
Hexactinellid sponges are sponges with a skeleton made of four- and/or six-pointed siliceous spicules, often referred to as glass sponges. They are usually classified along with other sponges in the phylum Porifera, but some researchers consider them sufficiently distinct to deserve their own phylum, Symplasma. Some experts believe glass sponges are the longest-lived animals on earth; these scientists tentatively estimate a maximum age of up to 15,000 years.

Hecate Strait is a wide but shallow strait between Haida Gwaii and the mainland of British Columbia, Canada. It merges with Queen Charlotte Sound to the south and Dixon Entrance to the north. About 140 kilometres (87 mi) wide at its southern end, Hecate Strait narrows in the north to about 48 kilometres (30 mi). It is about 260 kilometres (160 mi) in length.

Race Rocks Ecological Reserve is a BC Parks ecological reserve off the southern tip of Vancouver Island in the Strait of Juan de Fuca in Metchosin, British Columbia, Canada.
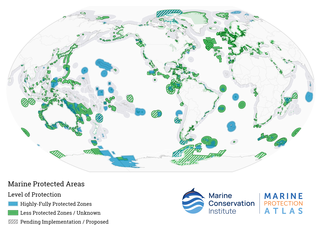
Marine protected areas (MPAs) are protected areas of the world's seas, oceans, estuaries or in the US, the Great Lakes. These marine areas can come in many forms ranging from wildlife refuges to research facilities. MPAs restrict human activity for a conservation purpose, typically to protect natural or cultural resources. Such marine resources are protected by local, state, territorial, native, regional, national, or international authorities and differ substantially among and between nations. This variation includes different limitations on development, fishing practices, fishing seasons and catch limits, moorings and bans on removing or disrupting marine life. In some situations, MPAs also provide revenue for countries, potentially equal to the income that they would have if they were to grant companies permissions to fish. The value of MPA to mobile species is unknown.

The Salish Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean located in the Canadian province of British Columbia and the U.S. state of Washington. It includes the Strait of Georgia, the Strait of Juan de Fuca, Puget Sound, and an intricate network of connecting channels and adjoining waterways.

The Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument (PMNM) is a World Heritage listed U.S. National Monument encompassing 583,000 square miles (1,510,000 km2) of ocean waters, including ten islands and atolls of the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. It was created in June 2006 with 140,000 square miles (360,000 km2) and expanded in August 2016 by moving its border to the limit of the exclusive economic zone, making it one of the world's largest protected areas. It is internationally known for its cultural and natural values as follows:
The area has deep cosmological and traditional significance for living Native Hawaiian culture, as an ancestral environment, as an embodiment of the Hawaiian concept of kinship between people and the natural world, and as the place where it is believed that life originates and to where the spirits return after death. On two of the islands, Nihoa and Mokumanamana, there are archaeological remains relating to pre-European settlement and use. Much of the monument is made up of pelagic and deepwater habitats, with notable features such as seamounts and submerged banks, extensive coral reefs and lagoons.

Apo Reef is a coral reef system in the Philippines situated in the western waters of Occidental Mindoro province in the Mindoro Strait. Encompassing 34 square kilometres (13 sq mi), it is considered the world's second-largest contiguous coral reef system, and is the largest in the country. The reef and its surrounding waters are protected areas administered as the Apo Reef Natural Park (ARNP). It is one of the best known and most popular diving regions in the country, and is in the tentative list for UNESCO World Heritage Sites.

Sponge reefs are reefs produced by sea sponges. All modern sponge reefs are formed by hexactinellid sponges, which have an endoskeleton made of silica spicules and are often referred to as "glass sponges", while historically the non-spiculed, calcite-skeletoned archaeocyathid and stromatoporoid sponges were the primary reef-builders.

The Coral Triangle (CT) is a roughly triangular area in the tropical waters around the Philippines, Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands and Timor-Leste. This area contains at least 500 species of reef-building corals in each ecoregion. The Coral Triangle is located between the Pacific and Indian oceans and encompasses portions of two biogeographic regions: the Indonesian-Philippines Region, and the Far Southwestern Pacific Region. As one of eight major coral reef zones in the world, the Coral Triangle is recognized as a global centre of marine biodiversity and a global priority for conservation. Its biological resources make it a global hotspot of marine biodiversity. Known as the "Amazon of the seas", it covers 5.7 million square kilometres (2,200,000 sq mi) of ocean waters. It contains more than 76% of the world's shallow-water reef-building coral species, 37% of its reef fish species, 50% of its razor clam species, six out of seven of the world's sea turtle species, and the world's largest mangrove forest. In 2014, the Asian Development Bank (ADB) reported that the gross domestic product of the marine ecosystem in the Coral Triangle is roughly $1.2 trillion per year and provides food to over 120 million people. According to the Coral Triangle Knowledge Network, the region annually brings in about $3 billion in foreign exchange income from fisheries exports, and another $3 billion from coastal tourism revenues.

Chatham Sound is a sound on the North Coast of British Columbia, Canada, bordering on Alaska, United States. It is located between the Dundas and Stephens Islands and the Tsimpsean Peninsula, it is part of the Inside Passage and extends from Portland Inlet in the north to Porcher Island in the south.

The Pacific North Coast Integrated Management Area is one of five Large Ocean Management Areas (LOMAs), areas of high ecological, social and economic importance, that have been identified by Fisheries and Oceans Canada (DFO) as priority regions for marine planning as part of Canada’s Oceans Action Plan.

Living Oceans Society is a Canadian environmental organization that has been a leader in the effort to protect Canada's oceans since 1998. It is based in Sointula, British Columbia, with a satellite office in Vancouver, British Columbia. Living Oceans Society's vision states that: "Canada's oceans are sustainably managed and thriving with abundant sea life that supports vibrant and resilient communities."

Hope Spots are ecologically unique areas of the ocean designated for protection under a global conservation campaign overseen by Mission Blue, a non-profit organization founded by Sylvia Earle with her 2009 TED prize wish.
The Helderberg Marine Protected Area is a small marine conservation area on the north-eastern side of False Bay in the Western Cape province of South Africa, It lies between the mouths of the Lourens River in the Strand, and the Eerste River in Macassar.
The Hluleka Marine Protected Area is an inshore conservation region in the territorial waters of the Eastern Cape province of South Africa.

Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) (French: zones de protection marine) are zones within Canadian waters where the marine environment receives a high level of environmental protection. Marine Protected Areas are governed by the Oceans Act of 1996 and administered by Fisheries and Oceans Canada. The federal government of Canada has committed to protecting 25% of its oceans as Marine Protected Areas by the year 2025, and a further 5% (30% of the ocean area of the Exclusive Economic Zone) by 2030.

Protected areas of Solomon Islands include marine protected areas that encompass coral reefs, lagoons, and seagrass meadows. East Rennell, which includes Lake Tegano, is the only area in the Solomon Islands listed by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. As of April 2024, the Solomons have not nominated any wetlands under the Convention on Wetlands of International Importance.
















