Related Research Articles

In biology, translation is the process in living cells in which proteins are produced using RNA molecules as templates. The generated protein is a sequence of amino acids. This sequence is determined by the sequence of nucleotides in the RNA. The nucleotides are considered three at a time. Each such triple results in addition of one specific amino acid to the protein being generated. The matching from nucleotide triple to amino acid is called the genetic code. The translation is performed by a large complex of functional RNA and proteins called ribosomes. The entire process is called gene expression.
Bacterial translation is the process by which messenger RNA is translated into proteins in bacteria.
Eukaryotic translation is the biological process by which messenger RNA is translated into proteins in eukaryotes. It consists of four phases: initiation, elongation, termination, and recapping.
The Kozak consensus sequence is a nucleic acid motif that functions as the protein translation initiation site in most eukaryotic mRNA transcripts. Regarded as the optimum sequence for initiating translation in eukaryotes, the sequence is an integral aspect of protein regulation and overall cellular health as well as having implications in human disease. It ensures that a protein is correctly translated from the genetic message, mediating ribosome assembly and translation initiation. A wrong start site can result in non-functional proteins. As it has become more studied, expansions of the nucleotide sequence, bases of importance, and notable exceptions have arisen. The sequence was named after the scientist who discovered it, Marilyn Kozak. Kozak discovered the sequence through a detailed analysis of DNA genomic sequences.
In molecular biology, initiation factors are proteins that bind to the small subunit of the ribosome during the initiation of translation, a part of protein biosynthesis.

EF-Tu is a prokaryotic elongation factor responsible for catalyzing the binding of an aminoacyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA) to the ribosome. It is a G-protein, and facilitates the selection and binding of an aa-tRNA to the A-site of the ribosome. As a reflection of its crucial role in translation, EF-Tu is one of the most abundant and highly conserved proteins in prokaryotes. It is found in eukaryotic mitochondria as TUFM.
Eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs) are proteins or protein complexes involved in the initiation phase of eukaryotic translation. These proteins help stabilize the formation of ribosomal preinitiation complexes around the start codon and are an important input for post-transcription gene regulation. Several initiation factors form a complex with the small 40S ribosomal subunit and Met-tRNAiMet called the 43S preinitiation complex. Additional factors of the eIF4F complex recruit the 43S PIC to the five-prime cap structure of the mRNA, from which the 43S particle scans 5'-->3' along the mRNA to reach an AUG start codon. Recognition of the start codon by the Met-tRNAiMet promotes gated phosphate and eIF1 release to form the 48S preinitiation complex, followed by large 60S ribosomal subunit recruitment to form the 80S ribosome. There exist many more eukaryotic initiation factors than prokaryotic initiation factors, reflecting the greater biological complexity of eukaryotic translation. There are at least twelve eukaryotic initiation factors, composed of many more polypeptides, and these are described below.
A bacterial initiation factor (IF) is a protein that stabilizes the initiation complex for polypeptide translation.
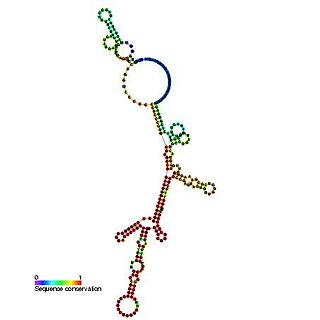
The Hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site, or HCV IRES, is an RNA structure within the 5'UTR of the HCV genome that mediates cap-independent translation initiation.

The prokaryotic small ribosomal subunit, or 30S subunit, is the smaller subunit of the 70S ribosome found in prokaryotes. It is a complex of the 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and 19 proteins. This complex is implicated in the binding of transfer RNA to messenger RNA (mRNA). The small subunit is responsible for the binding and the reading of the mRNA during translation. The small subunit, both the rRNA and its proteins, complexes with the large 50S subunit to form the 70S prokaryotic ribosome in prokaryotic cells. This 70S ribosome is then used to translate mRNA into proteins.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF5B gene.

EF-G is a prokaryotic elongation factor involved in mRNA translation. As a GTPase, EF-G catalyzes the movement (translocation) of transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) through the ribosome.

A protein synthesis inhibitor is a compound that stops or slows the growth or proliferation of cells by disrupting the processes that lead directly to the generation of new proteins.
Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2 (eIF2) is an eukaryotic initiation factor. It is required for most forms of eukaryotic translation initiation. eIF2 mediates the binding of tRNAiMet to the ribosome in a GTP-dependent manner. eIF2 is a heterotrimer consisting of an alpha, a beta, and a gamma subunit.
Bacterial initiation factor 1 is a bacterial initiation factor.
Translational regulation refers to the control of the levels of protein synthesized from its mRNA. This regulation is vastly important to the cellular response to stressors, growth cues, and differentiation. In comparison to transcriptional regulation, it results in much more immediate cellular adjustment through direct regulation of protein concentration. The corresponding mechanisms are primarily targeted on the control of ribosome recruitment on the initiation codon, but can also involve modulation of peptide elongation, termination of protein synthesis, or ribosome biogenesis. While these general concepts are widely conserved, some of the finer details in this sort of regulation have been proven to differ between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms.
The P-site is the second binding site for tRNA in the ribosome. The other two sites are the A-site (aminoacyl), which is the first binding site in the ribosome, and the E-site (exit), the third. During protein translation, the P-site holds the tRNA which is linked to the growing polypeptide chain. When a stop codon is reached, the peptidyl-tRNA bond of the tRNA located in the P-site is cleaved releasing the newly synthesized protein. During the translocation step of the elongation phase, the mRNA is advanced by one codon, coupled to movement of the tRNAs from the ribosomal A to P and P to E sites, catalyzed by elongation factor EF-G.

In molecular biology, translation initiation factor IF-3 is one of the three factors required for the initiation of protein biosynthesis in bacteria. IF-3 is thought to function as a fidelity factor during the assembly of the ternary initiation complex which consists of the 30S ribosomal subunit, the initiator tRNA and the messenger RNA. IF-3 is a basic protein that binds to the 30S ribosomal subunit. The chloroplast homolog enhances the poly(A,U,G)-dependent binding of the initiator tRNA to its ribosomal 30s subunits. IF1–IF3 may also perform ribosome recycling.
The 43S preinitiation complex is a ribonucleoprotein complex that exists during an early step of eukaryotic translation initiation. The 43S PIC contains the small ribosomal subunit (40S) bound by the initiation factors eIF1, eIF1A, eIF3, and the eIF2-Met-tRNAiMet-GTP ternary complex (eIF2-TC).
Archaeal initiation factors are proteins that are used during the translation step of protein synthesis in archaea. The principal functions these proteins perform include ribosome RNA/mRNA recognition, delivery of the initiator Met-tRNAiMet, methionine bound tRNAi, to the 40s ribosome, and proofreading of the initiation complex.
References
- ↑ Prokaryotic+Initiation+Factor-2 at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- ↑ D'Souza AR, Minczuk M (July 2018). "Mitochondrial transcription and translation: overview". Essays in Biochemistry. 62 (3): 309–320. doi:10.1042/EBC20170102. PMC 6056719 . PMID 30030363.