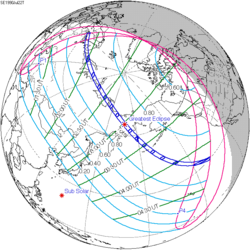
| Annular eclipse | |
| Gamma | 0.4091 |
|---|---|
| Magnitude | 0.9179 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 701 s (11 min 41 s) |
| Coordinates | 1°00′N169°42′W / 1°N 169.7°W |
| Max. width of band | 340 km (210 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 23:05:37 |
| References | |
| Saros | 141 (22 of 70) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9490 |
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit between Saturday, January 4 and Sunday, January 5, 1992, [1] with a magnitude of 0.9179. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 1.5 days before apogee (on January 6, 1992, at 11:40 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller. [2]
Contents
- Observations
- Eclipse timing
- Places experiencing annular eclipse
- Places experiencing partial eclipse
- Eclipse details
- Eclipse season
- Related eclipses
- Eclipses in 1992
- Metonic
- Tzolkinex
- Half-Saros
- Tritos
- Solar Saros 141
- Inex
- Triad
- Solar eclipses of 1990–1992
- Saros 141
- Metonic series
- Tritos series
- Inex series
- Notes
- References
- External links
The duration of annularity at maximum eclipse (closest to but slightly shorter than the longest duration) was 11 minutes, 40.9 seconds in the Pacific. It will have been the longest annular solar eclipse until January 2, 3062, but the solar eclipse of December 24, 1973 lasted longer. [3]
Annularity was visible in the Federal States of Micronesia, Nauru, Kiribati, Baker Island, Palmyra Atoll, Kingman Reef, and southwestern California, including the southwestern part of Los Angeles. [4] A partial eclipse was visible for parts of Northeast Asia, Northern Australia, Oceania, Hawaii, and western North America.