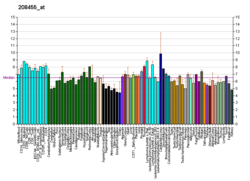
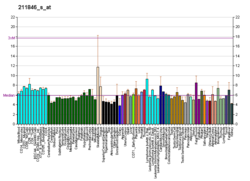
Poliovirus receptor-related 1 (PVRL1), also known as nectin-1 and CD111 (formerly herpesvirus entry mediator C, HVEC) is a human protein of the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF), also considered a member of the nectins. [5] It is a membrane protein with three extracellular immunoglobulin domains, a single transmembrane helix and a cytoplasmic tail. The protein can mediate Ca2+-independent cellular adhesion further characterizing it as IgSF cell adhesion molecule (IgSF CAM).