
Garibaldi Provincial Park, also called Garibaldi Park, is a wilderness park located on the coastal mainland of British Columbia, Canada, 70 kilometres (43.5 mi) north of Vancouver. It was established in 1920 and named a Class A Provincial Park of British Columbia in 1927. The park is a popular destination for outdoor recreation, with over 30,000 overnight campers and over 106,000 day users in the 2017/2018 season.

Okanagan Mountain Provincial Park is a provincial park within the Okanagan-Similkameen Regional District of British Columbia, Canada, focused on the mountain of the same name and located on the east side of Okanagan Lake, opposite Peachland and immediately south of the City of Kelowna. The park is one of the largest in the area, covering 110.38 square kilometres (42.62 sq mi). Most of the park is only accessible by foot, horseback, bicycle, or boat as motor vehicle access is restricted to BC Parks staff and technicians servicing the three telecommunications towers in the park.

A subglacial volcano, also known as a glaciovolcano, is a volcanic form produced by subglacial eruptions or eruptions beneath the surface of a glacier or ice sheet which is then melted into a lake by the rising lava. Today they are most common in Iceland and Antarctica; older formations of this type are found also in British Columbia and Yukon Territory, Canada.

Kakwa Provincial Park and Protected Area is a 170,890 ha provincial park in northeastern British Columbia, Canada. The park preserves the southernmost portion of the Hart Ranges and the northernmost portion of the Continental Ranges. The park also preserves significant marine fossil deposits located in the region.
Kitwanga Mountain Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada located on the north side of the Skeena River just west of the Gitxsan community of Kitwanga (Gitwangak).

The Purcell Wilderness Conservancy is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada. It was established in 1974, and encompasses six large drainages in the Purcell Mountains in the southeast of the province. It contains high peaks, alpine meadows and ridges, deep creek and river valleys, and hot springs at Dewar Creek.

A tuya is a flat-topped, steep-sided volcano formed when lava erupts through a thick glacier or ice sheet. They are rare worldwide, being confined to regions which were covered by glaciers and had active volcanism during the same period.
Tuya Butte is a tuya in the Tuya Range of north-central British Columbia, Canada. It is a bit less isolated from other ranges than neighbouring Mount Josephine. Some of the other volcanoes in the area include South Tuya, Ash Mountain, and Mathews Tuya.
Ash Mountain is the highest summit in the Tuya Range of the Stikine Ranges in northcentral British Columbia, Canada, located immediately north of High Tuya Lake at the north end of Tuya Mountains Provincial Park. It is one of the six tuyas clustered close to Tuya Lake. The base of the volcano comprises pillow lava and hyaloclastite indicating that the volcano formed beneath ice or under a large lake. The volcano comprises loose debris as well as dikes of basaltic rock that intruded into the volcanic pile. Other tuyas in the area include Tuya Butte, South Tuya and Mathews Tuya, although most of the group of tuyas are unnamed.
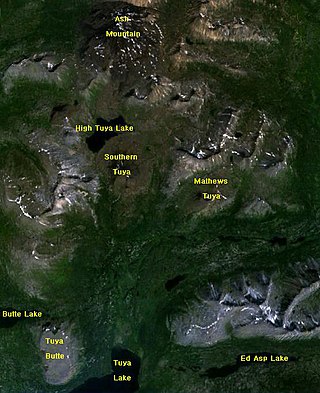
The Tuya Range is a mountain range in the Stikine Ranges of the Cassiar Mountains in the far north of the Canadian province of British Columbia, near its border with the Yukon Territory and to the southwest of Watson Lake, Yukon, which is the nearest major settlement.

The Interior Mountains or Northern Interior Mountains are the semi-official names for an expansive collection of mountain ranges that comprises much of the northern half of the Canadian province of British Columbia and a large area of southern Yukon.

Ring Mountain, also called Crucible Dome, is a tuya in the Mount Cayley volcanic field, British Columbia, Canada. It has a horseshoe shaped crater, located on the east side of the upper Squamish River. Outcrops on Ring Mountain's western side contain highly variable, fine-scale jointing and are locally broken down into many small spires and knobs. The age of Ring Mountain is unknown, but probably formed during the Fraser Glaciation like most tuyas in Canada.
McLeod Hill is a tuya, located 41 km (25 mi) north of Clearwater in the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field in Wells Gray Provincial Park, east-central British Columbia, Canada.

William Henry Mathews (1919–2003) was a Canadian geologist, volcanologist, engineer, and professor. He is considered a pioneer in the study of subglacial eruptions and volcano-ice interactions in North America. Many of his publications continue to be regarded as classics in their field.

The Powder Mountain Icefield, also called the Powder Mountain Icecap and the Cayley Icefield, is a glacial field in the Pacific Ranges of southwestern British Columbia, Canada, about 20 kilometres (12 mi) west of Whistler and about 90 kilometres (56 mi) north of Vancouver. On the west side of the icefield is the valley of the Squamish River, while on its east is the Callaghan Valley, which is the setting for the Nordic facilities for the 2010 Winter Olympics.

The Stikine Plateau is a plateau in northern British Columbia, Canada. It lies between the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains on the west and southwest and the Cassiar Mountains along its northeast, and between the Skeena Mountains on its south and southeast and the Jennings and Nakina Rivers on the north.
Tuya Lake, located in northwestern British Columbia, Canada, presumably derives its name from the presence of nearby steep-sided, flat-topped volcanoes, known as tuyas. The lake is situated just south of Tuya Butte at a latitude of about 59 degrees North and a longitude of about 131 degrees West.
The Cottonwood River is a tributary of the Dease River in the Cassiar Country of the Northern Interior of British Columbia, Canada. Rising in the northern Stikine Ranges just east of Toozaza Peak, and just south of the origins of the Jennings and Little Rancheria River near the border with Yukon, it flows south along the east flank of the Tuya Range to meet the Dease just north of that river's source at Dease Lake, between the north end of that lake and McDame Creek and the former mining centre and community of McDame Post.
The Tuya River is a major tributary of the Stikine River in northwest part of the province of British Columbia, Canada. From its source at High Tuya Lake in Tuya Mountains Provincial Park just south of Ash Mountain, the highest peak of the Tuya Range, the Tuya River flows south about 200 km (120 mi) to meet the Stikine River in the Grand Canyon of the Stikine. The Tuya River's main tributary is the Little Tuya River. The Tuya River divides the Tanzilla Plateau on the east from the Kawdy Plateau, to the northwest, and the Nahlin Plateau, to the southwest. All three are considered sub-plateaus of the Stikine Plateau. The Tuya River's watershed covers 3,575 km2 (1,380 sq mi), and its mean annual discharge is estimated at 36.9 m3/s (1,300 cu ft/s). The mouth of the Tuya River is located about 24 km (15 mi) northeast of Telegraph Creek, British Columbia, about 67 km (42 mi) southwest of Dease Lake, British Columbia, and about 210 km (130 mi) east of Juneau, Alaska. The Tuya River's watershed's land cover is classified as 35.7% shrubland, 31.4% conifer forest, 14.0% mixed forest, 7.2% herbaceous, and small amounts of other cover.
The Little Tuya River is a tributary of the Tuya River in northwest part of the province of British Columbia, Canada. It flows generally south and east about 71 km (44 mi) to join the Tuya River near Cariboo Meadows. The Little Tuya River's watershed covers 569 km2 (220 sq mi), and its mean annual discharge is an estimated 6.69 m3/s (236 cu ft/s).













