Related Research Articles

Ribosomes are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis. Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA molecules and many ribosomal proteins. The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the translational apparatus.

In biology, translation is the process in living cells in which proteins are produced using RNA molecules as templates. The generated protein is a sequence of amino acids. This sequence is determined by the sequence of nucleotides in the RNA. The nucleotides are considered three at a time. Each such triple results in addition of one specific amino acid to the protein being generated. The matching from nucleotide triple to amino acid is called the genetic code. The translation is performed by a large complex of functional RNA and proteins called ribosomes. The entire process is called gene expression.

Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and then bound to ribosomal proteins to form small and large ribosome subunits. rRNA is the physical and mechanical factor of the ribosome that forces transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) to process and translate the latter into proteins. Ribosomal RNA is the predominant form of RNA found in most cells; it makes up about 80% of cellular RNA despite never being translated into proteins itself. Ribosomes are composed of approximately 60% rRNA and 40% ribosomal proteins, though this ratio differs between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
The peptidyl transferase center is an aminoacyltransferase ribozyme located in the large subunit of the ribosome. It forms peptide bonds between adjacent amino acids during the translation process of protein biosynthesis. It is also responsible for peptidyl-tRNA hydrolysis, allowing the release of the synthesized peptide chain at the end of translation. Peptidyl transferase activity is not mediated by any ribosomal proteins, but entirely by ribosomal RNA (rRNA). The peptidyl transferase center is a significant piece of evidence supporting the RNA World hypothesis.
Bacterial translation is the process by which messenger RNA is translated into proteins in bacteria.
Eukaryotic translation is the biological process by which messenger RNA is translated into proteins in eukaryotes. It consists of four phases: initiation, elongation, termination, and recapping.
In molecular biology, initiation factors are proteins that bind to the small subunit of the ribosome during the initiation of translation, a part of protein biosynthesis.
A release factor is a protein that allows for the termination of translation by recognizing the termination codon or stop codon in an mRNA sequence. They are named so because they release new peptides from the ribosome.

EF-Tu is a prokaryotic elongation factor responsible for catalyzing the binding of an aminoacyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA) to the ribosome. It is a G-protein, and facilitates the selection and binding of an aa-tRNA to the A-site of the ribosome. As a reflection of its crucial role in translation, EF-Tu is one of the most abundant and highly conserved proteins in prokaryotes. It is found in eukaryotic mitochondria as TUFM.

Eukaryotic translation termination factor1 (eRF1), also referred to as TB3-1 or SUP45L1, is a protein that is encoded by the ERF1 gene. In Eukaryotes, eRF1 is an essential protein involved in stop codon recognition in translation, termination of translation, and nonsense mediated mRNA decay via the SURF complex.
Elongation factor 4 (EF-4) is an elongation factor that is thought to back-translocate on the ribosome during the translation of RNA to proteins. It is found near-universally in bacteria and in eukaryotic endosymbiotic organelles including the mitochondria and the plastid. Responsible for proofreading during protein synthesis, EF-4 is a recent addition to the nomenclature of bacterial elongation factors.
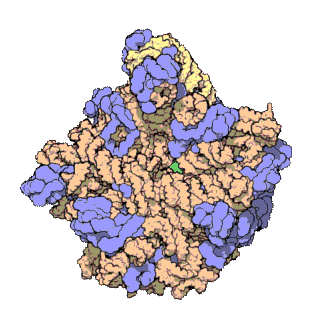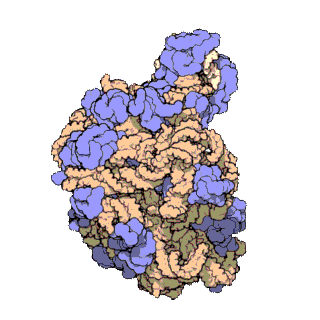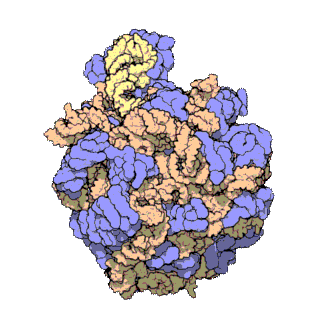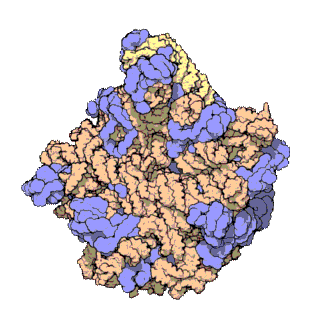
50S is the larger subunit of the 70S ribosome of prokaryotes, i.e. bacteria and archaea. It is the site of inhibition for antibiotics such as macrolides, chloramphenicol, clindamycin, and the pleuromutilins. It includes the 5S ribosomal RNA and 23S ribosomal RNA.

