
In probability theory and statistics, the binomial distribution with parameters n and p is the discrete probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of n independent experiments, each asking a yes–no question, and each with its own Boolean-valued outcome: success or failure. A single success/failure experiment is also called a Bernoulli trial or Bernoulli experiment, and a sequence of outcomes is called a Bernoulli process; for a single trial, i.e., n = 1, the binomial distribution is a Bernoulli distribution. The binomial distribution is the basis for the popular binomial test of statistical significance.

N,N-Dimethyltryptamine is a substituted tryptamine that occurs in many plants and animals, including humans, and which is both a derivative and a structural analog of tryptamine. DMT is used as a psychedelic drug and prepared by various cultures for ritual purposes as an entheogen.

The number e is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 2.71828 that is the base of the natural logarithm and exponential function. It is sometimes called Euler's number, after the Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler, though this can invite confusion with Euler numbers, or with Euler's constant, a different constant typically denoted . Alternatively, e can be called Napier's constant after John Napier. The Swiss mathematician Jacob Bernoulli discovered the constant while studying compound interest.

In mathematics, the Fibonacci sequence is a sequence in which each number is the sum of the two preceding ones. Numbers that are part of the Fibonacci sequence are known as Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted Fn . Many writers begin the sequence with 0 and 1, although some authors start it from 1 and 1 and some from 1 and 2. Starting from 0 and 1, the sequence begins

N, or n, is the fourteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages, and others worldwide. Its name in English is en, plural ens.
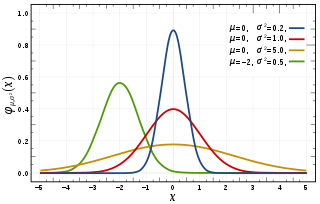
In probability theory and statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is The parameter is the mean or expectation of the distribution, while the parameter is the variance. The standard deviation of the distribution is (sigma). A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate.
The number π is a mathematical constant that is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, approximately equal to 3.14159. The number π appears in many formulae across mathematics and physics. It is an irrational number, meaning that it cannot be expressed exactly as a ratio of two integers, although fractions such as are commonly used to approximate it. Consequently, its decimal representation never ends, nor enters a permanently repeating pattern. It is a transcendental number, meaning that it cannot be a solution of an equation involving only finite sums, products, powers, and integers. The transcendence of π implies that it is impossible to solve the ancient challenge of squaring the circle with a compass and straightedge. The decimal digits of π appear to be randomly distributed, but no proof of this conjecture has been found.
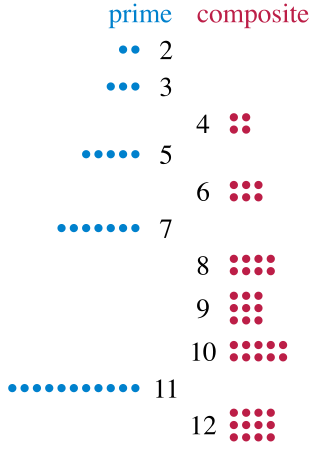
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, 1 × 5 or 5 × 1, involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product (2 × 2) in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order.
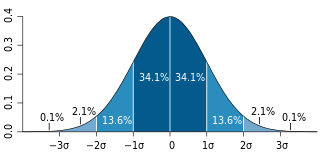
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation of the values of a variable about its mean. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range. The standard deviation is commonly used in the determination of what constitutes an outlier and what does not.

In mathematics, the Taylor series or Taylor expansion of a function is an infinite sum of terms that are expressed in terms of the function's derivatives at a single point. For most common functions, the function and the sum of its Taylor series are equal near this point. Taylor series are named after Brook Taylor, who introduced them in 1715. A Taylor series is also called a Maclaurin series when 0 is the point where the derivatives are considered, after Colin Maclaurin, who made extensive use of this special case of Taylor series in the 18th century.

In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expected value of the squared deviation from the mean of a random variable. The standard deviation (SD) is obtained as the square root of the variance. Variance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out from their average value. It is the second central moment of a distribution, and the covariance of the random variable with itself, and it is often represented by , , , , or .
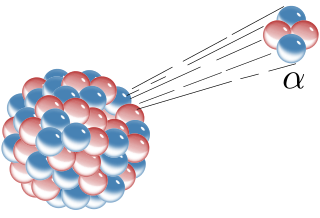
Radioactive decay is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Three of the most common types of decay are alpha, beta, and gamma decay. The weak force is the mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetic and nuclear forces.
10 (ten) is the even natural number following 9 and preceding 11. Ten is the base of the decimal numeral system, the most common system of denoting numbers in both spoken and written language.
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious and cultural significance in many societies.

Guns N' Roses is an American hard rock band formed in Los Angeles, California, in 1985, as the result of a merger between local bands Hollywood Rose and L.A. Guns. When they signed to Geffen Records in 1986, the band's "classic lineup" consisted of vocalist Axl Rose, lead guitarist Slash, rhythm guitarist Izzy Stradlin, bassist Duff McKagan, and drummer Steven Adler. The current lineup consists of Rose, Slash, McKagan, guitarist Richard Fortus, drummer Frank Ferrer and keyboardists Dizzy Reed and Melissa Reese.

In probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time if these events occur with a known constant mean rate and independently of the time since the last event. It can also be used for the number of events in other types of intervals than time, and in dimension greater than 1.
David Solga is a German footballer who plays as a midfielder for Borussia Dortmund II.
The molecular formula C11H17NO (molar mass : 179.25 g/mol, exact mass : 179.131014) may refer to:

Methylephedrine, sold under the brand name Metheph among others, is a sympathomimetic medication described as an antiasthmatic agent and used to treat coughing and nasal congestion. It is reported to be used in various over-the-counter cough and cold preparations throughout the world, including Japan.














