human leg, five of which are branches of the popliteal artery, that anastomose in the knee region in the patellar network or genicular anastomosis. They supply blood to the patella, together with contributions from the descending genicular artery, anterior tibial recurrent artery, and descending branch of lateral circumflex femoral artery.











