
The Canada goose is a large species of goose with a black head and neck, white cheeks, white under its chin, and a brown body. It is native to the arctic and temperate regions of North America, and it is occasionally found during migration across the Atlantic in northern Europe. It has been introduced to France, the United Kingdom, Ireland, Finland, Sweden, Denmark, New Zealand, Japan, Chile, Argentina, and the Falkland Islands. Like most geese, the Canada goose is primarily herbivorous and normally migratory; often found on or close to fresh water, the Canada goose is also common in brackish marshes, estuaries, and lagoons.
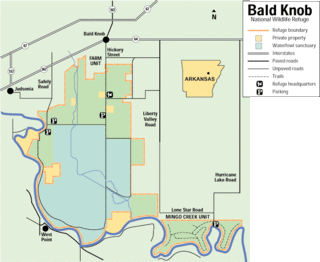
The Bald Knob National Wildlife Refuge is a 15,022 acres (60.79 km2) (2014) wildlife refuge located in White County, Arkansas about two miles south of the town of Bald Knob. The refuge is managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. The refuge features large numbers of migratory waterfowl and bald eagles during the winter months.
Montezuma National Wildlife Refuge is a wildlife preserve operated by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service, encompassing part of the Montezuma Swamp at the north end of Cayuga Lake. The 10,004-acre (40.48 km2) preserve is composed of swamps, pools and channels and is a stopping point for migratory birds. It is the largest contiguous wetland complex in the northeastern United States and comprises a portion of the larger Montezuma Wetlands Complex, which is a partnership between the USFWS, the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation, as well as several other non-profit support organizations.

The Shiawassee National Wildlife Refuge is a 9,870.35 acres (39.9439 km2) National Wildlife Refuge in Saginaw County managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. It is located in the central portion of the lower peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan, approximately 25 miles (40 km) south of the Saginaw Bay in Lake Huron and five miles (8 km) south of the city of Saginaw in the county's Spaulding and James townships. It was established in 1953 to provide habitat for migratory waterfowl.

Quivira National Wildlife Refuge in south central Kansas, United States, includes rare inland marshes. Located near the town of Stafford, it lies mostly in northeastern Stafford County, but small parts extend into southwestern Rice and northwestern Reno Counties. Its proximity to the Central Flyway migration route and the salt marshes on the refuge combine to endow the refuge with a large variety of birds. Many of these birds are uncommon in other parts of Kansas or even the central part of the continent.

The Edwin B. Forsythe National Wildlife Refuge is a U.S. National Wildlife Refuge located in southern and south-central New Jersey, along the Atlantic coast, north of Atlantic City, in Atlantic and Ocean counties. The refuge was created in 1984 out of two existing refuge parcels created to protect tidal wetland and shallow bay habitat for migratory water birds. The Barnegat Division is located in Ocean County on the inland side of Barnegat Bay. The Brigantine Division is located approximately 10 miles (16 km) north of Atlantic City along the south bank of the mouth of the Mullica River. The two divisions are separated by approximately 20 miles (32 km). The refuge is located along most active flight paths of the Atlantic Flyway, making it an important link in the network of national wildlife refuges administered nationwide by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Forsythe Refuge is a part of the Hudson River/New York Bight Ecosystem and The New Jersey Coastal Heritage Trail Route. The refuge is named for Edwin B. Forsythe, conservationist Congressman from New Jersey. The refuge was named as a Ramsar Site of international importance in 1986.

Humboldt Bay is a natural bay and a multi-basin, bar-built coastal lagoon located on the rugged North Coast of California, entirely within Humboldt County, United States. It is the largest protected body of water on the West Coast between San Francisco Bay and Puget Sound, the second-largest enclosed bay in California, and the largest port between San Francisco and Coos Bay, Oregon. The largest city adjoining the bay is Eureka, the regional center and county seat of Humboldt County, followed by the city of Arcata. These primary cities, together with adjoining unincorporated communities and several small towns, comprise a Humboldt Bay Area with a total population of nearly 80,000 people. This comprises nearly 60% of the population of Humboldt County. The bay is home to more than 100 plant species, 300 invertebrate species, 100 fish species, and 200 bird species. In addition, the bay and its complex system of marshes and grasses support hundreds of thousands of migrating and local shore birds. Commercially, this second-largest estuary in California is the site of the largest oyster production operations on the West Coast, producing more than half of all oysters farmed in California.

Browns Park National Wildlife Refuge is a 13,450-acre (5,440 ha) U.S. National Wildlife Refuge located in northwestern Colorado. It is located in Moffat County in the extreme northwestern corner of the state, in an isolated mountain valley of Browns Park on both sides of the Green River, approximately 25 miles (40 km) below Flaming Gorge Dam. Established in 1965, the refuge is managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service office in Maybell, Colorado. The refuge is approximately 53 miles (85 km) northwest of Maybell on State Highway 318. The refuge consists of bottomland and adjacent benchland. The western border of the refuge is the Colorado-Utah state line. The refuge is surrounded by adjacent lines of the Bureau of Land Management. The refuge contains the site of the former Fort Davy Crockett that was constructed in 1837 to protect trappers against attacks by Blackfoot Native Americans.

