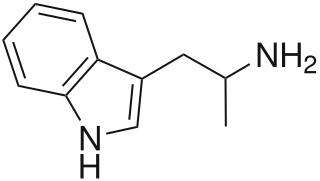
α-Methyltryptamine is a psychedelic, stimulant, and entactogen drug of the tryptamine class. It was originally developed as an antidepressant by workers at Upjohn in the 1960s, and was used briefly as an antidepressant in Russia under the trade name Indopan before being discontinued.
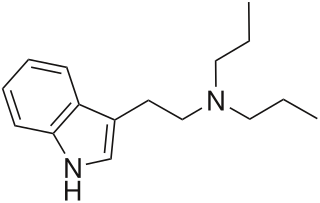
N,N-Dipropyltryptamine (DPT) is a psychedelic entheogen belonging to the tryptamine family. Use as a designer drug has been documented by law enforcement officials since as early as 1968. However, potential therapeutic use was not investigated until the 1970s. It is found either as a crystalline hydrochloride salt or as an oily or crystalline base. It has not been found to occur endogenously. It is a close structural homologue of dimethyltryptamine and diethyltryptamine.

2C-T-2 is a psychedelic and entactogenic phenethylamine of the 2C family. It was first synthesized in 1981 by Alexander Shulgin, and rated by him as one of the "magical half-dozen" most important psychedelic phenethylamine compounds. The drug has structural and pharmacodynamic properties similar to those of 2C-T-7.
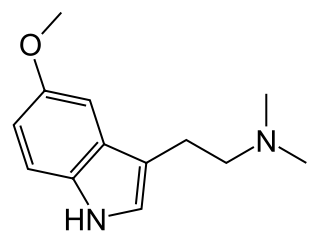
5-MeO-DMT (5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine) or O-methyl-bufotenin is a psychedelic of the tryptamine class. It is found in a wide variety of plant species, and also is secreted by the glands of at least one toad species, the Colorado River toad. Like its close relatives DMT and bufotenin (5-HO-DMT), it has been used as an entheogen in South America. Slang terms include Five-methoxy, The power, and Toad venom.
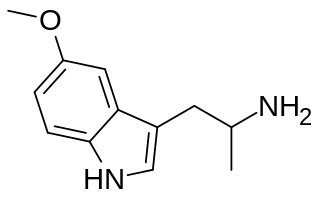
5-MeO-aMT or 5-methoxy-α-methyltryptamine, α,O-Dimethylserotonin (Alpha-O) is a potent psychedelic tryptamine. It is soluble in ethanol.
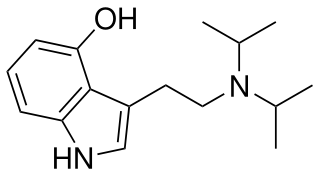
4-Hydroxy-N,N-diisopropyltryptamine is a synthetic psychedelic drug. It is a higher homologue of psilocin, 4-HO-DET, and is a positional isomer of 4-HO-DPT and has a tryptamine molecular sub-structure.

Diisopropyltryptamine is a psychedelic hallucinogenic drug of the tryptamine family that has a unique effect. While the majority of hallucinogens affect the visual sense, DiPT is primarily aural.

5-MeO-MiPT is a psychedelic and hallucinogenic drug, used by some as an entheogen. It has structural and pharmacodynamic properties similar to the drugs 5-MeO-DiPT, DiPT, and MiPT. It is commonly used as a "substitute" for 5-MeO-DiPT because of the very similar structure and effects.

5-MeO-DALT or N,N-di allyl-5-methoxy tryptamine is a psychedelic tryptamine first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin.

5-MeO-DET or 5-methoxy-N,N-diethyltryptamine is a hallucinogenic tryptamine.

5-MeO-DPT, is a psychedelic and entheogenic designer drug.
A serotonin releasing agent (SRA) is a type of drug that induces the release of serotonin into the neuronal synaptic cleft. A selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) is an SRA with less significant or no efficacy in producing neurotransmitter efflux at other types of monoamine neurons.
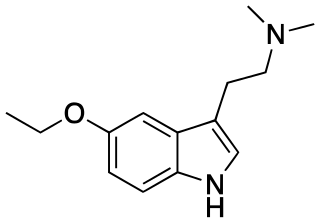
5-Ethoxy-DMT is a tryptamine derivative which has been previously synthesized as a chemical intermediate, but has not been studied to determine its pharmacology.
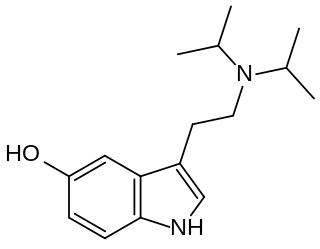
5-HO-DiPT (5-hydroxy-N,N-di-iso-propyltryptamine) is a tryptamine derivative which acts as a serotonin receptor agonist. It is primarily known as a metabolite of the better known psychoactive drug 5-MeO-DiPT, but 5-HO-DiPT has also rarely been encountered as a designer drug in its own right. Tests in vitro show 5-HO-DiPT to have high 5-HT2A affinity and good selectivity over 5-HT1A, while being more lipophilic than the related drug bufotenine (5-HO-DMT), which produces mainly peripheral effects.

5-Chloro-α-methyltryptamine (5-Chloro-αMT), also known as PAL-542, is a tryptamine derivative related to α-methyltryptamine (αMT) and one of only a few known specific serotonin-dopamine releasing agents (SDRAs). It has been investigated in animals as a potential treatment for cocaine dependence. The EC50 values of 5-chloro-αMT in evoking the in vitro release of serotonin (5-HT), dopamine (DA), and norepinephrine (NE) in rat synaptosomes were reported as 16 nM, 54 nM, and 3434 nM, with an NE/DA ratio of 63.6 and a DA/5-HT ratio of 3.38, indicating that it is a highly specific and well-balanced SDRA. However, 5-chloro-αMT has also been found to act as a potent full agonist of the 5-HT2A receptor, with an EC50 value of 6.27 nM and an efficacy of 105%, and almost assuredly acts as a potent agonist of other serotonin receptors as well.

5-MeO-MALT (5-methoxy-N-methyl-N-allyltryptamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug that is closely related to 5-MeO-DALT and has been sold online as a designer drug.

5-MeO-MET (5-Methoxy-N-methyl-N-ethyltryptamine) is a relatively rare designer drug from the substituted tryptamine family, related to compounds such as N-methyl-N-ethyltryptamine and 5-MeO-DMT. It was first synthesised in the 1960s and was studied to a limited extent, but was first identified on the illicit market in June 2012 in Sweden. It was made illegal in Norway in 2013, and is controlled under analogue provisions in numerous other jurisdictions.

MALT is a lesser-known drug from the tryptamine family. It is a novel compound with very little history of human use. It is closely related to methylpropyltryptamine (MPT), as well as N-methyltryptamine. It has been sold online as a designer drug. Very little information on the pharmacology or toxicity of MALT is available.



















