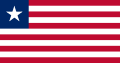
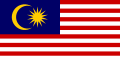
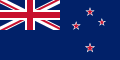
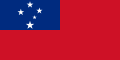
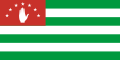
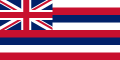
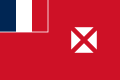
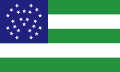
In vexillography, the canton is a rectangular emblem placed at the top left of a flag, usually occupying up to a quarter of a flag's area. The canton of a flag may be a flag in its own right. For instance, British ensigns have the Union Jack as their canton, as do their derivatives such as the national flags of Australia and New Zealand.
Contents
- Current flags using cantons
- Sovereign states
- Territories, regions, and provinces
- Military
- Other 2
- Former flags that used cantons
- States
- Territories, organizations, and subdivisions
- See also
- References
- External links
Following the practice of British ensigns, a canton sometimes contains a symbol of national unity, such as the blue field and white stars of the flag of the United States of America. In these cases, the canton may be called simply the union. [1]
The American flag's canton derives from Britain's use of the Union Jack in the flags of its possessions (including, historically, the Thirteen American Colonies). Subsequently, many New World nations (along with other later countries and regions, such as Liberia or Malaysia) that were inspired by the United States adopted flag elements that were inspired by the American flag. As a result, many extant uses of a prominent canton derive either from British territorial history, or American influence and inspiration.