The 23S rRNA is a 2,904 nucleotide long component of the large subunit (50S) of the bacterial/archean ribosome and makes up the peptidyl transferase center (PTC). The 23S rRNA is divided into six secondary structural domains titled I-VI, with the corresponding 5S rRNA being considered domain VII. The ribosomal peptidyl transferase activity resides in domain V of this rRNA, which is also the most common binding site for antibiotics that inhibit translation, making it a target for ribosomal engineering. A well-known member of this antibiotic class, chloramphenicol, acts by inhibiting peptide bond formation, with recent 3D-structural studies showing two different binding sites depending on the species of ribosome. Numerous mutations in domains of the 23S rRNA with Peptidyl transferase activity have resulted in antibiotic resistance. 23S rRNA genes typically have higher sequence variations, including insertions and/or deletions, compared to other rRNAs.

EF-G is a prokaryotic elongation factor involved in mRNA translation. As a GTPase, EF-G catalyzes the movement (translocation) of transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) through the ribosome.

A protein synthesis inhibitor is a compound that stops or slows the growth or proliferation of cells by disrupting the processes that lead directly to the generation of new proteins.
EF-Ts is one of the prokaryotic elongation factors. It is found in human mitochondria as TSFM. It is similar to eukaryotic EF-1B.
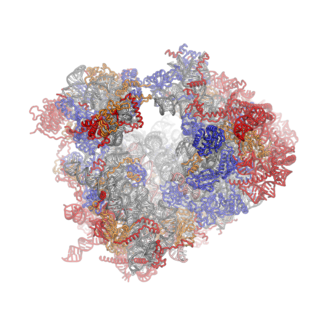
Ribosomes are a large and complex molecular machine that catalyzes the synthesis of proteins, referred to as translation. The ribosome selects aminoacylated transfer RNAs (tRNAs) based on the sequence of a protein-encoding messenger RNA (mRNA) and covalently links the amino acids into a polypeptide chain. Ribosomes from all organisms share a highly conserved catalytic center. However, the ribosomes of eukaryotes are much larger than prokaryotic ribosomes and subject to more complex regulation and biogenesis pathways. Eukaryotic ribosomes are also known as 80S ribosomes, referring to their sedimentation coefficients in Svedberg units, because they sediment faster than the prokaryotic (70S) ribosomes. Eukaryotic ribosomes have two unequal subunits, designated small subunit (40S) and large subunit (60S) according to their sedimentation coefficients. Both subunits contain dozens of ribosomal proteins arranged on a scaffold composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA). The small subunit monitors the complementarity between tRNA anticodon and mRNA, while the large subunit catalyzes peptide bond formation.
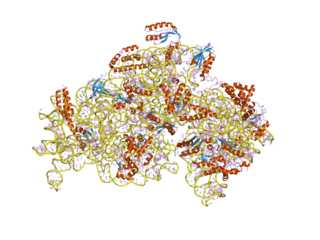
In molecular biology, S4 domain refers to a small RNA-binding protein domain found in a ribosomal protein named uS4. The S4 domain is approximately 60-65 amino acid residues long, occurs in a single copy at various positions in different proteins and was originally found in pseudouridine syntheses, a bacterial ribosome-associated protein.
The P-site is the second binding site for tRNA in the ribosome. The other two sites are the A-site (aminoacyl), which is the first binding site in the ribosome, and the E-site (exit), the third. During protein translation, the P-site holds the tRNA which is linked to the growing polypeptide chain. When a stop codon is reached, the peptidyl-tRNA bond of the tRNA located in the P-site is cleaved releasing the newly synthesized protein. During the translocation step of the elongation phase, the mRNA is advanced by one codon, coupled to movement of the tRNAs from the ribosomal A to P and P to E sites, catalyzed by elongation factor EF-G.
In molecular biology, VAR1 protein domain, otherwise known as variant protein 1, is a ribosomal protein that forms part of the small ribosomal subunit in yeast mitochondria. Mitochondria possess their own ribosomes responsible for the synthesis of a small number of proteins encoded by the mitochondrial genome. VAR1 is the only protein in the yeast mitochondrial ribosome to be encoded in the mitochondria - the remaining approximately 80 ribosomal proteins are encoded in the nucleus. VAR1 along with 15S rRNA are necessary for the formation of mature 37S subunits.
References
- ↑ Ramakrishnan V, Moore PB (April 2001). "Atomic structures at last: the ribosome in 2000". Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 11 (2): 144–54. doi:10.1016/s0959-440x(00)00184-6. PMID 11297922.
- 1 2 Maguire BA, Zimmermann RA (March 2001). "The ribosome in focus". Cell. 104 (6): 813–6. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00278-1 . PMID 11290319. S2CID 8174178.
- ↑ Chandra Sanyal S, Liljas A (December 2000). "The end of the beginning: structural studies of ribosomal proteins". Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 10 (6): 633–6. doi:10.1016/S0959-440X(00)00143-3. PMID 11114498.
- ↑ Kuwano Y, Olvera J, Wool IG (March 1991). "The primary structure of rat ribosomal protein L38". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 175 (2): 551–5. doi:10.1016/0006-291x(91)91600-h. PMC 338234 . PMID 1840484.
- ↑ Wool IG, Chan YL, Paz V, Olvera J (August 1990). "The primary structure of rat ribosomal proteins: the amino acid sequences of L27a and L28 and corrections in the sequences of S4 and S12". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1050 (1–3): 69–73. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(90)90143-p. PMID 2207170.