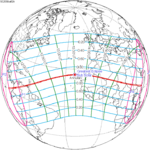
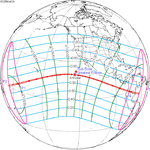
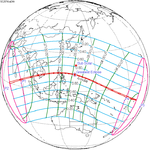
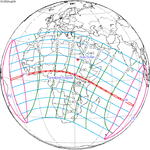
A partial solar eclipse took place on 19 April 2004. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. It was largely visible over the south Atlantic Ocean and north shores of Antarctica, most prominently the Antarctic Peninsula. The eclipse was deep enough to be seen from a large portion of southern Africa, with over 50% totality at Cape Town, South Africa at approximately 4:10 PM. However, the eclipse remained visible to cities such as Harare, Maseru, Durban, and Bloemfontein, although to a much lesser extent.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on January 15, 2010 with a magnitude of 0.9190. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. It was the longest annular solar eclipse of the millennium, and the longest until December 23, 3043, with the length of maximum eclipse of 11 minutes, 7.8 seconds, and the longest duration of 11 minutes, 10.7 seconds. This is about 4 minutes longer than total solar eclipses could ever get.

A total solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of the orbit on June 13, 2132. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. This is one of the solar eclipses occurring on Friday the 13th.

An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of the orbit on February 7, 2008. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring 7 days after apogee and 6.9 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was near the average diameter.

An annular solar eclipse will occur on January 5, 2038. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of the orbit on March 29, 1987. It was a hybrid eclipse, with only a small portion of the central path as total, lasting a maximum of only 7.57 seconds. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Totality of this eclipse was not visible on any land, while annularity was visible in southern Argentina, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Sudan, Ethiopia, Djibouti and Somaliland.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on January 4–5, 1992. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible in the Federal States of Micronesia, Nauru, Kiribati, Baker Island, Palmyra Atoll, Kingman Reef, and southwestern California, including the southwestern part of Los Angeles.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on January 26, 1990. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.
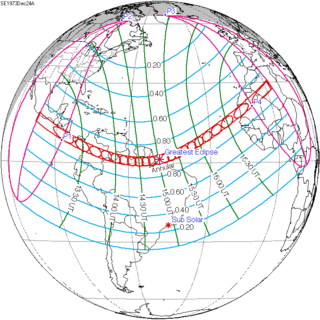
An annular solar eclipse occurred on December 24, 1973. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from southern Mexico, southwestern Nicaragua, Costa Rica including the capital city San José, Panama, Colombia including the capital city Bogotá, southern Venezuela, Brazil, southern Guyana, southern Dutch Guiana, southern French Guiana, Portuguese Cape Verde including the capital city Praia, Mauritania including the capital city Nouakchott, Spanish Sahara, Mali, and Algeria.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on December 14, 1955. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from French Equatorial Africa, Libya, Anglo-Egyptian Sudan including the capital city Khartoum, French Somaliland including the capital Djibouti City, British Somaliland including the capital city Hargeisa, the Trust Territory of Somaliland, the Maldives, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Burma, Thailand including the capital city Bangkok, Cambodia, Laos, North Vietnam and South Vietnam, China, British Hong Kong, Taiwan, and Ryukyu Islands. It was the third central solar eclipse visible from Bangkok from 1948 to 1958, where it is rare for a large city to witness 4 central solar eclipses in just 9.945 years. This is the 20th member Solar Saros 141, and the last of first set of solar eclipses without a penumbral internal contact, the next event is the 1973 Dec 24 event, which is the first of 19 solar eclipses with a penumbral internal contact until 2298 Jul 09.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on January 16, 1972. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.
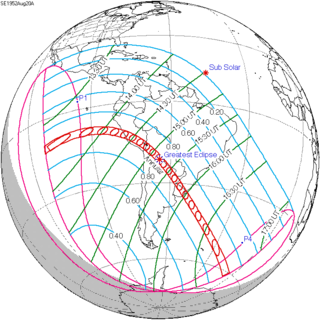
An annular solar eclipse occurred on August 20, 1952. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from Peru including the capital city Lima, northeastern Chile, Bolivia including the constitutional capital Sucre and seat of government La Paz, Argentina, Paraguay, southern Brazil and Uruguay.

