In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sucrose and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of hydrocarbons, confering hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur.
In chemistry, a hydration reaction is a chemical reaction in which a substance combines with water. In organic chemistry, water is added to an unsaturated substrate, which is usually an alkene or an alkyne. This type of reaction is employed industrially to produce ethanol, isopropanol, and butan-2-ol.

Iodoform (also known as triiodomethane and, inaccurately, as carbon triiodide) is the organoiodine compound with the chemical formula CHI3. A pale yellow, crystalline, volatile substance, it has a penetrating and distinctive odor (in older chemistry texts, the smell is sometimes referred to as that of hospitals, where the compound is still commonly used) and, analogous to chloroform, sweetish taste. It is occasionally used as a disinfectant.
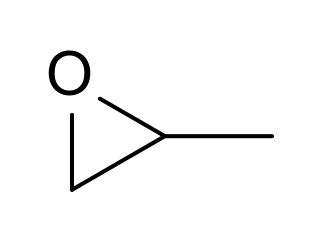
Propylene oxide is an acutely toxic and carcinogenic organic compound with the molecular formula CH3CHCH2O. This colourless volatile liquid with an odour similar to ether, is produced on a large scale industrially. Its major application is its use for the production of polyether polyols for use in making polyurethane plastics. It is a chiral epoxide, although it is commonly used as a racemic mixture.

Cyclohexanol is the organic compound with the formula HOCH(CH2)5. The molecule is related to cyclohexane by replacement of one hydrogen atom by a hydroxyl group. This compound exists as a deliquescent colorless solid with a camphor-like odor, which, when very pure, melts near room temperature. Millions of tonnes are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon.

Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3CO)2O. Commonly abbreviated Ac2O, it is the simplest isolable anhydride of a carboxylic acid and is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is a colorless liquid that smells strongly of acetic acid, which is formed by its reaction with moisture in the air.

Acetone, is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CO. It is the simplest and smallest ketone. It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odor.

tert-Butyl alcohol is the simplest tertiary alcohol, with a formula of (CH3)3COH (sometimes represented as t-BuOH). Its isomers are 1-butanol, isobutanol, and butan-2-ol. tert-Butyl alcohol is a colorless solid, which melts near room temperature and has a camphor-like odor. It is miscible with water, ethanol and diethyl ether.
There are two isomers of propanol.
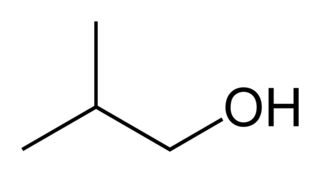
Isobutanol (IUPAC nomenclature: 2-methylpropan-1-ol) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CHCH2OH (sometimes represented as i-BuOH). This colorless, flammable liquid with a characteristic smell is mainly used as a solvent either directly or as its esters. Its isomers are 1-butanol, 2-butanol, and tert-butanol, all of which are important industrially.

Allyl alcohol is an organic compound with the structural formula CH2=CHCH2OH. Like many alcohols, it is a water-soluble, colourless liquid. It is more toxic than typical small alcohols. Allyl alcohol is used as a raw material for the production of glycerol, but is also used as a precursor to many specialized compounds such as flame-resistant materials, drying oils, and plasticizers. Allyl alcohol is the smallest representative of the allylic alcohols.

Propyl acetate, also known as propyl ethanoate, is an organic compound. Nearly 20,000 tons are produced annually for use as a solvent. This colorless liquid is known by its characteristic odor of pears. Due to this fact, it is commonly used in fragrances and as a flavor additive. It is formed by the esterification of acetic acid and propan-1-ol, often via Fischer–Speier esterification, with sulfuric acid as a catalyst and water produced as a byproduct.

2-Methoxyethanol, or methyl cellosolve, is an organic compound with formula C
3H
8O
2 that is used mainly as a solvent. It is a clear, colorless liquid with an ether-like odor. It is in a class of solvents known as glycol ethers which are notable for their ability to dissolve a variety of different types of chemical compounds and for their miscibility with water and other solvents. It can be formed by the nucleophilic attack of methanol on protonated ethylene oxide followed by proton transfer:

1-Butanol, also known as butan-1-ol or n-butanol, is a primary alcohol with the chemical formula C4H9OH and a linear structure. Isomers of 1-butanol are isobutanol, butan-2-ol and tert-butanol. The unmodified term butanol usually refers to the straight chain isomer.

Crotonaldehyde is a chemical compound with the formula CH3CH=CHCHO. The compound is usually sold as a mixture of the E- and Z-isomers, which differ with respect to the relative position of the methyl and formyl groups. The E-isomer is more common (data given in Table is for the E-isomer). This lachrymatory liquid is moderately soluble in water and miscible in organic solvents. As an unsaturated aldehyde, crotonaldehyde is a versatile intermediate in organic synthesis. It occurs in a variety of foodstuffs, e.g. soybean oils.
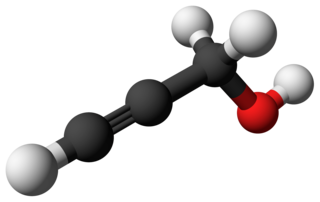
Propargyl alcohol, or 2-propyn-1-ol, is an organic compound with the formula C3H4O. It is the simplest stable alcohol containing an alkyne functional group. Propargyl alcohol is a colorless viscous liquid that is miscible with water and most polar organic solvents.
Propyl propanoate (propyl propionate) is the organic compound with the molecular formula C6H12O2. It is the ester of propanol and propionic acid. Like most esters, propyl propanoate is a colorless liquid with a fruity odor. The scent of propyl propionate is described as a chemically tinged pineapple or pear. It is used in perfumery and as a solvent. The refractive index at 20 °C is 1.393.
Isopropyl alcohol is a colorless, flammable organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor. As an isopropyl group linked to a hydroxyl group it is the simplest example of a secondary alcohol, where the alcohol carbon atom is attached to two other carbon atoms. It is a structural isomer of propan-1-ol and ethyl methyl ether.
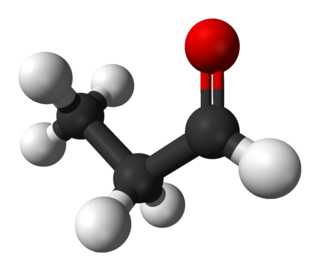
Propionaldehyde or propanal is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH2CHO. It is the 3-carbon aldehyde. It is a colourless, flammable liquid with a slightly fruity odour. It is produced on a large scale industrially.
Propionitrile, also known as ethyl cyanide and propanenitrile, is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2CN. It is a simple aliphatic nitrile. The compound is a colourless, water-soluble liquid. It is used as a solvent and a precursor to other organic compounds.