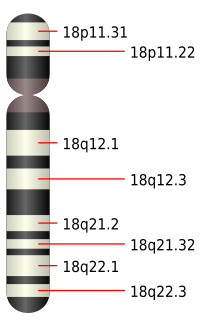
Edwards syndrome, also known as trisomy 18, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of a third copy of all or part of chromosome 18. Many parts of the body are affected. Babies are often born small and have heart defects. Other features include a small head, small jaw, clenched fists with overlapping fingers, and severe intellectual disability.
Potter sequence is the atypical physical appearance of a baby due to oligohydramnios experienced when in the uterus. It includes clubbed feet, pulmonary hypoplasia and cranial anomalies related to the oligohydramnios. Oligohydramnios is the decrease in amniotic fluid volume sufficient to cause deformations in morphogenesis of the baby.

Fraser syndrome is an autosomal recessive congenital disorder. Fraser syndrome is named for the geneticist George R. Fraser, who first described the syndrome in 1962.
Vaginal atresia is a condition in which the vagina is abnormally closed or absent. The main causes can either be complete vaginal hypoplasia, or a vaginal obstruction, often caused by an imperforate hymen or, less commonly, a transverse vaginal septum. It results in uterovaginal outflow tract obstruction. This condition does not usually occur by itself within an individual, but coupled with other developmental disorders within the female. The disorders that are usually coupled with a female who has vaginal atresia are Rokitansky-Mayer- Küster-Hauser syndrome, Bardet-Biedl syndrome, or Fraser syndrome. One out of every 5,000 women have this abnormality.

Dandy–Walker malformation (DWM), also known as Dandy–Walker syndrome (DWS), is a rare congenital brain malformation in which the part joining the two hemispheres of the cerebellum does not fully form, and the fourth ventricle and space behind the cerebellum are enlarged with cerebrospinal fluid. Most of those affected develop hydrocephalus within the first year of life, which can present as increasing head size, vomiting, excessive sleepiness, irritability, downward deviation of the eyes and seizures. Other, less common symptoms are generally associated with comorbid genetic conditions and can include congenital heart defects, eye abnormalities, intellectual disability, congenital tumours, other brain defects such as agenesis of the corpus callosum, skeletal abnormalities, an occipital encephalocele or underdeveloped genitalia or kidneys. It is sometimes discovered in adolescents or adults due to mental health problems.
This is a shortened version of the fourth chapter of the ICD-10: Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases. It covers ICD codes E00.0 to E90. All versions of the ICD-10, including the most recent one (2019), can be browsed freely on the website of the World Health Organisation (WHO). The ICD-10 can also be downloaded in PDF-form.
This is a shortened version of the third chapter of the ICD-10: Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs, and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism. It covers ICD codes D50.0 to D89.9. All versions of the ICD-10, including the most recent one (2019), can be browsed freely on the website of the World Health Organisation (WHO). The ICD-10 can also be downloaded in PDF-form.

Down syndrome is a chromosomal abnormality characterized by the presence of an extra copy of genetic material on chromosome 21, either in whole or part. The effects of the extra copy varies greatly from individual to individual, depending on the extent of the extra copy, genetic background, environmental factors, and random chance. Down syndrome can occur in all human populations, and analogous effects have been found in other species, such as chimpanzees and mice. In 2005, researchers have been able to create transgenic mice with most of human chromosome 21.

Intestinal atresia is any congenital malformation of the structure of the intestine that causes bowel obstruction. The malformation can be a narrowing (stenosis), absence or malrotation of a portion of the intestine. These defects can either occur in the small or large intestine.
3C syndrome is a rare condition whose symptoms include heart defects, cerebellar hypoplasia, and cranial dysmorphism. It was first described in the medical literature in 1987 by Ritscher and Schinzel, for whom the disorder is sometimes named.

Cat eye syndrome or Schmid–Fraccaro syndrome, is a rare condition caused by the short arm (p) and a small section of the long arm (q) of human chromosome 22 being present three (trisomic) or four times (tetrasomic) instead of the usual two times. There is no significant reduction in life expectancy in patients who are not afflicted with one of CES' life-threatening abnormalities.

Fryns syndrome is an autosomal recessive multiple congenital anomaly syndrome that is usually lethal in the neonatal period. Fryns (1987) reviewed the syndrome.
Genitopatellar syndrome is a rare disorder with characteristic craniofacial features, congenital flexion contractures of the lower limbs, absent or abnormal patellae, urogenital anomalies, and severe psychomotor retardation. In 2012, it was shown that mutations in the gene KAT6B cause the syndrome.
Young–Madders syndrome, alternatively known as Pseudotrisomy 13 syndrome or holoprosencephaly–polydactyly syndrome, is a genetic disorder resulting from defective and duplicated chromosomes which result in holoprosencephaly, polydactyly, facial malformations and mental retardation, with a significant variance in the severity of symptoms being seen across known cases. Many cases often suffer with several other genetic disorders, and some have presented with hypoplasia, cleft lip, cardiac lesions and other heart defects. In one case in 1991 and another in 2000 the condition was found in siblings who were the product of incest. Many cases are diagnosed prenatally and often in siblings. Cases are almost fatal in the prenatal stage with babies being stillborn.

13q deletion syndrome is a rare genetic disease caused by the deletion of some or all of the large arm of human chromosome 13. Depending upon the size and location of the deletion on chromosome 13, the physical and mental manifestations will vary. It has the potential to cause intellectual disability and congenital malformations that affect a variety of organ systems. Because of the rarity of the disease in addition to the variations in the disease, the specific genes that cause this disease are unknown. This disease is also known as: