A hierarchical organization or hierarchical organisation is an organizational structure where every entity in the organization, except one, is subordinate to a single other entity. This arrangement is a form of a hierarchy. In an organization, the hierarchy usually consists of a singular/group of power at the top with subsequent levels of power beneath them. This is the dominant mode of organization among large organizations; most corporations, governments, criminal enterprises, and organized religions are hierarchical organizations with different levels of management, power or authority. For example, the broad, top-level overview of the general organization of the Catholic Church consists of the Pope, then the Cardinals, then the Archbishops, and so on.

In metaphysics, ontology is the philosophical study of being. It investigates what types of entities exist, how they are grouped into categories, and how they are related to one another on the most fundamental level. Ontologists often try to determine what the categories or highest kinds are and how they form a system of categories that encompasses the classification of all entities. Commonly proposed categories include substances, properties, relations, states of affairs, and events. These categories are characterized by fundamental ontological concepts, including particularity and universality, abstractness and concreteness, or possibility and necessity. Of special interest is the concept of ontological dependence, which determines whether the entities of a category exist on the most fundamental level. Disagreements within ontology are often about whether entities belonging to a certain category exist and, if so, how they are related to other entities.
In computer science, pseudocode is a description of the steps in an algorithm using a mix of conventions of programming languages with informal, usually self-explanatory, notation of actions and conditions. Although pseudocode shares features with regular programming languages, it is intended for human reading rather than machine control. Pseudocode typically omits details that are essential for machine implementation of the algorithm. The programming language is augmented with natural language description details, where convenient, or with compact mathematical notation. The purpose of using pseudocode is that it is easier for people to understand than conventional programming language code, and that it is an efficient and environment-independent description of the key principles of an algorithm. It is commonly used in textbooks and scientific publications to document algorithms and in planning of software and other algorithms.
Administrative divisions are geographical areas into which a particular independent sovereign state is divided. Such a unit usually has an administrative authority with the power to take administrative or policy decisions for its area.
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposes in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French comté denoting a jurisdiction under the sovereignty of a count (earl) or a viscount. Literal equivalents in other languages, derived from the equivalent of "count", are now seldom used officially, including comté, contea, contado, comtat, condado, Grafschaft, graafschap, and zhupa in Slavic languages; terms equivalent to 'commune' or 'community' are now often instead used.
An independent city or independent town is a city or town that does not form part of another general-purpose local government entity.

A town is a type of a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world.
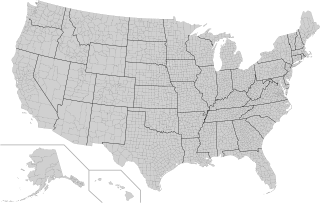
In the United States, a county or county equivalent is an administrative or political subdivision of a state which consists of a geographic region with specific boundaries and usually some level of governmental authority. The term "county" is used in 48 states, while Louisiana and Alaska have functionally equivalent subdivisions called parishes and boroughs, respectively. The specific governmental powers of counties vary widely between the states, with many providing some level of services to civil townships, municipalities, and unincorporated areas. Certain municipalities are in multiple counties; New York City is uniquely partitioned into five counties, referred to at the city government level as boroughs. Some municipalities have been consolidated with their county government to form consolidated city-counties, or have been legally separated from counties altogether to form independent cities. Conversely, those counties in Connecticut, Rhode Island, eight of Massachusetts's 14 counties, and Alaska's Unorganized Borough have no government power, existing only as geographic distinctions.

A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions of municipalities, school district, or political district.

The municipalities of Sweden are its lower-level local government entities. There are 290 municipalities which are responsible for a large proportion of local services, including schools, emergency services and physical planning.

In mathematics, a simple Lie group is a connected non-abelian Lie group G which does not have nontrivial connected normal subgroups. The list of simple Lie groups can be used to read off the list of simple Lie algebras and Riemannian symmetric spaces.

A powiat is the second-level unit of local government and administration in Poland, equivalent to a county, district or prefecture in other countries. The term "powiat" is most often translated into English as "county" or "district". In historical contexts, this may be confusing because the Polish term hrabstwo (an administrative unit administered/owned by a hrabia is also literally translated as "county".
A tax treaty, also called double tax agreement (DTA) or double tax avoidance agreement (DTAA), is an agreement between two countries to avoid or mitigate double taxation. Such treaties may cover a range of taxes including income taxes, inheritance taxes, value added taxes, or other taxes. Besides bilateral treaties, multilateral treaties are also in place. For example, European Union (EU) countries are parties to a multilateral agreement with respect to value added taxes under auspices of the EU, while a joint treaty on mutual administrative assistance of the Council of Europe and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is open to all countries. Tax treaties tend to reduce taxes of one treaty country for residents of the other treaty country to reduce double taxation of the same income.
A geocode is a code that represents a geographic entity. It is a unique identifier of the entity, to distinguish it from others in a finite set of geographic entities. In general the geocode is a human-readable and short identifier.
An organizational structure defines how activities such as task allocation, coordination, and supervision are directed toward the achievement of organizational aims.

Most U.S. states and territories have at least two tiers of local government: counties and municipalities. Louisiana uses the term parish and Alaska uses the term borough for what the U.S. Census Bureau terms county equivalents in those states. Civil townships or towns are used as subdivisions of a county in 20 states, mostly in the Northeast and Midwest.

The town is the basic unit of local government and local division of state authority in the six New England states. Most other U.S. states lack a direct counterpart to the New England town. New England towns overlay the entire area of a state, similar to civil townships in other states where they exist, but they are fully functioning municipal corporations, possessing powers similar to cities and counties in other states. New Jersey's system of equally powerful townships, boroughs, towns, and cities is the system which is most similar to that of New England. New England towns are often governed by a town meeting, an assembly of eligible town residents. The great majority of municipal corporations in New England are based on the town model; there, statutory forms based on the concept of a compact populated place are uncommon, though elsewhere in the U.S. they are prevalent. County government in New England states is typically weak at best, and in some states nonexistent. Connecticut, for example, has no county governments, nor does Rhode Island. Both of those states retain counties only as geographic subdivisions with no governmental authority, while Massachusetts has abolished eight of fourteen county governments so far. Counties serve mostly as dividing lines for the states' judicial systems and some other state services in the southern New England states, while providing varying services in the more sparsely populated three northern New England states.

A matrix number is an alphanumeric code stamped or handwritten into the run-out groove area of a phonograph record. This is the non-grooved area between the end of the final band on a record's side and the label, also known as the run-off groove area, end-groove area, matrix area, or "dead wax".
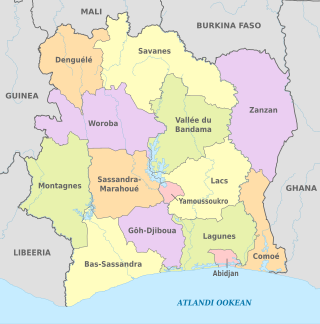
Ivory Coast is a relatively decentralised state. The country divided into 14 districts, of which two are cities organised as autonomous districts. The other 12 districts are subdivided into 31 second-level regions. The autonomous districts and the regions are divided into 111 third-level departments. The departments are divided into 510 fourth-level sub-prefectures. Sub-prefectures contain villages and, in some instances, several villages are combined into fifth-level communes. There are 197 communes.
The U.S. state of Minnesota currently has 3,672 local government entities operating in its borders. These are either counties, towns, cities, school districts, or other special-purpose districts. In addition to the current levels of local government, villages and one borough historically also existed in the state, but they have all been abolished.










