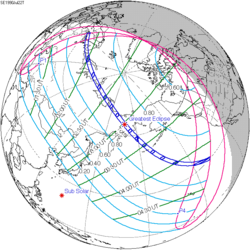
| Total eclipse | |
| Gamma | 0.6135 |
|---|---|
| Magnitude | 1.0357 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 155 s (2 min 35 s) |
| Coordinates | 60°30′N4°12′E / 60.5°N 4.2°E |
| Max. width of band | 153 km (95 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 12:32:38 |
| References | |
| Saros | 126 (44 of 72) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9408 |
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Wednesday, June 30, 1954, [1] with a magnitude of 1.0357. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 3.1 days after perigee (on June 27, 1954, at 11:10 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. [2]