Ankeny National Wildlife Refuge is located in the fertile Willamette Valley of northwestern Oregon, 12 miles (19 km) south of Salem. The valley was once a rich mix of wildlife habitats. Valley wetlands were once extensive, with meandering stream channels and vast seasonal marshes. Today, the valley is a mix of farmland and growing cities, with few areas remaining for wildlife.

The Atlantic Flyway is a major north-south flyway for migratory birds in North America. The route generally starts in Greenland, then follows the Atlantic coast of Canada, then south down the Atlantic Coast of the United States to the tropical areas of South America and the Caribbean. Every year, migratory birds travel up and down this route following food sources, heading to breeding grounds, or traveling to overwintering sites.

The Lanphere Dunes National Natural Landmark a unit of the Humboldt Bay National Wildlife Refuge Complex, is located in Humboldt County, California. The dune complex consists of the wave slope, fore dune, herbaceous and woody swales, coniferous and riparian forest, freshwater swamp, freshwater marsh, brackish marsh, salt marsh, and intertidal mudflats. The site exemplifies dunes succession.

The Izembek National Wildlife Refuge is the smallest of the National Wildlife Refuges located in the U.S. state of Alaska. It lies on the northwest coastal side of central Aleutians East Borough. Almost all of the refuge was designated as wilderness in 1980 under the Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act (Anilca). The refuge is administered from offices in Cold Bay.
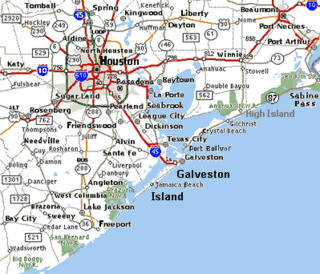
The Brazoria National Wildlife Refuge is a 44,414-acre (179.74 km2) wildlife conservation area along the coast of Texas (USA), east of the towns of Angleton and Lake Jackson, Texas. It borders Christmas Bay and the Intracoastal Waterway, separated from the Gulf of Mexico by Follet's Island.
The San Luis National Wildlife Refuge Complex is located in the northern San Joaquin Valley, within Merced County and Stanislaus County of California. The complex, with four federal National Wildlife Refuges, is managed by the U.S Fish & Wildlife Service.

The Sonny Bono Salton Sea National Wildlife Refuge is located in the Imperial Valley of California, 40 miles (64 km) north of the Mexican border. Situated at the southern end of the Salton Sea, the refuge protects one of the most important nesting sites and stopovers along the Pacific Flyway. Despite its location in the Colorado Desert, a subdivision of the larger Sonoran Desert, the refuge contains marine, freshwater, wetland, and agricultural habitats which provide sanctuary for hundreds of birds and wetland species, including several that have been listed as endangered or sensitive by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.

Castle Rock National Wildlife Refuge is 0.5 miles (0.80 km) offshore from Crescent City in northern California. This coastal rock covers approximately 14 acres (57,000 m2), and rises steeply 335 feet (102 m) above sea level. The refuge provides an important sanctuary for the Aleutian cackling goose and nesting seabirds.

Located in Coos County, New Hampshire, and Oxford County, Maine, Umbagog National Wildlife Refuge is a northern treasure in the National Wildlife Refuge System. The diversity of exceptional habitats provides excellent breeding and foraging areas for migratory birds, endangered species, resident wildlife, and rare plants. The refuge protects over 25,650 acres (103.8 km2) of wetland and forested upland habitat along Umbagog Lake. About 70% of its area is in New Hampshire and 30% in Maine.

Hagerman National Wildlife Refuge (HNWR), a haven for migratory birds and other wildlife, lies in northwestern Grayson County, Texas, on the Big Mineral Arm of Lake Texoma, on the Red River between Oklahoma and Texas. This National Wildlife Refuge is made up of water, marsh, and upland habitat. Visitors can hike, observe wildlife, hunt, and fish throughout the year.

The Umatilla National Wildlife Refuge is located on and around the Columbia River about 15 miles (24 km) northwest of Hermiston, Oregon and includes 8,907 acres (3,605 ha) in Oregon, and 14,876 acres (6,020 ha) in Washington. It was established in 1969 to help mitigate habitat lose due to the flooding that occurred following the construction of the John Day Dam. The refuge is popular with birdwatchers and wildlife enthusiasts.

The San Joaquin River National Wildlife Refuge is a protected area of along the San Joaquin River in the northern San Joaquin Valley, California. It is within San Joaquin County and Stanislaus County.



















