
Levonorgestrel is a hormonal medication which is used in a number of birth control methods. It is combined with an estrogen to make combination birth control pills. As an emergency birth control, sold under the brand names Plan B One-Step and Julie, among others, it is useful within 72 hours of unprotected sex. The more time that has passed since sex, the less effective the medication becomes, and it does not work after pregnancy (implantation) has occurred. Levonorgestrel works by preventing ovulation or fertilization from occurring. It decreases the chances of pregnancy by 57–93%. In an intrauterine device (IUD), such as Mirena among others, it is effective for the long-term prevention of pregnancy. A levonorgestrel-releasing implant is also available in some countries.

A contraceptive patch, also known as "the patch", is a transdermal patch applied to the skin that releases synthetic oestrogen and progestogen hormones to prevent pregnancy. They have been shown to be as effective as the combined oral contraceptive pill with perfect use, and the patch may be more effective in typical use.

Ethinylestradiol (EE) is an estrogen medication which is used widely in birth control pills in combination with progestins. In the past, EE was widely used for various indications such as the treatment of menopausal symptoms, gynecological disorders, and certain hormone-sensitive cancers. It is usually taken by mouth but is also used as a patch and vaginal ring.
Extended or continuous cycle combined oral contraceptive pills are a packaging of combined oral contraceptive pills (COCPs) that reduce or eliminate the withdrawal bleeding that would occur once every 28 days in traditionally packaged COCPs. It works by reducing the frequency of the pill-free or placebo days. Extended cycle use of COCPs may also be called menstrual suppression, although other hormonal medications or medication delivery systems may also be used to suppress menses. Any brand of combined oral contraceptive pills can be used in an extended or continuous manner by simply discarding the placebo pills; this is most commonly done with monophasic pills in which all of the pills in a package contain the same fixed dosing of a synthetic estrogen and a progestin in each active pill.
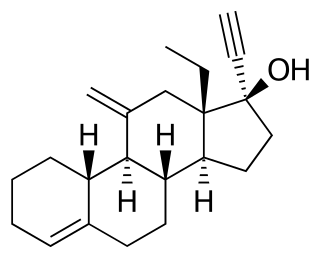
Desogestrel is a progestin medication which is used in birth control pills. It is also used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms in women. The medication is available and used alone or in combination with an estrogen. It is taken by mouth.

Drospirenone is a progestin and antiandrogen medication which is used in birth control pills to prevent pregnancy and in menopausal hormone therapy, among other uses. It is available both alone under the brand name Slynd and in combination with an estrogen under the brand name Yasmin among others. The medication is an analog of the drug spironolactone. Drospirenone is taken by mouth.
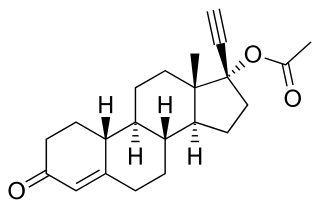
Norethisterone acetate (NETA), also known as norethindrone acetate and sold under the brand name Primolut-Nor among others, is a progestin medication which is used in birth control pills, menopausal hormone therapy, and for the treatment of gynecological disorders. The medication available in low-dose and high-dose formulations and is used alone or in combination with an estrogen. It is ingested orally.

Norelgestromin, or norelgestromine, sold under the brand names Evra and Ortho Evra among others, is a progestin medication which is used as a method of birth control for women. The medication is available in combination with an estrogen and is not available alone. It is used as a patch that is applied to the skin.

Norgestimate, sold under the brand names Ortho Tri-Cyclen and Previfem among others, is a progestin medication which is used in birth control pills for women and in menopausal hormone therapy. The medication is available in combination with an estrogen and is not available alone. It is taken by mouth.

Norgestrel is a progestin which is used in birth control pills sold under the brand name Ovral in combination with the estrogen ethinylestradiol and Opill by itself. It is also used in menopausal hormone therapy. It is taken by mouth.

Norethisterone, also known as norethindrone and sold under many brand names, is a progestin medication used in birth control pills, menopausal hormone therapy, and for the treatment of gynecological disorders. The medication is available in both low-dose and high-dose formulations and both alone and in combination with an estrogen. It is used by mouth or, as norethisterone enanthate, by injection into muscle.

Gestodene, sold under the brand names Femodene and Minulet among others, is a progestin medication which is used in birth control pills for women. It is also used in menopausal hormone therapy. The medication is available almost exclusively in combination with an estrogen. It is taken by mouth.

Norgestrienone, sold under the brand names Ogyline, Planor, and Miniplanor, is a progestin medication which has been used in birth control pills, sometimes in combination with ethinylestradiol. It was developed by Roussel Uclaf and has been registered for use only in France. Under the brand name Planor, it has been marketed in France as 2 mg norgestrienone and 50 μg ethinylestradiol tablets. It is taken by mouth.

Mestranol, sold under the brand names Enovid, Norinyl, and Ortho-Novum among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in birth control pills, menopausal hormone therapy, and the treatment of menstrual disorders. It is formulated in combination with a progestin and is not available alone. It is taken by mouth.

Dienogest, sold under the brand name Visanne among others, is a progestin medication which is used in birth control pills and in the treatment of endometriosis. It is also used in menopausal hormone therapy and to treat heavy periods. Dienogest is available both alone and in combination with estrogens. It is taken by mouth.

Norethisterone enanthate (NETE), also known as norethindrone enanthate, is a form of hormonal birth control which is used to prevent pregnancy in women. It is used both as a form of progestogen-only injectable birth control and in combined injectable birth control formulations. It may be used following childbirth, miscarriage, or abortion. The failure rate per year in preventing pregnancy for the progestogen-only formulation is 2 per 100 women. Each dose of this form lasts two months with only up to two doses typically recommended.

Estradiol/norethisterone (E2/NET), tentative brand name Netagen or Netagen 403, was a combination of estradiol (E2), an estrogen, and norethisterone (NET), a progestin, which was studied as a birth control pill to prevent pregnancy in women. It was taken by mouth and contained 4 mg micronized E2 and 3 mg NET per tablet. The medication was developed by Novo Pharmaceuticals in Denmark and was never marketed.

Ethinylestradiol/cyproterone acetate (EE/CPA), also known as co-cyprindiol and sold under the brand names Diane and Diane-35 among others, is a combination of ethinylestradiol (EE), an estrogen, and cyproterone acetate (CPA), a progestin and antiandrogen, which is used as a birth control pill to prevent pregnancy in women. It is also used to treat androgen-dependent conditions in women such as acne, seborrhea, excessive facial/body hair growth, scalp hair loss, and high androgen levels associated with ovaries with cysts. The medication is taken by mouth once daily for 21 days, followed by a 7-day free interval.














