
The tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily (TNFRSF) is a protein superfamily of cytokine receptors characterized by the ability to bind tumor necrosis factors (TNFs) via an extracellular cysteine-rich domain. With the exception of nerve growth factor (NGF), all TNFs are homologous to the archetypal TNF-alpha. In their active form, the majority of TNF receptors form trimeric complexes in the plasma membrane. Accordingly, most TNF receptors contain transmembrane domains (TMDs), although some can be cleaved into soluble forms, and some lack a TMD entirely. In addition, most TNF receptors require specific adaptor protein such as TRADD, TRAF, RIP and FADD for downstream signalling. TNF receptors are primarily involved in apoptosis and inflammation, but they can also take part in other signal transduction pathways, such as proliferation, survival, and differentiation. TNF receptors are expressed in a wide variety of tissues in mammals, especially in leukocytes.

B-cell activating factor (BAFF) also known as tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 13B and CD257 among other names, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFSF13B gene. BAFF is also known as B Lymphocyte Stimulator (BLyS) and TNF- and APOL-related leukocyte expressed ligand (TALL-1) and the Dendritic cell-derived TNF-like molecule.

TNF receptor-associated factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRAF1 gene.

Lymphotoxin-alpha (LT-α) formerly known as tumor necrosis factor-beta (TNF-β) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LTA gene. Belonging to the hematopoietic cell line, LT-α exhibits anti-proliferative activity and causes the cellular destruction of tumor cell lines. As a cytotoxic protein, LT-α performs a variety of important roles in immune regulation depending on the form that it is secreted as. Unlike other members of the TNF superfamily, LT-α is only found as a soluble homotrimer, when found at the cell surface it is found only as a heterotrimer with LTβ.

TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRAF3 gene.

LIGHT, also known as tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 14 (TNFSF14), is a secreted protein of the TNF superfamily. It is recognized by herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM), as well as decoy receptor 3.

Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 12 also known as TNF-related weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFSF12 gene.

Decoy receptor 3 (Dcr3), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6B (TNFRSF6B), TR6 and M68, is a soluble protein of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily which inhibits Fas ligand-induced apoptosis.

Transmembrane activator and CAML interactor (TACI), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 13B (TNFRSF13B) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFRSF13B gene.

BAFF receptor, also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 13C (TNFRSF13C) and BLyS receptor 3 (BR3), is a membrane protein of the TNF receptor superfamily which recognizes BAFF, an essential factor for B cell maturation and survival. In humans it is encoded by the TNFRSF13C gene.

Death receptor 3 (DR3), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 25 (TNFRSF25), is a cell surface receptor of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily which mediates apoptotic signalling and differentiation. Its only known TNFSF ligand is TNF-like protein 1A (TL1A).

Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 12A also known as the TWEAK receptor (TWEAKR) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFRSF12A gene.

Vascular endothelial growth inhibitor (VEGI), also known as TNF-like ligand 1A (TL1A) and TNF superfamily member 15 (TNFSF15), is protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFSF15 gene. VEGI is an anti-angiogenic protein. It belongs to tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, where it is member 15. It is the sole known ligand for death receptor 3, and it can also be recognized by decoy receptor 3.

B-cell maturation antigen, also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 17 (TNFRSF17), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFRSF17 gene.

Calcium modulating ligand, also known as calcium-modulating cyclophilin ligand, is a signalling protein recognized by the TNF receptor TACI.

Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 18 (TNFRSF18), also known as glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein (GITR) or CD357. GITR is encoded and tnfrsf18 gene at chromosome 4 in mice. GITR is type I transmembrane protein and is described in 4 different isoforms. GITR human orthologue, also called activation-inducible TNFR family receptor (AITR), is encoded by the TNFRSF18 gene at chromosome 1.
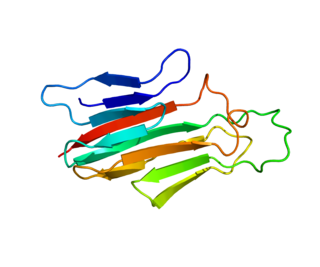
Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 18 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFSF18 gene.

Tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 12-member 13, also known as TNFSF12-TNFSF13, is a human gene.

Tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 (TNFR2), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1B (TNFRSF1B) and CD120b, is one of two membrane receptors that binds tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα). Like its counterpart, tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1), the extracellular region of TNFR2 consists of four cysteine-rich domains which allow for binding to TNFα. TNFR1 and TNFR2 possess different functions when bound to TNFα due to differences in their intracellular structures, such as TNFR2 lacking a death domain (DD).
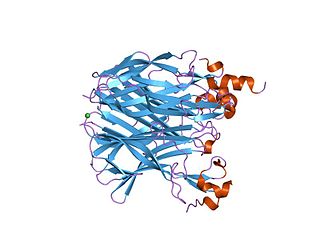
In molecular biology, TACI-CRD2 represents the second cysteine-rich protein domain found in the TACI family of proteins. Members of this family are predominantly found in tumour necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 13b (TACI), and are required for binding to the ligands APRIL and BAFF. TACI-CRD2 stands for Transmembrane Activator and CAML Interactor- Cysteine Rich Domain 2.




