A total solar eclipse will occur on May 1, 2079, with a maximum eclipse at 10:48:25.6 UTC. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The eclipse will be visible in Greenland, parts of eastern Canada and parts of the northeastern United States .[
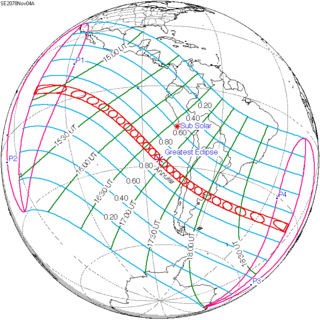
An annular solar eclipse will occur on November 4, 2078. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. The path of annularity will cross Pacific Ocean, South America, and Atlantic Ocean. The tables below contain detailed predictions and additional information on the Annular Solar Eclipse of 4 November 2078.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on December 25, 1935. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. This was the 5th solar eclipse in 1935, the maximum possible. The next time this will occur is 2206.

A total solar eclipse will occur on July 5, 2168. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Lasting a maximum of 7 minutes, 26 seconds, it will be the longest eclipse since the 11th century, which lasted 7 minutes and 20 seconds, as well with the next two occurrences. This is the largest total solar eclipse of Saros 139. Greatest Eclipse occurs 1,468 km north of the Equator.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on November 11, 1901. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from the Italian island Sicily, the whole British Malta, Ottoman Tripolitania, Egypt, Ottoman Empire, Emirate of Jabal Shammar, Aden Protectorate, Muscat and Oman, British Raj, British Ceylon, Siam, French Indochina, Bombay Reef in the Paracel Islands, and Philippines.
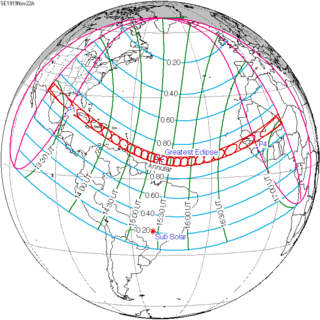
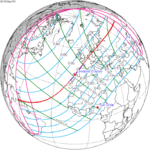
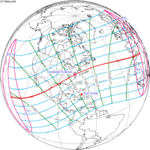
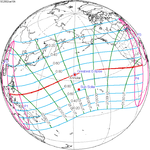
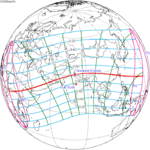
An annular solar eclipse occurred on Saturday, November 22, 1919. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. It occurred in over half of North America, much of South America, a part of Western Europe and about a third of Africa.
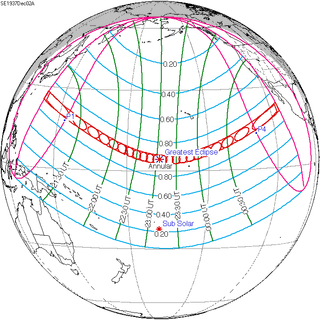
An annular solar eclipse occurred on December 2, 1937. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from Ogasawara, Tokyo and South Pacific Mandate in Japan, and Gilbert and Ellice Islands.
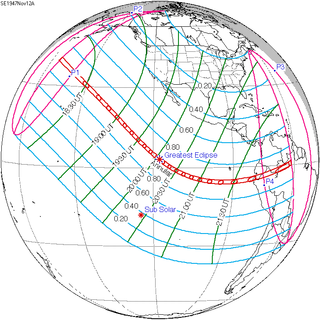
An annular solar eclipse occurred on November 12, 1947. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from the Pacific Ocean, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia and Brazil.